Abstract
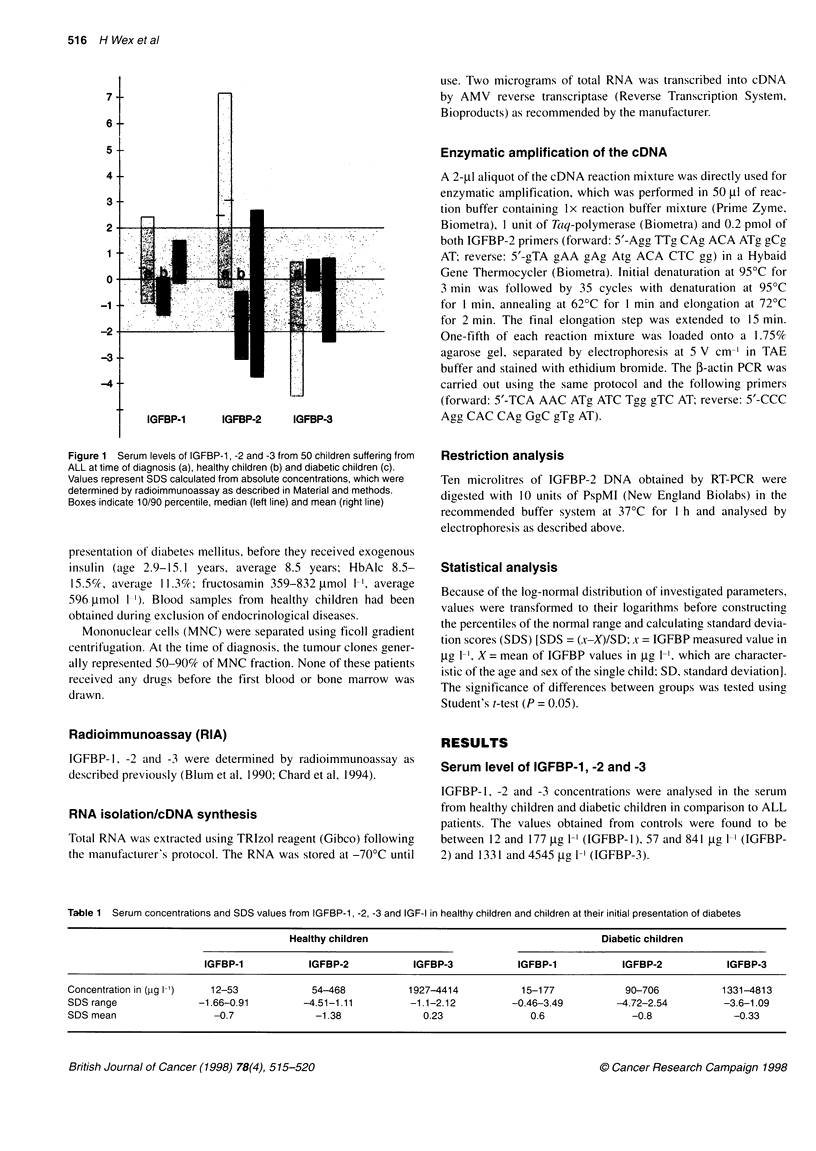
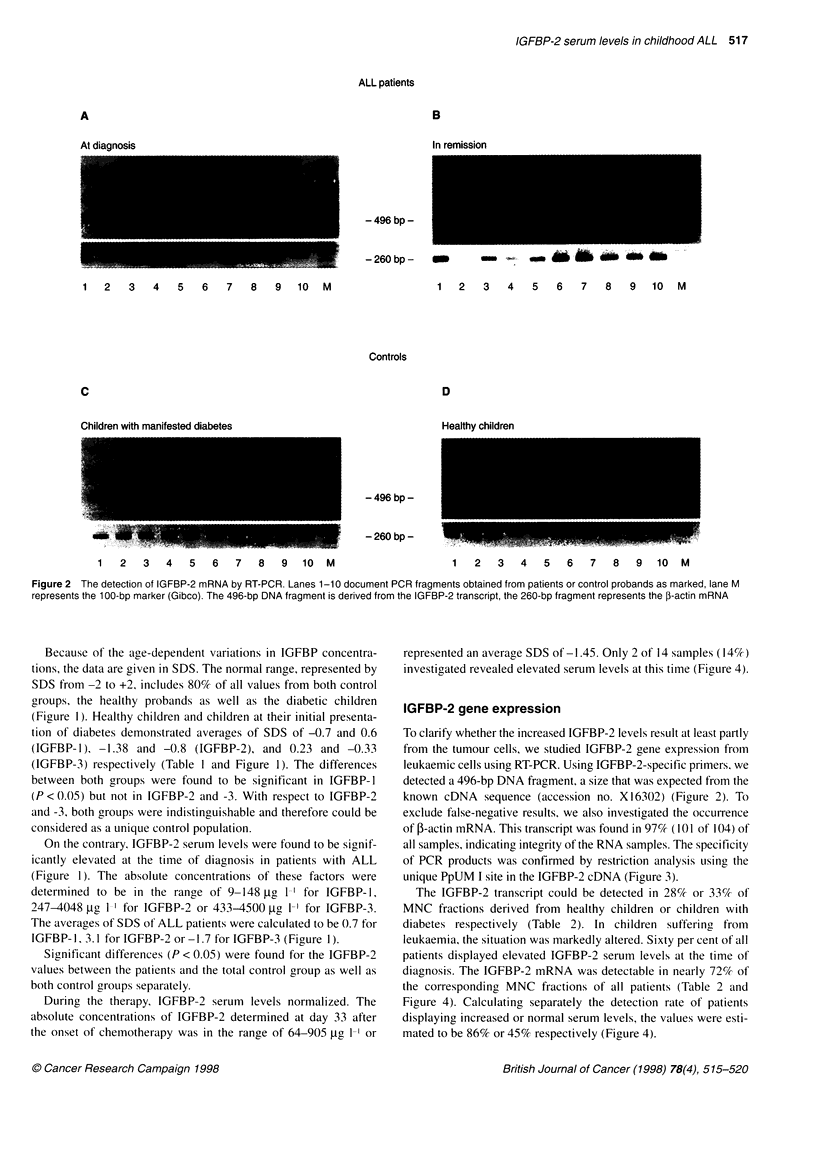
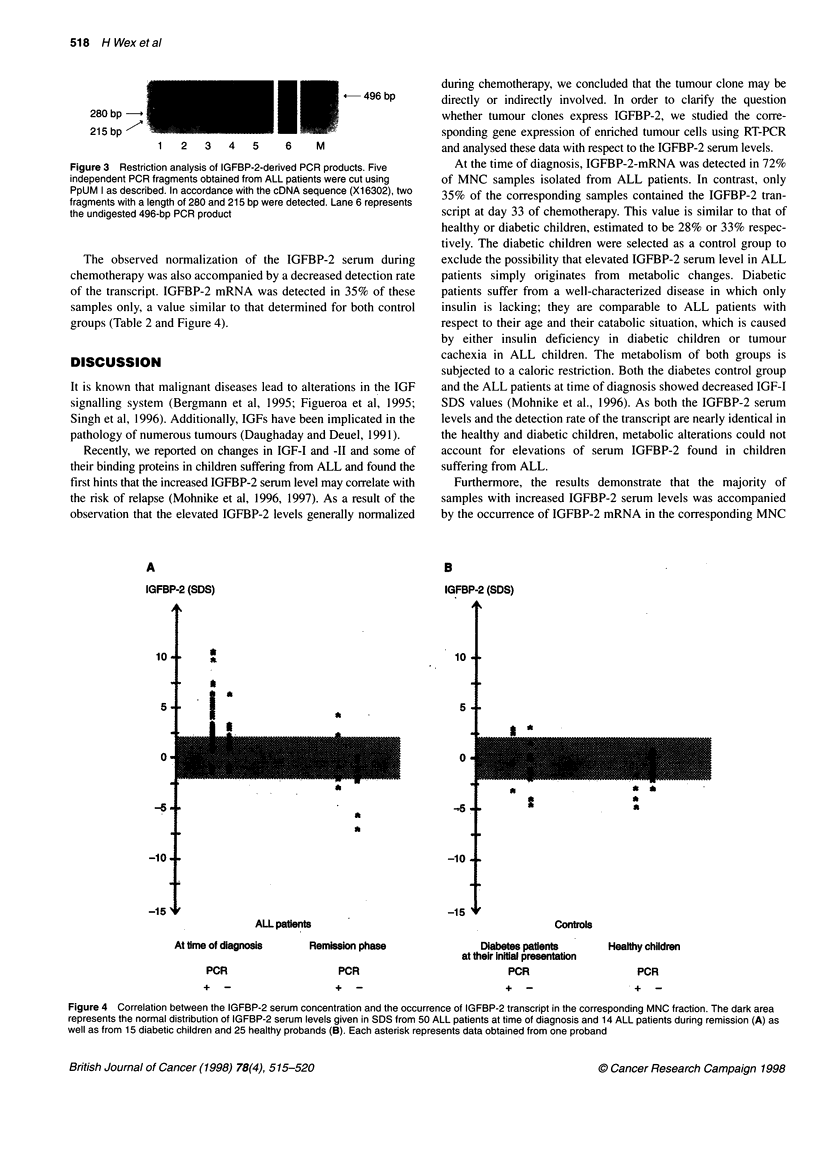
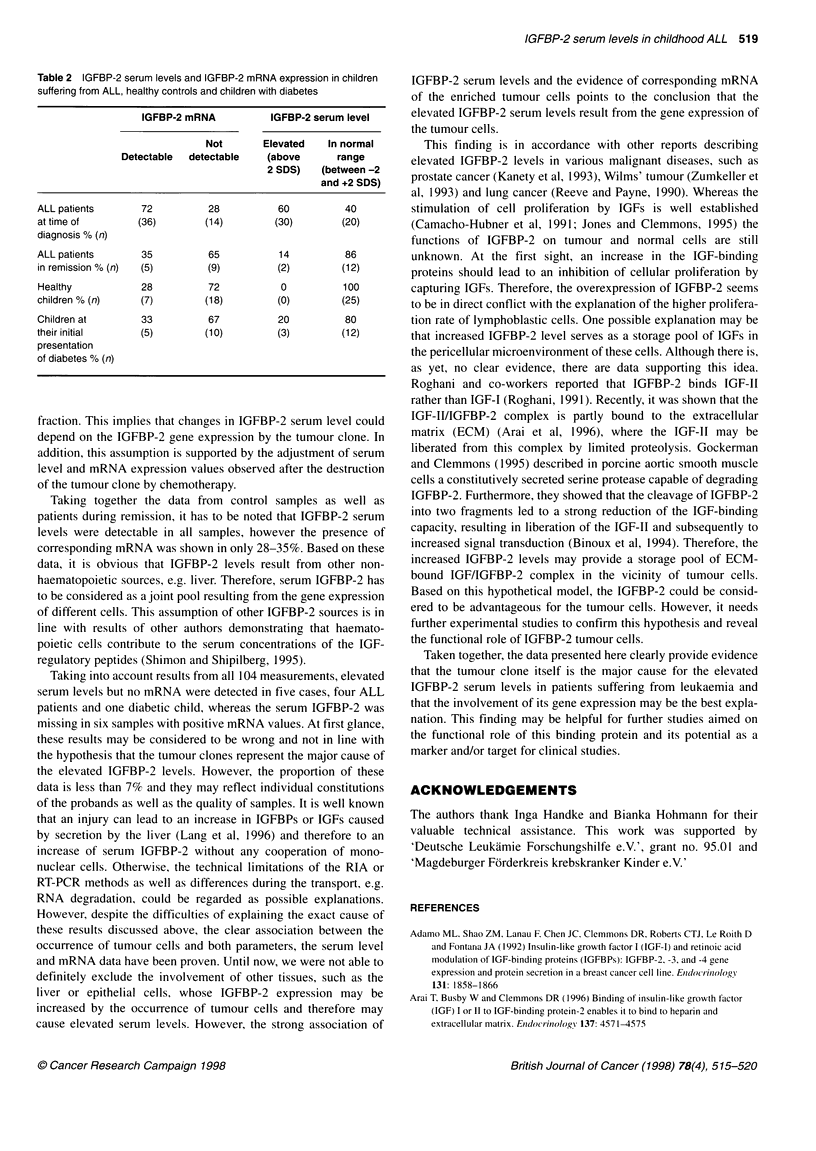
Insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins (IGFBPs) are important modulators of IGF action. In 50 children suffering from acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL), we studied the serum levels of IGFBP-1,-2 and-3. The mean standard deviation score (SDS) values were estimated to be 0.7, 3.1 and -1.7 for the IGFBP-1,-2 and-3, respectively, compared with the normal range defined by a SDS from -2 to +2. IGFBP-1 and-3 were normal, but for IGFBP-2 we found a significantly elevated serum level compared with control groups (P < 0.05). However, during chemotherapy this increased serum IGFBP-2 normalized. In addition, we found a correlation between higher serum levels and the detection rate of the IGFBP-2 transcript in corresponding cells. In patients with ALL, the detection rates of IGFBP-2 mRNA were estimated to be 72% and 35% at the time of diagnosis and at day 33 of chemotherapy respectively; in the control groups (healthy children and children at their initial presentation of diabetes mellitus), the values were 28% and 33% respectively. Based on the correlation between IGFBP-2 serum levels and the corresponding gene expression as well as the normalization of IGFBP-2 levels during chemotherapy, we concluded that the increased serum level mainly originated from the tumour clone itself. Furthermore, possible functional consequences of elevated IGFBP-2 were outlined.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamo M. L., Shao Z. M., Lanau F., Chen J. C., Clemmons D. R., Roberts C. T., Jr, LeRoith D., Fontana J. A. Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and retinoic acid modulation of IGF-binding proteins (IGFBPs): IGFBP-2, -3, and -4 gene expression and protein secretion in a breast cancer cell line. Endocrinology. 1992 Oct;131(4):1858–1866. