Abstract
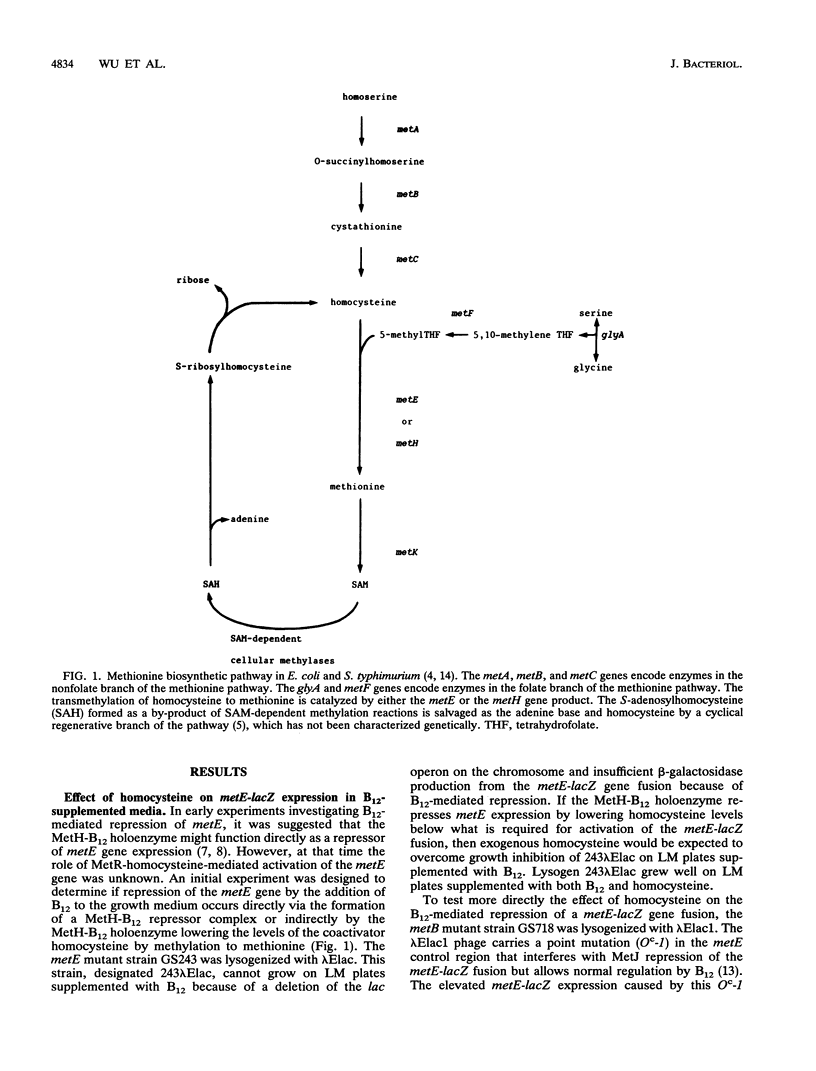
The vitamin B12 (B12)-mediated repression of the metE gene in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium requires the B12-dependent transmethylase, the metH gene product. It has been proposed that the MetH-B12 holoenzyme complex is involved directly in the repression mechanism. Using Escherichia coli strains lysogenized with a lambda phage carrying a metE-lacZ gene fusion, we examined B12-mediated repression of the metE-lacZ gene fusion. Although B12 supplementation results in a 10-fold repression of metE-lacZ expression, homocysteine addition to the growth medium overrides the B12-mediated repression. In addition, B12-mediated repression of the metE-lacZ fusion is dependent on a functional MetR protein. When a metB mutant was transformed with a high-copy-number plasmid carrying the metE gene, which would be expected to reduce intracellular levels of homocysteine, metE-lacZ expression was reduced and B12 supplementation had no further effect. In a metJ mutant, B12 represses metE-lacZ expression less than twofold. When the metJ mutant was transformed with a high-copy-number plasmid carrying the metH gene, which would be expected to reduce intracellular levels of homocysteine, B12 repression of the metE-lacZ fusion was partially restored. The results indicate that B12-mediated repression of the metE gene is primarily a loss of MetR-mediated activation due to depletion of the coactivator homocysteine, rather than a direct repression by the MetH-B12 holoenzyme.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cai X. Y., Maxon M. E., Redfield B., Glass R., Brot N., Weissbach H. Methionine synthesis in Escherichia coli: effect of the MetR protein on metE and metH expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4407–4411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai X. Y., Redfield B., Maxon M., Weissbach H., Brot N. The effect of homocysteine on MetR regulation of metE, metR and metH expression in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 30;163(1):79–83. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92101-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes J., Foster M. A. Vitamin B 12 and methionine synthesis in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 22;237(3):455–464. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90263-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dev I. K., Harvey R. J. Regulation of synthesis of serine hydroxymethyltransferase in chemostat cultures of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8394–8401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene R. C. Methionine limitation in Escherichia coli K-12 by growth on the sulfoxides of D-methionine. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):230–234. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.230-234.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene R. C., Williams R. D., Kung H. F., Spears C., Weissbach H. Effect of methionine and vitamin B-12 on the activities of methionine biosynthetic enzymes in metJ mutants of Escherichia coli K12. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Sep;158(1):249–256. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90619-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung H. F., Spears C., Greene R. C., Weissbach H. Regulation of the terminal reactions in methionine biosynthesis by vitamin B 12 and methionine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 May;150(1):23–31. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxon M. E., Redfield B., Cai X. Y., Shoeman R., Fujita K., Fisher W., Stauffer G., Weissbach H., Brot N. Regulation of methionine synthesis in Escherichia coli: effect of the MetR protein on the expression of the metE and metR genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):85–89. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner L., Whitfield C., Weissbach H. Effect of L-methionine and vitamin B 12 on methionine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Sep;133(2):413–419. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90470-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan J. T., Margolin W., Krueger J. H., Walker G. C. Mutations affecting regulation of methionine biosynthetic genes isolated by use of met-lac fusions. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):609–619. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.609-619.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plamann L. S., Urbanowski M. L., Stauffer G. V. Salmonella typhimurium metE operator-constitutive mutations. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):201–208. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90326-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saint-Girons I., Parsot C., Zakin M. M., Bârzu O., Cohen G. N. Methionine biosynthesis in Enterobacteriaceae: biochemical, regulatory, and evolutionary aspects. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1988;23 (Suppl 1):S1–42. doi: 10.3109/10409238809083374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulte L. L., Stauffer L. T., Stauffer G. V. Cloning and characterization of the Salmonella typhimurium metE gene. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):928–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.928-933.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada K., Weisberg R. A., Gottesman M. E. Prophage lambda at unusual chromosomal locations. I. Location of the secondary attachment sites and the properties of the lysogens. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 14;63(3):483–503. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90443-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer G. V., Plamann M. D., Stauffer L. T. Construction and expression of hybrid plasmids containing the Escherichia coli glyA genes. Gene. 1981 Jun-Jul;14(1-2):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbanowski M. L., Stauffer G. V. Autoregulation by tandem promoters of the Salmonella typhimurium LT2 metJ gene. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):740–745. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.740-745.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbanowski M. L., Stauffer G. V. Genetic and biochemical analysis of the MetR activator-binding site in the metE metR control region of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5620–5629. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5620-5629.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbanowski M. L., Stauffer G. V. Regulation of the metR gene of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5841–5844. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5841-5844.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbanowski M. L., Stauffer G. V. Role of homocysteine in metR-mediated activation of the metE and metH genes in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3277–3281. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3277-3281.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbanowski M. L., Stauffer G. V. The control region of the metH gene of Salmonella typhimurium LT2: an atypical met promoter. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):193–200. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90325-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbanowski M. L., Stauffer L. T., Plamann L. S., Stauffer G. V. A new methionine locus, metR, that encodes a trans-acting protein required for activation of metE and metH in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1391–1397. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1391-1397.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse J. M., Smith D. A. Methionine and vitamin B 12 repression and precursor induction in the regulation of homocysteine methylation in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1973;120(4):341–353. doi: 10.1007/BF00268148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


