Abstract
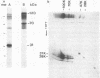
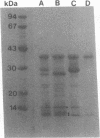
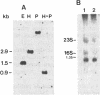
The major outer membrane protein of Legionella pneumophila exhibits an apparent molecular mass of 100 kDa. Previous studies revealed the oligomer to be composed of 28- and 31-kDa subunits; the latter subunit is covalently bound to peptidoglycan. These proteins exhibit cross-reactivity with polyclonal anti-31-kDa protein serum. In this study, we present evidence to confirm that the 31-kDa subunit is a 28-kDa subunit containing a bound fragment of peptidoglycan. Peptide maps of purified proteins were generated following cyanogen bromide cleavage or proteolysis with staphylococcal V8 protease. A comparison of the banding patterns resulting from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) revealed a common pattern. Selected peptide fragments were sequenced on a gas phase microsequencer, and the sequence was compared with the sequence obtained for the 28-kDa protein. While the amino terminus of the 31-kDa protein was blocked, peptide fragments generated by cyanogen bromide treatment exhibited a sequence identical to that of the amino terminus of the 28-kDa protein, but beginning at amino acid four (glycine), which is preceded by methionine at the third position. This sequence, (Gly-Thr-Met)-Gly-Pro-Val-Trp-Thr-Pro-Gly-Asn ... , confirms that these proteins have a common amino terminus. An oligonucleotide synthesized from the codons of the common N-terminal amino acid sequence was used to establish by Southern and Northern (RNA) blot analyses that a single gene coded for both proteins. With regard to the putative porin structure, we have identified two major bands at 70 kDa and at approximately 120 kDa by nonreducing SDS-PAGE. The former may represent the typical trimeric motif, while the latter may represent either a double trimer or an aggregate. Analysis of these two forms by two-dimensional SDS-PAGE (first dimensions, nonreducing; second dimensions, reducing) established that both were composed of 31- and 28-kDa subunits cross-linked via interchain disulfide bonds. These studies confirm that the novel L. pneumophila major outer protein is covalently bound to peptidoglycan via a modified 28-kDa subunit (31-kDa anchor protein) and cross-linked to other 28-kDa subunits via interchain disulfide bonds.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bavoil P., Ohlin A., Schachter J. Role of disulfide bonding in outer membrane structure and permeability in Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):479–485. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.479-485.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bavoil P., Stephens R. S., Falkow S. A soluble 60 kiloDalton antigen of Chlamydia spp. is a homologue of Escherichia coli GroEL. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Mar;4(3):461–469. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00612.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler C. A., Hoffman P. S. Characterization of a major 31-kilodalton peptidoglycan-bound protein of Legionella pneumophila. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2401–2407. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2401-2407.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler C. A., Street E. D., Hatch T. P., Hoffman P. S. Disulfide-bonded outer membrane proteins in the genus Legionella. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):14–18. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.14-18.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catrenich C. E., Johnson W. Characterization of the selective inhibition of growth of virulent Legionella pneumophila by supplemented Mueller-Hinton medium. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1862–1864. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1862-1864.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciotto N. P., Eisenstein B. I., Mody C. H., Toews G. B., Engleberg N. C. A Legionella pneumophila gene encoding a species-specific surface protein potentiates initiation of intracellular infection. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1255–1262. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1255-1262.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleberg N. C., Pearlman E., Dixon D., Eisenstein B. I. Antibodies isolated by using cloned surface antigens recognize antigenically related components of Legionella pneumophila and other Legionella species. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1415–1417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabay J. E., Blake M., Niles W. D., Horwitz M. A. Purification of Legionella pneumophila major outer membrane protein and demonstration that it is a porin. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):85–91. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.85-91.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E. Role of porins in outer membrane permeability. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):929–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.929-933.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Allan I., Pearce J. H. Structural and polypeptide differences between envelopes of infective and reproductive life cycle forms of Chlamydia spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):13–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.13-20.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindahl M. S., Iglewski B. H. Cloning and expression of a common Legionella outer membrane antigen in Escherichia coli. Microb Pathog. 1987 Feb;2(2):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindahl M. S., Iglewski B. H. Isolation and characterization of the Legionella pneumophila outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.107-113.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. S., Butler C. A., Quinn F. D. Cloning and temperature-dependent expression in Escherichia coli of a Legionella pneumophila gene coding for a genus-common 60-kilodalton antigen. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1731–1739. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1731-1739.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. S., Houston L., Butler C. A. Legionella pneumophila htpAB heat shock operon: nucleotide sequence and expression of the 60-kilodalton antigen in L. pneumophila-infected HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3380–3387. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3380-3387.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. S., Pine L., Bell S. Production of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide in medium used to culture Legionella pneumophila: catalytic decomposition by charcoal. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):784–791. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.784-791.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. S., Ripley M., Weeratna R. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of a gene (ompS) encoding the major outer membrane protein of Legionella pneumophila. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):914–920. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.914-920.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroczek R. A., Siebert E. Optimization of northern analysis by vacuum-blotting, RNA-transfer visualization, and ultraviolet fixation. Anal Biochem. 1990 Jan;184(1):90–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne N. R., Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of Legionella pneumophila is mediated by human monocyte complement receptors. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1377–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine L., George J. R., Reeves M. W., Harrell W. K. Development of a chemically defined liquid medium for growth of Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 May;9(5):615–626. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.5.615-626.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid J., Fung H., Gehring K., Klebba P. E., Nikaido H. Targeting of porin to the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. Rate of trimer assembly and identification of a dimer intermediate. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7753–7759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen K., Nikaido H. Lipopolysaccharide structure required for in vitro trimerization of Escherichia coli OmpF porin. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):926–928. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.926-928.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz I., Rheinheimer C., Hübner I., Bitter-Suermann D. Genus-specific epitope on the 60-kilodalton Legionella heat shock protein recognized by a monoclonal antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Feb;29(2):346–354. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.2.346-354.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff W. A., Parr T. R., Jr, Hancock R. E., Hanne L. F., Nicas T. I., Iglewski B. H. Expression in Escherichia coli and function of Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane porin protein F. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):473–479. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.473-479.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]