Abstract
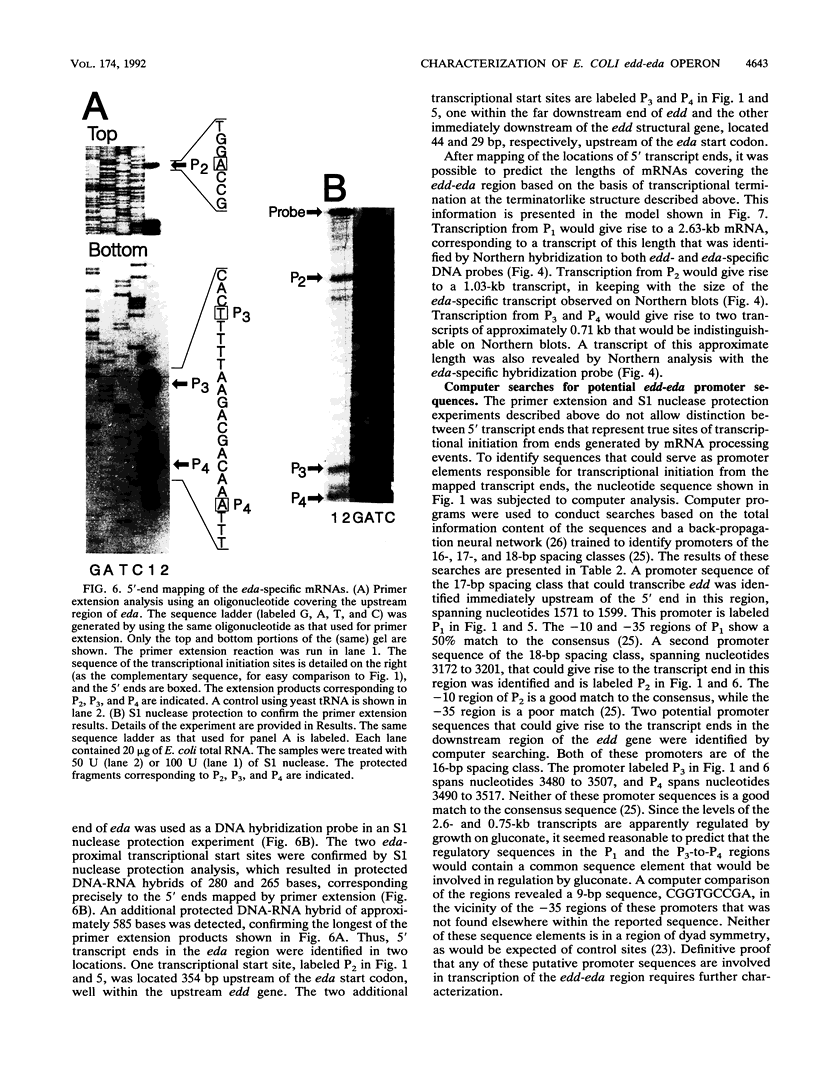
The nucleotide sequence of the entire Escherichia coli edd-eda region that encodes the enzymes of the Entner-Doudoroff pathway was determined. The edd structural gene begins 236 bases downstream of zwf. The eda structural gene begins 34 bases downstream of edd. The edd reading frame is 1,809 bases long and encodes the 602-amino-acid, 64,446-Da protein 6-phosphogluconate dehydratase. The deduced primary amino acid sequences of the E. coli and Zymomonas mobilis dehydratase enzymes are highly conserved. The eda reading frame is 642 bases long and encodes the 213-amino-acid, 22,283-Da protein 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate aldolase. This enzyme had been previously purified and sequenced by others on the basis of its related enzyme activity, 2-keto-4-hydroxyglutarate aldolase. The data presented here provide proof that the two enzymes are identical. The primary amino acid sequences of the E. coli, Z. mobilis, and Pseudomonas putida aldolase enzymes are highly conserved. When E. coli is grown on gluconate, the edd and eda genes are cotranscribed. Four putative promoters within the edd-eda region were identified by transcript mapping and computer analysis. P1, located upstream of edd, appears to be the primary gluconate-responsive promoter of the edd-eda operon, responsible for induction of the Entner-Doudoroff pathway, as mediated by the gntR product. High basal expression of eda is explained by constitutive transcription from P2, P3, and/or P4 but not P1.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamowicz M., Conway T., Nickerson K. W. Nutritional complementation of oxidative glucose metabolism in Escherichia coli via pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent glucose dehydrogenase and the Entner-Doudoroff pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jul;57(7):2012–2015. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.7.2012-2015.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnell W. O., Yi K. C., Conway T. Sequence and genetic organization of a Zymomonas mobilis gene cluster that encodes several enzymes of glucose metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7227–7240. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7227-7240.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. A colony bank containing synthetic Col El hybrid plasmids representative of the entire E. coli genome. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway T., Fliege R., Jones-Kilpatrick D., Liu J., Barnell W. O., Egan S. E. Cloning, characterization and expression of the Zymononas mobilis eda gene that encodes 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate aldolase of the Entner-Doudoroff pathway. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Dec;5(12):2901–2911. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01850.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway T., Ingram L. O. Similarity of Escherichia coli propanediol oxidoreductase (fucO product) and an unusual alcohol dehydrogenase from Zymomonas mobilis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3754–3759. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3754-3759.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway T., Yi K. C., Egan S. E., Wolf R. E., Jr, Rowley D. L. Locations of the zwf, edd, and eda genes on the Escherichia coli physical map. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(17):5247–5248. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.17.5247-5248.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. L., Cox B. J., Fidanza V., Calhoun D. H. The complete nucleotide sequence of the ilvGMEDA cluster of Escherichia coli K-12. Gene. 1987;56(2-3):185–198. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENTNER N., DOUDOROFF M. Glucose and gluconic acid oxidation of Pseudomonas saccharophila. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;196(2):853–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. C., Dobrogosz W. J. Gluconate metabolism in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):941–949. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.941-949.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fradkin J. E., Fraenkel D. G. 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate 6-phosphate aldolase mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1277–1283. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1277-1283.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel D. G., Banerjee S. Deletion mapping of zwf, the gene for a constitutive enzyme, glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1972 Aug;71(4):481–489. doi: 10.1093/genetics/71.4.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel D. G., Levisohn S. R. Glucose and gluconate metabolism in an Escherichia coli mutant lacking phosphoglucose isomerase. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1571–1578. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1571-1578.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner P. R., Fridovich I. Superoxide sensitivity of the Escherichia coli 6-phosphogluconate dehydratase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1478–1483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. C., Dekker E. E. Malyl-CoA formation in the NAD-, CoASH-, and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase-dependent oxidation of 2-keto-4-hydroxyglutarate. Possible coupled role of this reaction with 2-keto-4-hydroxyglutarate aldolase activity in a pyruvate-catalyzed cyclic oxidation of glyoxylate. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10012–10019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesman T. L., Barnell W. O., Conway T. Cloning, characterization, and nucleotide sequence analysis of a Zymomonas mobilis phosphoglucose isomerase gene that is subject to carbon source-dependent regulation. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(10):3215–3223. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.10.3215-3223.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Istúriz T., Palmero E., Vitelli-Flores J. Mutations affecting gluconate catabolism in Escherichia coli. Genetic mapping of the locus for the thermosensitive gluconokinase. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Nov;132(11):3209–3219. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-11-3209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOVACHEVICH R., WOOD W. A. Carbohydrate metabolism by Pseudomonas fluorescens. III. Purification and properties of a 6-phosphogluconate dehydrase. J Biol Chem. 1955 Apr;213(2):745–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao S. M., Hassan H. M. Biochemical characterization of a paraquat-tolerant mutant of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10478–10481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg H. L. The role and control of the glyoxylate cycle in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1966 Apr;99(1):1–11. doi: 10.1042/bj0990001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E., Delbrück M. Mutations of Bacteria from Virus Sensitivity to Virus Resistance. Genetics. 1943 Nov;28(6):491–511. doi: 10.1093/genetics/28.6.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill M. C. Escherichia coli promoters. I. Consensus as it relates to spacing class, specificity, repeat substructure, and three-dimensional organization. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5522–5530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill M. C. Training back-propagation neural networks to define and detect DNA-binding sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 25;19(2):313–318. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patil R. V., Dekker E. E. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, overexpression, and inactivation of the Escherichia coli 2-keto-4-hydroxyglutarate aldolase gene. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):102–107. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.102-107.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouysségur J. M., Stoeber F. R. Rameau dégradatif commun des hexuronates chez Escherichia coli K12. Mécanisme d'induction des enzymes assurant le métabolisme du 2-céto-3-désoxy-gluconate. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Nov 7;30(3):479–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley D. L., Pease A. J., Wolf R. E., Jr Genetic and physical analyses of the growth rate-dependent regulation of Escherichia coli zwf expression. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4660–4667. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4660-4667.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley D. L., Wolf R. E., Jr Molecular characterization of the Escherichia coli K-12 zwf gene encoding glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):968–977. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.968-977.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Wood W. A. Complete primary structure of 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate aldolase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3427–3435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson J., Gerstenberger P. D., Goldberg D. E., Gociar E., Orozco de Silva A., Fraenkel D. G. ColE1 hybrid plasmids for Escherichia coli genes of glycolysis and the hexose monophosphate shunt. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):502–506. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.502-506.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinopal R. T., Hillman J. D., Schulman H., Reznikoff W. S., Fraenkel D. G. New phosphoglucose isomerase mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):1172–1174. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.1172-1174.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlahos C. J., Dekker E. E. The complete amino acid sequence and identification of the active-site arginine peptide of Escherichia coli 2-keto-4-hydroxyglutarate aldolase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11683–11691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf R. E., Jr Integration of specialized transducing bacteriophage lambda cI857 St68 h80 dgnd his by an unusual pathway promotes formation of deletions and generates a new translocatable element. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):588–602. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.588-602.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zablotny R., Fraenkel D. G. Glucose and gluconate metabolism in a mutant of Escherichia coli lacking gluconate-6-phosphate dehydrase. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1579–1581. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1579-1581.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]