Abstract
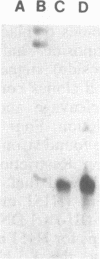
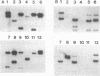
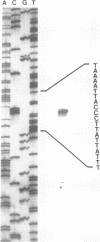
The major outer membrane protein of Legionella pneumophila is composed of 28- and 31-kDa subunits cross-linked by interchain disulfide bonds. The oligomer is covalently anchored to the underlying peptidoglycan via the 31-kDa subunit. We have cloned the structural gene ompS encoding both proteins. Oligonucleotide probes synthesized from the codons of the N-terminal amino acid sequence of purified 28- and 31-kDa subunits were used to identify cloned sequences. A 2.9-kb HindIII fragment cloned into pBluescript (clone H151) contained the ompS gene. Nucleotide sequence analysis revealed an open reading frame of 891 bp encoding a polypeptide of 297 amino acids. A leader sequence of 21 amino acids was identified, and the mature protein contained 276 amino acids. The deduced amino acid sequence of OmpS matched the experimentally determined amino acid sequence (32 amino acids), with the exception of two cysteine residues. The deduced amino acid sequence was rich in glycine and aromatic amino acids and contained four cysteine residues, two in the amino terminus and two in the carboxy region. Primer extension analysis (total RNA from L. pneumophila) identified the transcription start at 96 to 98 bp upstream of the translation start, but no Escherichia coli-like promoter sequences were evident. While an mRNA transcript from clone H151 was detected, no cross-reactive protein was detected by immunoblotting with either monoclonal or polyclonal antibody. Attempts to subclone the gene in the absence of the putative promoter region (i.e., under the control of the lac promoter) proved unsuccessful, possibly because of overproduction lethality in E. coli. The ompS DNA sequence was highly conserved among the serogroups of L. pneumophila, and related species also exhibited homology in Southern blot analysis at a moderately high stringency. Evidence is presented to suggest that this gene may be environmentally regulated in L. pneumophila.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aricó B., Miller J. F., Roy C., Stibitz S., Monack D., Falkow S., Gross R., Rappuoli R. Sequences required for expression of Bordetella pertussis virulence factors share homology with prokaryotic signal transduction proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6671–6675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow A. K., Heckels J. E., Clarke I. N. Molecular cloning and expression of Neisseria meningitidis class 1 outer membrane protein in Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2734–2740. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2734-2740.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellinger-Kawahara C., Horwitz M. A. Complement component C3 fixes selectively to the major outer membrane protein (MOMP) of Legionella pneumophila and mediates phagocytosis of liposome-MOMP complexes by human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1990 Oct 1;172(4):1201–1210. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.4.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black W. J., Quinn F. D., Tompkins L. S. Legionella pneumophila zinc metalloprotease is structurally and functionally homologous to Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2608–2613. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2608-2613.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler C. A., Hoffman P. S. Characterization of a major 31-kilodalton peptidoglycan-bound protein of Legionella pneumophila. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2401–2407. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2401-2407.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler C. A., Street E. D., Hatch T. P., Hoffman P. S. Disulfide-bonded outer membrane proteins in the genus Legionella. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):14–18. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.14-18.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catrenich C. E., Johnson W. Characterization of the selective inhibition of growth of virulent Legionella pneumophila by supplemented Mueller-Hinton medium. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1862–1864. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1862-1864.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles I. G., Dougan G., Pickard D., Chatfield S., Smith M., Novotny P., Morrissey P., Fairweather N. F. Molecular cloning and characterization of protective outer membrane protein P.69 from Bordetella pertussis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3554–3558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. H., Emory S. A., Bricker A. L., Bouvet P., Belasco J. G. Structure and function of a bacterial mRNA stabilizer: analysis of the 5' untranslated region of ompA mRNA. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4578–4586. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4578-4586.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciotto N. P., Eisenstein B. I., Mody C. H., Engleberg N. C. A mutation in the mip gene results in an attenuation of Legionella pneumophila virulence. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):121–126. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciotto N. P., Eisenstein B. I., Mody C. H., Toews G. B., Engleberg N. C. A Legionella pneumophila gene encoding a species-specific surface protein potentiates initiation of intracellular infection. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1255–1262. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1255-1262.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus L. A. Virulence associated ingestion of Legionella pneumophila by HeLa cells. Microb Pathog. 1987 Jul;3(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleberg N. C., Carter C., Weber D. R., Cianciotto N. P., Eisenstein B. I. DNA sequence of mip, a Legionella pneumophila gene associated with macrophage infectivity. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1263–1270. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1263-1270.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleberg N. C., Pearlman E., Dixon D., Eisenstein B. I. Antibodies isolated by using cloned surface antigens recognize antigenically related components of Legionella pneumophila and other Legionella species. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1415–1417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabay J. E., Blake M., Niles W. D., Horwitz M. A. Purification of Legionella pneumophila major outer membrane protein and demonstration that it is a porin. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):85–91. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.85-91.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosting L. H., Cabrian K., Sturge J. C., Goldstein L. C. Identification of a species-specific antigen in Legionella pneumophila by a monoclonal antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1031–1035. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1031-1035.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Seiff M. E., Blake M. S., Koomey M. Porin protein of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: cloning and gene structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8135–8139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindahl M. S., Iglewski B. H. Cloning and expression of a common Legionella outer membrane antigen in Escherichia coli. Microb Pathog. 