Abstract
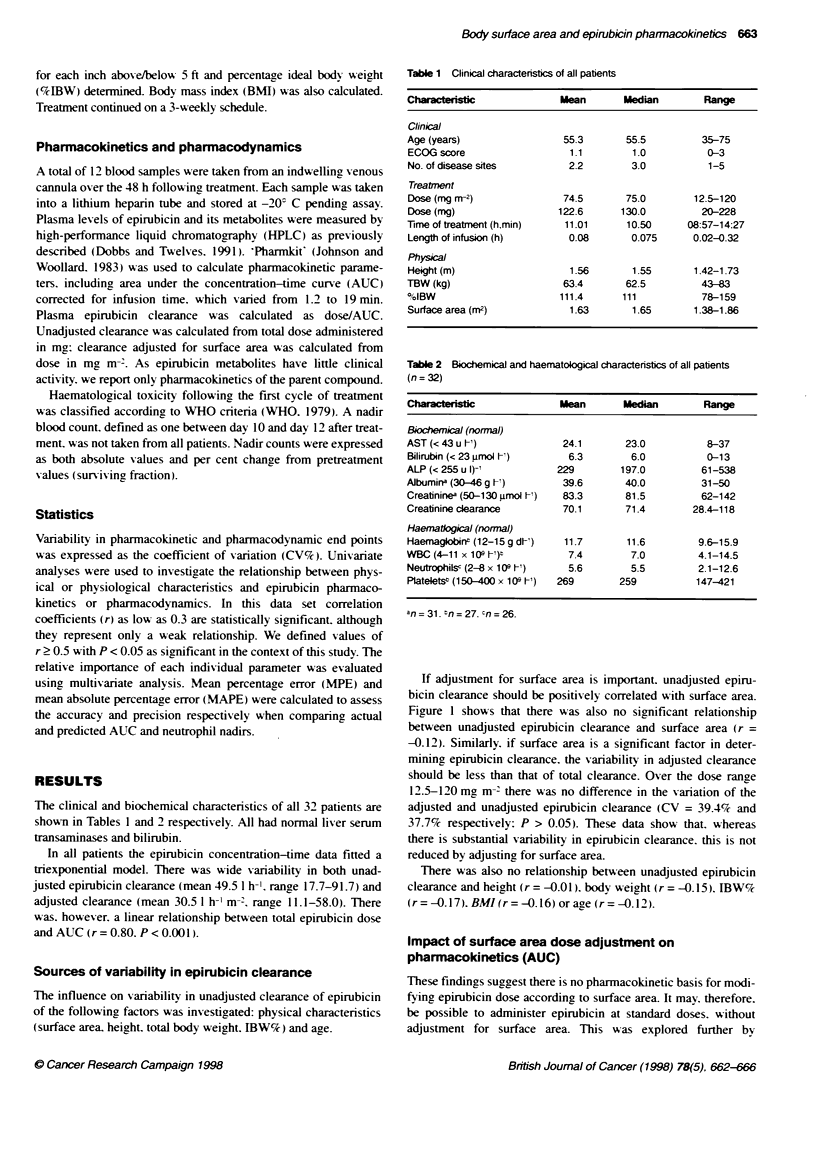
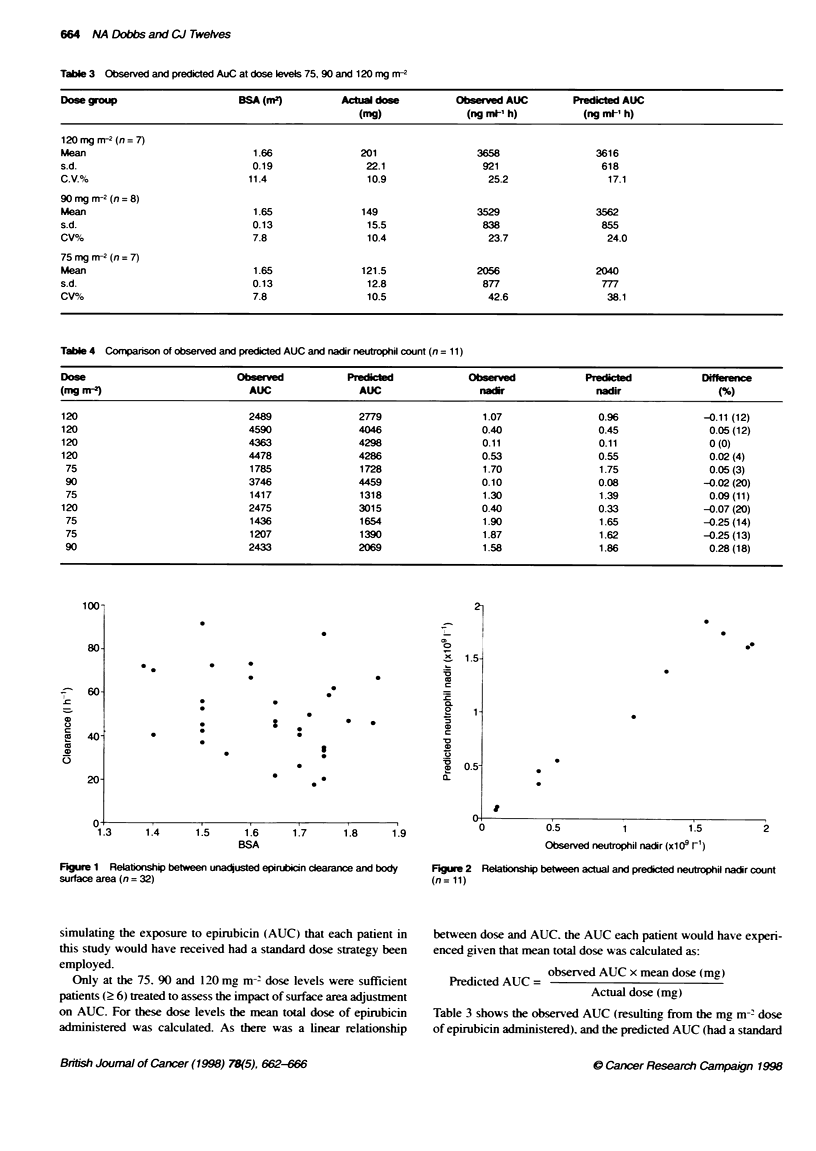
Doses of cytotoxic drugs are routinely adjusted according to body surface area. We have evaluated this practice in 32 women with advanced breast cancer treated with single-agent epirubicin 12.5-120 mg m(-2). Epirubicin and its metabolites were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Unadjusted plasma clearance was calculated from dose in mg, and adjusted clearance from dose in mg m(-2). Unadjusted clearance did not correlate with surface area, height, weight, per cent ideal body weight or body mass index. There was no difference in the coefficient of variation (CV) of adjusted and unadjusted clearance (39.4% and 37.7% respectively). The AUC that would have resulted from giving an unadjusted dose was calculated. This predicted AUC was accurate, unbiased and had the same CV as the actual AUC. Similarly, in 11 patients an analysis of actual and predicted neutropenia confirmed that unadjusted dosing would have had no significant effect on the pattern of myelosuppression. Normalization of epirubicin dosage according to surface area appears not to reduce either pharmacokinetic or pharmacodynamic variability.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackland S. P., Ratain M. J., Vogelzang N. J., Choi K. E., Ruane M., Sinkule J. A. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of long-term continuous-infusion doxorubicin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1989 Apr;45(4):340–347. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1989.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosolo W. C., Morgan D. J., Seeman E., Zimet A. S., McKendrick J. J., Zalcberg J. R. Lean body mass, body surface area and epirubicin kinetics. Anticancer Drugs. 1994 Jun;5(3):293–297. doi: 10.1097/00001813-199406000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbs N. A., Twelves C. J., Gillies H., James C. A., Harper P. G., Rubens R. D. Gender affects doxorubicin pharmacokinetics in patients with normal liver biochemistry. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1995;36(6):473–476. doi: 10.1007/BF00685796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grochow L. B., Baraldi C., Noe D. Is dose normalization to weight or body surface area useful in adults? J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Feb 21;82(4):323–325. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.4.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly J. J., Workman P. Is body composition an important variable in the pharmacokinetics of anticancer drugs? A review and suggestions for further research. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1994;34(1):3–13. doi: 10.1007/BF00686105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert J., Armand J. P., Huet S., Klink-Alakl M., Recondo G., Hurteloup P. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of 4'-iodo-4'-deoxy-doxorubicin in humans. J Clin Oncol. 1992 Jul;10(7):1183–1190. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1992.10.7.1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert J., Hoerni B. Age dependence of the early-phase pharmacokinetics of doxorubicin. Cancer Res. 1983 Sep;43(9):4467–4469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twelves C. J., Dobbs N. A., Lawrence M. A., Ramirez A. J., Summerhayes M., Richards M. A., Towlson K. E., Rubens R. D. Iododoxorubicin in advanced breast cancer: a phase II evaluation of clinical activity, pharmacology and quality of life. Br J Cancer. 1994 Apr;69(4):726–731. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1994.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twelves C. J., Dobbs N. A., Michael Y., Summers L. A., Gregory W., Harper P. G., Rubens R. D., Richards M. A. Clinical pharmacokinetics of epirubicin: the importance of liver biochemistry tests. Br J Cancer. 1992 Oct;66(4):765–769. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. R., Kelman A. W., Kerr D. J., Robert J., Whiting B. Variability in the pharmacokinetics of epirubicin: a population analysis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1992;29(5):391–395. doi: 10.1007/BF00686009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