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.4.1382963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai T., Busby W., Jr, Clemmons D. R. Binding of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) I or II to IGF-binding protein-2 enables it to bind to heparin and extracellular matrix. Endocrinology. 1996 Nov;137(11):4571–4575. doi: 10.1210/endo.137.11.8895319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann U., Funatomi H., Yokoyama M., Beger H. G., Korc M. Insulin-like growth factor I overexpression in human pancreatic cancer: evidence for autocrine and paracrine roles. Cancer Res. 1995 May 15;55(10):2007–2011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum W. F., Ranke M. B., Kietzmann K., Gauggel E., Zeisel H. J., Bierich J. R. A specific radioimmunoassay for the growth hormone (GH)-dependent somatomedin-binding protein: its use for diagnosis of GH deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 May;70(5):1292–1298. doi: 10.1210/jcem-70-5-1292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chard T., Blum W. F., Brunjes J., Campbell D. J., Wathen N. C. Levels of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 and insulin-like growth factor-II in maternal serum, amniotic fluid and extraembryonic coelomic fluid at 9-20 weeks of pregnancy. J Endocrinol. 1994 Aug;142(2):379–383. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1420379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christofori G., Naik P., Hanahan D. A second signal supplied by insulin-like growth factor II in oncogene-induced tumorigenesis. Nature. 1994 Jun 2;369(6479):414–418. doi: 10.1038/369414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Busby W. H., Arai T., Nam T. J., Clarke J. B., Jones J. I., Ankrapp D. K. Role of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in the control of IGF actions. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1995;6(2-4):357–366. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(95)00013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R. Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins: roles in regulating IGF physiology. J Dev Physiol. 1991 Feb;15(2):105–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Signal transmission by the insulin-like growth factors. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Deuel T. F. Tumor secretion of growth factors. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1991 Sep;20(3):539–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Badry O. M., Romanus J. A., Helman L. J., Cooper M. J., Rechler M. M., Israel M. A. Autonomous growth of a human neuroblastoma cell line is mediated by insulin-like growth factor II. J Clin Invest. 1989 Sep;84(3):829–839. doi: 10.1172/JCI114243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gockerman A., Clemmons D. R. Porcine aortic smooth muscle cells secrete a serine protease for insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2. Circ Res. 1995 Apr;76(4):514–521. doi: 10.1161/01.res.76.4.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino K., Seppälä M., Heinonen P. K., Sipponen P., Rutanen E. M. Elevated levels of a somatomedin-binding protein PP12 in patients with ovarian cancer. Cancer. 1986 Nov 15;58(10):2294–2297. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19861115)58:10<2294::aid-cncr2820581023>3.0.co;2-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. I., Clemmons D. R. Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions. Endocr Rev. 1995 Feb;16(1):3–34. doi: 10.1210/edrv-16-1-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanety H., Madjar Y., Dagan Y., Levi J., Papa M. Z., Pariente C., Goldwasser B., Karasik A. Serum insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 (IGFBP-2) is increased and IGFBP-3 is decreased in patients with prostate cancer: correlation with serum prostate-specific antigen. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Jul;77(1):229–233. doi: 10.1210/jcem.77.1.7686915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. S., Nagalla S. R., Oh Y., Wilson E., Roberts C. T., Jr, Rosenfeld R. G. Identification of a family of low-affinity insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBPs): characterization of connective tissue growth factor as a member of the IGFBP superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Nov 