Abstract
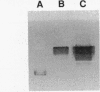
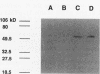
The gene encoding Rhizobium meliloti isocitrate dehydrogenase (ICD) was cloned by complementation of an Escherichia coli icd mutant with an R. meliloti genomic library constructed in pUC18. The complementing DNA was located on a 4.4-kb BamHI fragment. It encoded an ICD that had the same mobility as R. meliloti ICD in nondenaturing polyacrylamide gels. In Western immunoblot analysis, antibodies raised against this protein reacted with R. meliloti ICD but not with E. coli ICD. The complementing DNA fragment was mutated with transposon Tn5 and then exchanged for the wild-type allele by recombination by a novel method that employed the Bacillus subtilis levansucrase gene. No ICD activity was found in the two R. meliloti icd::Tn5 mutants isolated, and the mutants were also found to be glutamate auxotrophs. The mutants formed nodules, but they were completely ineffective. Faster-growing pseudorevertants were isolated from cultures of both R. meliloti icd::Tn5 mutants. In addition to lacking all ICD activity, the pseudorevertants also lacked citrate synthase activity. Nodule formation by these mutants was severely affected, and inoculated plants had only callus structures or small spherical structures.
Full text
PDF


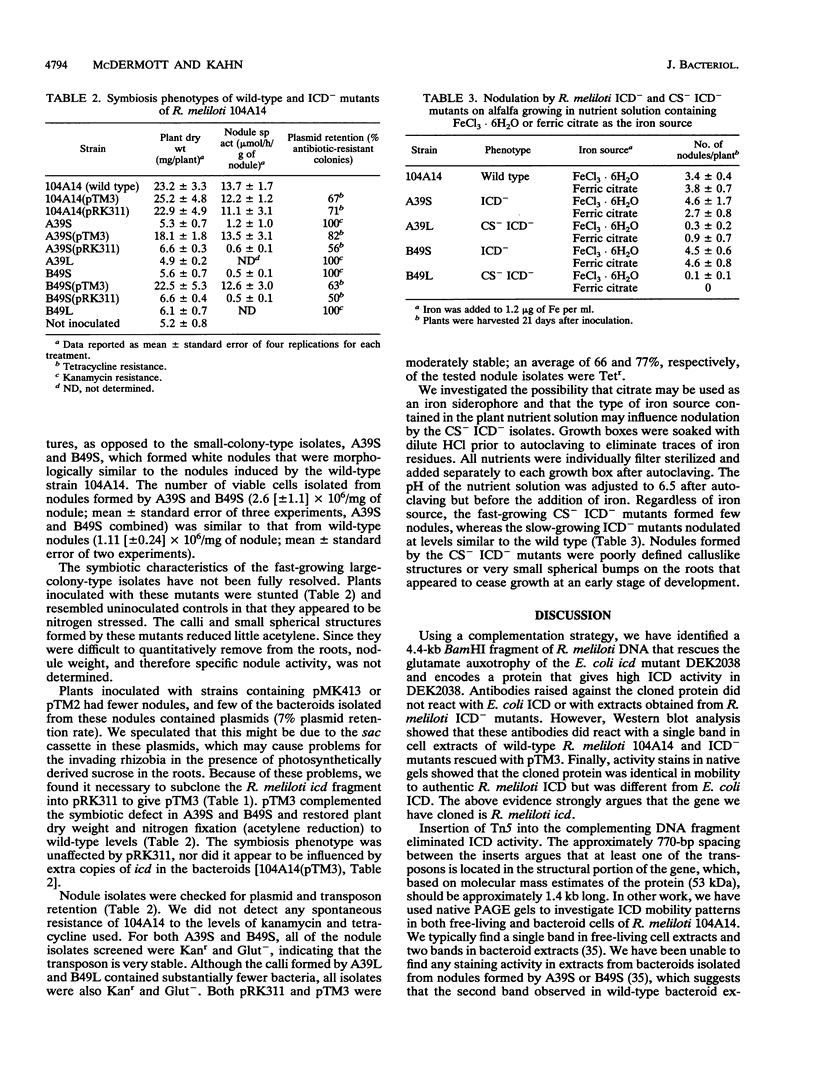



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg C. M., Wang M. D., Vartak N. B., Liu L. Acquisition of new metabolic capabilities: multicopy suppression by cloned transaminase genes in Escherichia coli K-12. Gene. 1988 May 30;65(2):195–202. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90456-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekharan Nambiar P. T., Shethna Y. I. Purification and properties of an NADP+-specific isocitrate dehydrogenase from Rhizobium meliloti. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1976;42(4):471–482. doi: 10.1007/BF00410178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaney R. L., Brown J. C., Tiffin L. O. Obligatory reduction of ferric chelates in iron uptake by soybeans. Plant Physiol. 1972 Aug;50(2):208–213. doi: 10.1104/pp.50.2.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Schmidhauser T., Yakobson E., Lu P., Liang X. W., Finlay D. R., Guiney D., Helinski D. R. Plasmids related to the broad host range vector, pRK290, useful for gene cloning and for monitoring gene expression. Plasmid. 1985 Mar;13(2):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan M. J., Fraenkel D. G. alpha-Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase mutant of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):415–419. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.415-419.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finan T. M., Wood J. M., Jordan D. C. Symbiotic properties of C4-dicarboxylic acid transport mutants of Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1403–1413. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1403-1413.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fougère F., Le Rudulier D., Streeter J. G. Effects of Salt Stress on Amino Acid, Organic Acid, and Carbohydrate Composition of Roots, Bacteroids, and Cytosol of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Physiol. 1991 Aug;96(4):1228–1236. doi: 10.1104/pp.96.4.1228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnak M., Reeves H. C. Phosphorylation of Isocitrate dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli. Science. 1979 Mar 16;203(4385):1111–1112. doi: 10.1126/science.34215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnak M., Reeves H. C. Purification and properties of phosphorylated isocitrate dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7915–7920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay P., Le Coq D., Steinmetz M., Berkelman T., Kado C. I. Positive selection procedure for entrapment of insertion sequence elements in gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):918–921. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.918-921.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerinot M. L., Meidl E. J., Plessner O. Citrate as a siderophore in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3298–3303. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3298-3303.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes M. F., Quandt J., O'Connell M. P., Pühler A. Direct selection for curing and deletion of Rhizobium plasmids using transposons carrying the Bacillus subtilis sacB gene. Gene. 1989 May 15;78(1):111–120. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90319-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irigoyen Juan Jose, Sanchez-Diaz Manuel, Emerich David W. Carbon Metabolism Enzymes of Rhizobium meliloti Cultures and Bacteroids and Their Distribution within Alfalfa Nodules. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Aug;56(8):2587–2589. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.8.2587-2589.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S., Lin E. C. arcA (dye), a global regulatory gene in Escherichia coli mediating repression of enzymes in aerobic pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1888–1892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson F. A., Dawes E. A. Regulation of the tricarboxylic acid cycle and poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate metabolism in Azotobacter beijerinckii grown under nitrogen or oxygen limitation. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Dec;97(2):303–312. doi: 10.1099/00221287-97-2-303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. V., Evans H. J., Ching T. Enzymes of the glyoxylate cycle in rhizobia and nodules of legumes. Plant Physiol. 1966 Oct;41(8):1330–1336. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.8.1330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karr D. B., Waters J. K., Suzuki F., Emerich D. W. Enzymes of the Poly-beta-Hydroxybutyrate and Citric Acid Cycles of Rhizobium japonicum Bacteroids. Plant Physiol. 1984 Aug;75(4):1158–1162. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.4.1158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kittell B. L., Helinski D. R., Ditta G. S. Aromatic aminotransferase activity and indoleacetic acid production in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5458–5466. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5458-5466.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurz W. G., LaRUE T. A. Citric acid cycle enzymes and nitrogenase in nodules of Pisum sativum. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Sep;23(9):1197–1200. doi: 10.1139/m77-180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmi T. M., Helling R. B. Selection for citrate synthase deficiency in icd mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):76–83. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.76-83.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh J. A., Reed J. W., Hanks J. F., Hirsch A. M., Walker G. C. Rhizobium meliloti mutants that fail to succinylate their calcofluor-binding exopolysaccharide are defective in nodule invasion. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osburne M. S. Rhizobium meliloti mutants altered in ammonium utilization. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1633–1636. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1633-1636.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastogi V. K., Watson R. J. Aspartate aminotransferase activity is required for aspartate catabolism and symbiotic nitrogen fixation in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):2879–2887. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.2879-2887.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reibach P. H., Streeter J. G. Evaluation of active versus passive uptake of metabolites by Rhizobium japonicum bacteroids. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):47–52. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.47-52.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reibach P. H., Streeter J. G. Metabolism of C-labeled photosynthate and distribution of enzymes of glucose metabolism in soybean nodules. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jul;72(3):634–640. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.3.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ried J. L., Collmer A. An nptI-sacB-sacR cartridge for constructing directed, unmarked mutations in gram-negative bacteria by marker exchange-eviction mutagenesis. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):239–246. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90127-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronson C. W., Lyttleton P., Robertson J. G. C(4)-dicarboxylate transport mutants of Rhizobium trifolii form ineffective nodules on Trifolium repens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4284–4288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendahl L., Vance C. P., Pedersen W. B. Products of Dark CO(2) Fixation in Pea Root Nodules Support Bacteroid Metabolism. Plant Physiol. 1990 May;93(1):12–19. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Ausubel F. M. A general method for site-directed mutagenesis in prokaryotes. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):85–88. doi: 10.1038/289085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salminen S. O., Streeter J. G. Involvement of glutamate in the respiratory metabolism of Bradyrhizobium japonicum bacteroids. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):495–499. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.495-499.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stovall I., Cole M. Organic Acid Metabolism by Isolated Rhizobium japonicum Bacteroids. Plant Physiol. 1978 May;61(5):787–790. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeter J. G. Carbohydrate, organic Acid, and amino Acid composition of bacteroids and cytosol from soybean nodules. Plant Physiol. 1987 Nov;85(3):768–773. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.3.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wych R. D., Rains D. W. Simultaneous measurement of nitrogen fixation estimated by acetylene-ethylene assay and nitrate absorption by soybeans. Plant Physiol. 1978 Sep;62(3):443–448. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.3.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn F. J., Lupski J. R. The use of transposon Tn5 mutagenesis in the rapid generation of correlated physical and genetic maps of DNA segments cloned into multicopy plasmids--a review. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):131–149. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]