Abstract
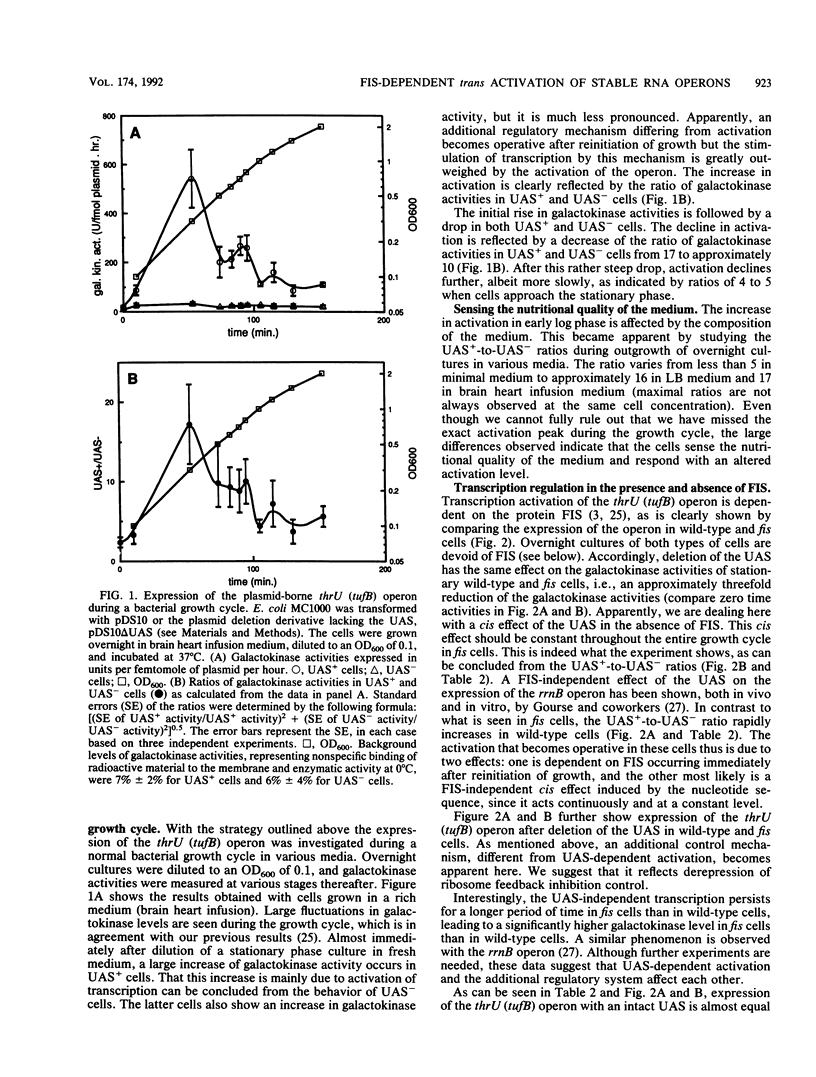
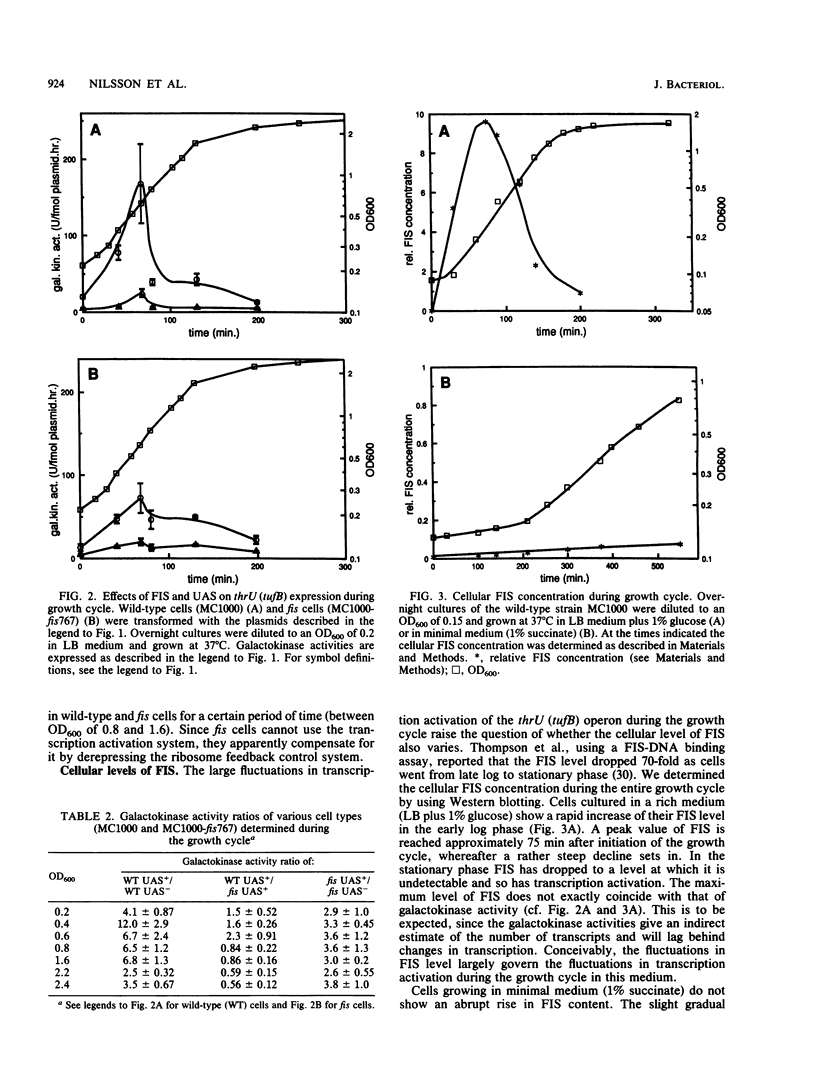
In Escherichia coli transcription of the tRNA operon thrU (tufB) and the rRNA operon rrnB is trans-activated by the protein FIS. This protein, which stimulates the inversion of various viral DNA segments, binds specifically to a cis-acting sequence (designated UAS) upstream of the promoter of thrU (tufB) and the P1 promoter of the rrnB operon. There are indications that this type of regulation is representative for the regulation of more stable RNA operons. In the present investigation we have studied UAS-dependent transcription activation of the thrU (tufB) operon in the presence and absence of FIS during a normal bacterial growth cycle and after a nutritional shift-up. In early log phase the expression of the operon rises steeply in wild-type cells, whereafter it declines. Concomitantly, a peak of the cellular FIS concentration is observed. Cells in the stationary phase are depleted of FIS. The rather abrupt increase of transcription activation depends on the nutritional quality of the medium. It is not seen in minimal medium. After a shift from minimal to rich medium, a peak of transcription activation and of FIS concentration is measured. This peak gets higher as the medium gets more strongly enriched. We conclude that a correlation between changes of the UAS-dependent activation of the thrU (tufB) operon and changes of the cellular FIS concentration under a variety of experimental conditions exists. This correlation strongly suggests that the production of FIS responds to environmental signals, thereby trans-activating the operon. Cells unable to produce FIS (fis cells) also show an increase of operon transcription in the early log phase and after a nutritional shift-up, albeit less pronounced than that wild-type cells. Presumably it is controlled by the ribosome feedback regulatory system. cis activation of the operon by the upstream activator sequence is apparent in the absence of FIS. This activation is constant throughout the entire growth cycle and is independent of nutritional factors. The well-known growth rate-dependent control, displayed by exponentially growing cells studied under various nutritional conditions, is governed by two regulatory mechanisms: repression, presumably by ribosome feedback inhibition, and stimulation by trans activation. FIS allows very fast bacterial growth.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams C. W., Hatfield G. W. Effects of promoter strengths and growth conditions on copy number of transcription-fusion vectors. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7399–7403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch L., Nilsson L., Vijgenboom E., Verbeek H. FIS-dependent trans-activation of tRNA and rRNA operons of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90184-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bétermier M., Lefrère V., Koch C., Alazard R., Chandler M. The Escherichia coli protein, Fis: specific binding to the ends of phage Mu DNA and modulation of phage growth. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Apr;3(4):459–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole J. R., Olsson C. L., Hershey J. W., Grunberg-Manago M., Nomura M. Feedback regulation of rRNA synthesis in Escherichia coli. Requirement for initiation factor IF2. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 5;198(3):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90288-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis P. P., Bremer H. Differential rate of ribosomal protein synthesis in Escherichia coli B/r. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 15;84(3):407–422. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90449-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaal T., Gourse R. L. Guanosine 3'-diphosphate 5'-diphosphate is not required for growth rate-dependent control of rRNA synthesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5533–5537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gausing K. Regulation of ribosome production in Escherichia coli: synthesis and stability of ribosomal RNA and of ribosomal protein messenger RNA at different growth rates. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):335–354. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gausing K. Ribosomal protein in E. coli: rate of synthesis and pool size at different growth rates. Mol Gen Genet. 1974 Mar 6;129(1):61–75. doi: 10.1007/BF00269266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gille H., Egan J. B., Roth A., Messer W. The FIS protein binds and bends the origin of chromosomal DNA replication, oriC, of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4167–4172. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., Takebe Y., Sharrock R. A., Nomura M. Feedback regulation of rRNA and tRNA synthesis and accumulation of free ribosomes after conditional expression of rRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1069–1073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., de Boer H. A., Nomura M. DNA determinants of rRNA synthesis in E. coli: growth rate dependent regulation, feedback inhibition, upstream activation, antitermination. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90498-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jinks-Robertson S., Gourse R. L., Nomura M. Expression of rRNA and tRNA genes in Escherichia coli: evidence for feedback regulation by products of rRNA operons. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):865–876. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Ball C. A., Pfeffer D., Simon M. I. Isolation of the gene encoding the Hin recombinational enhancer binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3484–3488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Simon M. I. Hin-mediated site-specific recombination requires two 26 bp recombination sites and a 60 bp recombinational enhancer. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):781–791. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josaitis C. A., Gaal T., Ross W., Gourse R. L. Sequences upstream of the-35 hexamer of rrnB P1 affect promoter strength and upstream activation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):307–311. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahmann R., Rudt F., Koch C., Mertens G. G inversion in bacteriophage Mu DNA is stimulated by a site within the invertase gene and a host factor. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):771–780. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80058-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl L., Zengel J. M. Expression of ribosomal genes in bacteria. Adv Genet. 1982;21:53–121. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl L., Zengel J. M. Ribosomal genes in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:297–326. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.001501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura A., Krueger J. H., Itoh S., de Boer H. A., Nomura M. Growth-rate-dependent regulation of ribosome synthesis in E. coli: expression of the lacZ and galK genes fused to ribosomal promoters. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):773–782. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson L., Vanet A., Vijgenboom E., Bosch L. The role of FIS in trans activation of stable RNA operons of E. coli. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):727–734. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08166.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Gourse R., Baughman G. Regulation of the synthesis of ribosomes and ribosomal components. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:75–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.000451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Thompson J. F., Newlands J. T., Gourse R. L. E.coli Fis protein activates ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro and in vivo. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3733–3742. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryals J., Little R., Bremer H. Control of rRNA and tRNA syntheses in Escherichia coli by guanosine tetraphosphate. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1261–1268. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1261-1268.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takebe Y., Miura A., Bedwell D. M., Tam M., Nomura M. Increased expression of ribosomal genes during inhibition of ribosome assembly in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Moitoso de Vargas L., Koch C., Kahmann R., Landy A. Cellular factors couple recombination with growth phase: characterization of a new component in the lambda site-specific recombination pathway. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):901–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90516-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Delft J. H., Verbeek H. M., De Jong P. J., Schmidt D. S., Talens A., Bosch L. Control of the tRNA-tufB operon in Escherichia coli. 1. rRNA gene dosage effects and growth-rate-dependent regulation. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 1;175(2):355–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbeek H., Nilsson L., Baliko G., Bosch L. Potential binding sites of the trans-activator FIS are present upstream of all rRNA operons and of many but not all tRNA operons. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):302–306. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90185-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijgenboom E., Nilsson L., Bosch L. The elongation factor EF-Tu from E. coli binds to the upstream activator region of the tRNA-tufB operon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):10183–10197. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.10183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Delft J. H., Mariñon B., Schmidt D. S., Bosch L. Transcription of the tRNA-tufB operon of Escherichia coli: activation, termination and antitermination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9515–9530. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