25;94(24):12981–12986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.24.12981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang C. H., Fan J., Frost R. A., Gelato M. C., Sakurai Y., Herndon D. N., Wolfe R. R. Regulation of the insulin-like growth factor system by insulin in burn patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996 Jul;81(7):2474–2480. doi: 10.1210/jcem.81.7.8675563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. M., Singleton J. R., Meghani M. A., Feldman E. L. IGF receptor function and regulation in autocrine human neuroblastoma cell growth. Regul Pept. 1993 Oct 20;48(1-2):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(93)90351-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melino G., Knight R. A., Thiele C. J. New insight on the biology of neuroectodermal tumors. Workshop report from the University of Rome Tor Vergata and the IDI-IRCCS on the genetics and control of growth, differentiation, and programmed cell death. Cancer Res. 1993 Feb 15;53(4):926–928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohnike K. L., Kluba U., Mittler U., Aumann V., Vorwerk P., Blum W. F. Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor-I, -II and insulin-like growth factor binding proteins -2 and -3 in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Eur J Pediatr. 1996 Feb;155(2):81–86. doi: 10.1007/BF02075755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neely E. K., Beukers M. W., Oh Y., Cohen P., Rosenfeld R. G. Insulin-like growth factor receptors. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl. 1991;372:116–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1991.tb17985.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve J. G., Brinkman A., Hughes S., Mitchell J., Schwander J., Bleehen N. M. Expression of insulinlike growth factor (IGF) and IGF-binding protein genes in human lung tumor cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Apr 15;84(8):628–634. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.8.