Abstract
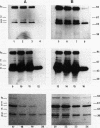
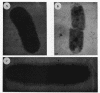
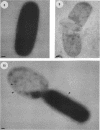
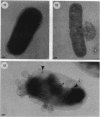
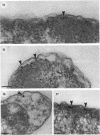
The precise ultrastructural localization of penicillin-binding protein (PBP)-antibiotic complexes in Escherichia coli JM101, JM101 (pBS96), and JM101(pPH116) was investigated by high-resolution electron microscopy. We used mercury-penicillin V (Hg-pen V) as a heavy-metal-labeled, electron-dense probe for accurately localizing PBPs in situ in single bacterial cells grown to exponential growth phase. Biochemical data derived from susceptibility tests and bacteriolysis experiments revealed no significant differences between Hg-pen V and the parent compound, penicillin V, or between strains. Both antibiotics revealed differences in the binding affinities for PBPs of all strains. Deacylation rates for PBPs were slow despite the relatively low binding affinities of antibiotics. Cells bound most of the Hg-pen V added to cultures, and the antibiotic-PBP complex could readily be seen by electron microscopy of unstained whole mounts as distinct, randomly situated electron-dense particles. Fifty to 60% of the antibiotic was retained by cells during processing for conventional embedding so that thin sections could also be examined. These revealed similar electron-dense particles located predominantly on the plasma membrane and less frequently in the cytoplasm. Particles positioned on the plasma membranes were occasionally shown to protrude into the periplasmic space, thereby reflecting the high resolution of the Hg-pen V probe. Moreover, some particles were observed free in the periplasm, suggesting, for the first time, that a proportion of PBPs may not be restricted to the plasma membrane but may be tightly associated with the peptidoglycan for higher efficiency of peptidoglycan assembly. All controls were devoid of the electron-dense particles. The presence of electron-dense particles in cells of the wild-type JM101, demonstrated that our probe could identify PBPs in naturally occurring strains without inducing PBP overproduction.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbas J. A., Díaz J., Rodríguez-Tébar A., Vázquez D. Specific location of penicillin-binding proteins within the cell envelope of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):269–275. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.269-275.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. H., Keck W., Bayer M. E. Localization of penicillin-binding protein 1b in Escherichia coli: immunoelectron microscopy and immunotransfer studies. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):125–135. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.125-135.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendayan M., Nanci A., Kan F. W. Effect of tissue processing on colloidal gold cytochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Sep;35(9):983–996. doi: 10.1177/35.9.3302022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broome-Smith J. K., Hedge P. J., Spratt B. G. Production of thiol-penicillin-binding protein 3 of Escherichia coli using a two primer method of site-directed mutagenesis. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):231–235. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02340.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER P. D. Site of action of radiopenicillin. Bacteriol Rev. 1956 Mar;20(1):28–48. doi: 10.1128/br.20.1.28-48.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig S., Goodchild D. J. Post-embedding immunolabelling. Some effects of tissue preparation on the antigenicity of plant proteins. Eur J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;28(2):251–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham L. L., Beveridge T. J. Evaluation of freeze-substitution and conventional embedding protocols for routine electron microscopic processing of eubacteria. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):2141–2149. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.2141-2149.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobot J. A., Rogers H. J. Intracellular location of the autolytic N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanine amidase in Bacillus subtilis 168 and in an autolysis-deficient mutant by immunoelectron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):961–967. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.961-967.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson J. M., Labia R. Synthesis of a 125I-radiolabeled penicillin for penicillin-binding proteins studies. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jan;128(1):164–168. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90357-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuhashi M., Takagaki Y., Maruyama I. N., Tamaki S., Nishimura Y., Suzuki H., Ogino U., Hirota Y. Mutants of Escherichia coli lacking in highly penicillin-sensitive D-alanine carboxypeptidase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2976–2979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Gronenborn B., Müller-Hill B., Hans Hopschneider P. Filamentous coliphage M13 as a cloning vehicle: insertion of a HindII fragment of the lac regulatory region in M13 replicative form in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3642–3646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa J., Matsuhashi M. Molecular divergence of a major peptidoglycan synthetase with transglycosylase-transpeptidase activities in Escherichia coli --- penicillin-binding protein 1Bs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Apr 29;105(4):1546–1553. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90964-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt J. M., Holland I. B., Spratt B. G. Precursor forms of penicillin-binding proteins 5 and 6 of E. coli cytoplasmic membrane. Nature. 1981 Sep 24;293(5830):307–309. doi: 10.1038/293307a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt J. M., Jackson M. E., Holland I. B. The C terminus of penicillin-binding protein 5 is essential for localisation to the E. coli inner membrane. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2399–2405. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04510.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston D. A., Wu C. Y., Blaszczak L. C., Seitz D. E., Halligan N. G. Biological characterization of a new radioactive labeling reagent for bacterial penicillin-binding proteins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 May;34(5):718–721. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.5.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Tébar A., Barbas J. A., Vázquez D. Location of some proteins involved in peptidoglycan synthesis and cell division in the inner and outer membranes of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):243–248. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.243-248.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Distinct penicillin binding proteins involved in the division, elongation, and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Pardee A. B. Penicillin-binding proteins and cell shape in E. coli. Nature. 1975 Apr 10;254(5500):516–517. doi: 10.1038/254516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Penicillin-binding proteins and the future of beta-lactam antibiotics. The Seventh Fleming Lecture. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 May;129(5):1247–1260. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-5-1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Properties of the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K12,. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):341–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Temperature-sensitive cell division mutants of Escherichia coli with thermolabile penicillin-binding proteins. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):293–305. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.293-305.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Nishimura Y., Hirota Y. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli: a series of mutants of E. coli altered in the penicillin-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):664–668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki S., Nakajima S., Matsuhashi M. Thermosensitive mutation in Escherichia coli simultaneously causing defects in penicillin-binding protein-1Bs and in enzyme activity for peptidoglycan synthesis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5472–5476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. From penicillin-binding proteins to the lysis and death of bacteria: a 1979 view. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 May-Jun;1(3):434–467. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.3.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walderich B., Höltje J. V. Subcellular distribution of the soluble lytic transglycosylase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5668–5676. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5668-5676.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Strominger J. L. Penicillin-binding proteins and the mechanism of action of beta-lactam antibiotics. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:825–869. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.004141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Blaauwen T., Nanninga N. Topology of penicillin-binding protein 1b of Escherichia coli and topography of four antigenic determinants studied by immunocolabeling electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):71–79. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.71-79.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]