1987 Feb;2(2):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindahl M. S., Iglewski B. H. Isolation and characterization of the Legionella pneumophila outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.107-113.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindahl M. S., Iglewski B. H. Outer membrane proteins from Legionella pneumophila serogroups and other Legionella species. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):94–101. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.94-101.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. S., Butler C. A., Quinn F. D. Cloning and temperature-dependent expression in Escherichia coli of a Legionella pneumophila gene coding for a genus-common 60-kilodalton antigen. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1731–1739. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1731-1739.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. S., Houston L., Butler C. A. Legionella pneumophila htpAB heat shock operon: nucleotide sequence and expression of the 60-kilodalton antigen in L. pneumophila-infected HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3380–3387. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3380-3387.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. S., Seyer J. H., Butler C. A. Molecular characterization of the 28- and 31-kilodalton subunits of the Legionella pneumophila major outer membrane protein. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):908–913. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.908-913.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Intracellular multiplication of Legionnaires' disease bacteria (Legionella pneumophila) in human monocytes is reversibly inhibited by erythromycin and rifampin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jan;71(1):15–26. doi: 10.1172/JCI110744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) multiples intracellularly in human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):441–450. doi: 10.1172/JCI109874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klickstein L. B., Wong W. W., Smith J. A., Weis J. H., Wilson J. G., Fearon D. T. Human C3b/C4b receptor (CR1). Demonstration of long homologous repeating domains that are composed of the short consensus repeats characteristics of C3/C4 binding proteins. J Exp Med. 1987 Apr 1;165(4):1095–1112. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.4.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Walsh C. T. Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans-isomerase from Escherichia coli: a periplasmic homolog of cyclophilin that is not inhibited by cyclosporin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4028–4032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig B., Schmid A., Marre R., Hacker J. Cloning, genetic analysis, and nucleotide sequence of a determinant coding for a 19-kilodalton peptidoglycan-associated protein (Ppl) of Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2515–2521. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2515-2521.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marra A., Horwitz M. A., Shuman H. A. The HL-60 model for the interaction of human macrophages with the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2738–2744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Mizushima S. Signal transduction and gene regulation through the phosphorylation of two regulatory components: the molecular basis for the osmotic regulation of the porin genes. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1077–1082. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. A., Woodruff W. A., Hancock R. E. Antibiotic uptake pathways across the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1987;39:172–181. doi: 10.1159/000414344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldham L. J., Rodgers F. G. Adhesion, penetration and intracellular replication of Legionella pneumophila: an in vitro model of pathogenesis. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Apr;131(4):697–706. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-4-697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne N. R., Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of Legionella pneumophila is mediated by human monocyte complement receptors. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1377–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn F. D., Tompkins L. S. Analysis of a cloned sequence of Legionella pneumophila encoding a 38 kD metalloprotease possessing haemolytic and cytotoxic activities. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jun;3(6):797–805. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowbotham T. J. Preliminary report on the pathogenicity of Legionella pneumophila for freshwater and soil amoebae. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Dec;33(12):1179–1183. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.12.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson J. S., Plikaytis B. B., Wilkinson H. W. Immunologic response of patients with legionellosis against major protein-containing antigens of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 as shown by immunoblot analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jan;23(1):92–99. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.1.92-99.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. S., Kuo C. C., Newport G., Agabian N. Molecular cloning and expression of Chlamydia trachomatis major outer membrane protein antigens in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):713–718. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.713-718.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. S., Mullenbach G., Sanchez-Pescador R., Agabian N. Sequence analysis of the major outer membrane protein gene from Chlamydia trachomatis serovar L2. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1277–1282. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1277-1282.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. S., Wagar E. A., Edman U. Developmental regulation of tandem promoters for the major outer membrane protein gene of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):744–750. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.744-750.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacker W. L., Wilkinson H. W., Plikaytis B. B., Steigerwalt A. G., Mayberry W. R., Moss C. W., Brenner D. J. Second serogroup of Legionella feeleii strains isolated from humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.1-4.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tropschug M., Wachter E., Mayer S., Schönbrunner E. R., Schmid F. X. Isolation and sequence of an FK506-binding protein from N. crassa which catalyses protein folding. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):674–677. doi: 10.1038/346674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadowsky R. M., Butler L. J., Cook M. K., Verma S. M., Paul M. A., Fields B. S., Keleti G., Sykora J. L., Yee R. B. Growth-supporting activity for Legionella pneumophila in tap water cultures and implication of hartmannellid amoebae as growth factors. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Nov;54(11):2677–2682. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.11.2677-2682.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao X., Dreyfus L. A. Expression and nucleotide sequence analysis of the Legionella pneumophila recA gene. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Jul;58(2):227–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb13983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]