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve J. G., Kirby L. B., Brinkman A., Hughes S. A., Schwander J., Bleehen N. M. Insulin-like growth-factor-binding protein gene expression and protein production by human tumour cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1992 Jul 9;51(5):818–821. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910510525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve J. G., Payne J. A., Bleehen N. M. Production of immunoreactive insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF-I binding proteins by human lung tumours. Br J Cancer. 1990 May;61(5):727–731. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1990.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roghani M., Lassarre C., Zapf J., Povoa G., Binoux M. Two insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding proteins are responsible for the selective affinity for IGF-II of cerebrospinal fluid binding proteins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Sep;73(3):658–666. doi: 10.1210/jcem-73-3-658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimon I., Shpilberg O. The insulin-like growth factor system in regulation of normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Leuk Res. 1995 Apr;19(4):233–240. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(94)00133-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh P., Dai B., Yallampalli U., Lu X., Schroy P. C. Proliferation and differentiation of a human colon cancer cell line (CaCo2) is associated with significant changes in the expression and secretion of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) IGF-II and IGF binding protein-4: role of IGF-II. Endocrinology. 1996 May;137(5):1764–1774. doi: 10.1210/endo.137.5.8612513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumkeller W., Schwander J., Mitchell C. D., Morrell D. J., Schofield P. N., Preece M. A. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, -II and IGF binding protein-2 (IGFBP-2) in the plasma of children with Wilms' tumour. Eur J Cancer. 1993;29A(14):1973–1977. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(93)90455-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




