Abstract
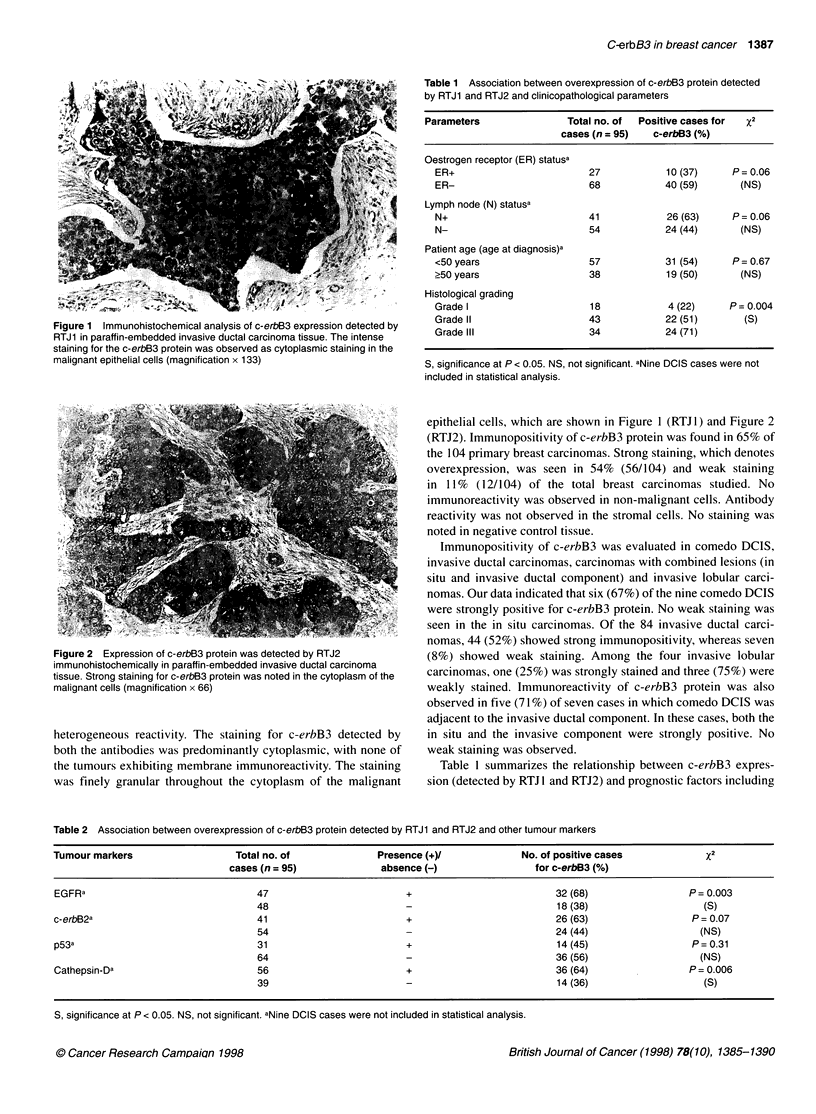
Expression of c-erbB3 protein was investigated in 104 primary breast carcinomas comprising nine comedo ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), 91 invasive ductal carcinomas and four invasive lobular carcinomas using two monoclonal antibodies, RTJ1 and RTJ2. Of the 91 invasive ductal carcinomas, seven contained the comedo DCIS component adjacent to the invasive component. An immunohistochemical technique was used to evaluate the association between expression of c-erbB3 and clinical parameters and tumour markers such as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), c-erbB2, cathepsin-D and p53 in archival formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tumour tissues. Our results indicated that RTJ1 and RTJ2 gave identical staining patterns and concordant results. It was found that the overexpression of c-erbB3 protein was observed in 67% (6/9) of comedo DCIS, 52% (44/84) of invasive ductal carcinomas, 71% (5/7) of carcinomas containing both the in situ and invasive lesions and 25% (1/4) of invasive lobular carcinomas. A significant relationship (P < 0.05) was observed between strong immunoreactivity of c-erbB3 protein and histological grade, EGFR and cathepsin-D, but not with expression of c-erbB2, p53, oestrogen receptor status, lymph node metastases or age of patient. However, we noted that a high percentage of oestrogen receptor-negative tumours (59%), lymph node-positive tumours (63%) and c-erbB2 (63%) were strongly positive for c-erbB3 protein. We have also documented that a high percentage of EGFR (67%), c-erbB2 (67%), p53 (75%) and cathepsin-D-positive DCIS (60%) were strongly positive for c-erbB3. These observations suggest that overexpression of c-erbB3 protein could play an important role in tumour progression from non-invasive to invasive and, also, that it may have the potential to be used as a marker for poor prognosis of breast cancer.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOOM H. J., RICHARDSON W. W. Histological grading and prognosis in breast cancer; a study of 1409 cases of which 359 have been followed for 15 years. Br J Cancer. 1957 Sep;11(3):359–377. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1957.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betsill W. L., Jr, Rosen P. P., Lieberman P. H., Robbins G. F. Intraductal carcinoma. Long-term follow-up after treatment by biopsy alone. JAMA. 1978 May 5;239(18):1863–1867. doi: 10.1001/jama.239.18.1863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway K. L., 3rd, Sliwkowski M. X., Akita R., Platko J. V., Guy P. M., Nuijens A., Diamonti A. J., Vandlen R. L., Cantley L. C., Cerione R. A. The erbB3 gene product is a receptor for heregulin. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):14303–14306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs L. M., Oliver S., Sweeney E., Knowles M. Immunocytochemical localization of c-erbB-2 protein in transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. J Pathol. 1993 Jan;169(1):35–42. doi: 10.1002/path.1711690107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Potter C. R., Quatacker J., Maertens G., Van Daele S., Pauwels C., Verhofstede C., Eechaute W., Roels H. The subcellular localization of the neu protein in human normal and neoplastic cells. Int J Cancer. 1989 Dec 15;44(6):969–974. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910440604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasparini G., Gullick W. J., Maluta S., Dalla Palma P., Caffo O., Leonardi E., Boracchi P., Pozza F., Lemoine N. R., Bevilacqua P. c-erbB-3 and c-erbB-2 protein expression in node-negative breast carcinoma--an immunocytochemical study. Eur J Cancer. 1994;30A(1):16–22. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(05)80010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasparini G. Tamoxifen and chemotherapy in the treatment of metastatic melanoma: are there other possible mechanisms explaining their potentiation? J Clin Oncol. 1994 Sep;12(9):1994–1996. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1994.12.9.1994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isola J., Visakorpi T., Holli K., Kallioniemi O. P. Association of overexpression of tumor suppressor protein p53 with rapid cell proliferation and poor prognosis in node-negative breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Jul 15;84(14):1109–1114. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.14.1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. H., Sierke S. L., Koland J. G. Epidermal growth factor-dependent association of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase with the erbB3 gene product. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 7;269(40):24747–24755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus M. H., Issing W., Miki T., Popescu N. C., Aaronson S. A. Isolation and characterization of ERBB3, a third member of the ERBB/epidermal growth factor receptor family: evidence for overexpression in a subset of human mammary tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9193–9197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar R., Shepard H. M., Mendelsohn J. Regulation of phosphorylation of the c-erbB-2/HER2 gene product by a monoclonal antibody and serum growth factor(s) in human mammary carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):979–986. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagios M. D. Duct carcinoma in situ. Pathology and treatment. Surg Clin North Am. 1990 Aug;70(4):853–871. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)45185-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagios M. D., Margolin F. R., Westdahl P. R., Rose M. R. Mammographically detected duct carcinoma in situ. Frequency of local recurrence following tylectomy and prognostic effect of nuclear grade on local recurrence. Cancer. 1989 Feb 15;63(4):618–624. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19890215)63:4<618::aid-cncr2820630403>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemoine N. R., Lobresco M., Leung H., Barton C., Hughes C. M., Prigent S. A., Gullick W. J., Klöppel G. The erbB-3 gene in human pancreatic cancer. J Pathol. 1992 Nov;168(3):269–273. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S., Locker A., Todd J. H., Bell J. A., Nicholson R., Elston C. W., Blamey R. W., Ellis I. O. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor in breast carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 1990 May;43(5):385–389. doi: 10.1136/jcp.43.5.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandai M., Konishi I., Koshiyama M., Mori T., Arao S., Tashiro H., Okamura H., Nomura H., Hiai H., Fukumoto M. Expression of metastasis-related nm23-H1 and nm23-H2 genes in ovarian carcinomas: correlation with clinicopathology, EGFR, c-erbB-2, and c-erbB-3 genes, and sex steroid receptor expression. Cancer Res. 1994 Apr 1;54(7):1825–1830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson S., Wright C., Sainsbury J. R., Halcrow P., Kelly P., Angus B., Farndon J. R., Harris A. L. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFr) as a marker for poor prognosis in node-negative breast cancer patients: neu and tamoxifen failure. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1990 Dec 20;37(6):811–814. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(90)90424-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pertschuk L. P., Kim D. S., Nayer K., Feldman J. G., Eisenberg K. B., Carter A. C., Rong Z. T., Thelmo W. L., Fleisher J., Greene G. L. Immunocytochemical estrogen and progestin receptor assays in breast cancer with monoclonal antibodies. Histopathologic, demographic, and biochemical correlations and relationship to endocrine response and survival. Cancer. 1990 Oct 15;66(8):1663–1670. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19901015)66:8<1663::aid-cncr2820660802>3.0.co;2-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plowman G. D., Whitney G. S., Neubauer M. G., Green J. M., McDonald V. L., Todaro G. J., Shoyab M. Molecular cloning and expression of an additional epidermal growth factor receptor-related gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4905–4909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poller D. N., Spendlove I., Baker C., Church R., Ellis I. O., Plowman G. D., Mayer R. J. Production and characterization of a polyclonal antibody to the c-erbB-3 protein: examination of c-erbB-3 protein expression in adenocarcinomas. J Pathol. 1992 Nov;168(3):275–280. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popescu N. C., King C. R., Kraus M. H. Localization of the human erbB-2 gene on normal and rearranged chromosomes 17 to bands q12-21.32. Genomics. 1989 Apr;4(3):362–366. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90343-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prigent S. A., Lemoine N. R., Hughes C. M., Plowman G. D., Selden C., Gullick W. J. Expression of the c-erbB-3 protein in normal human adult and fetal tissues. Oncogene. 1992 Jul;7(7):1273–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn C. M., Ostrowski J. L., Lane S. A., Loney D. P., Teasdale J., Benson F. A. c-erbB-3 protein expression in human breast cancer: comparison with other tumour variables and survival. Histopathology. 1994 Sep;25(3):247–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1994.tb01324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajkumar T., Stamp G. W., Pandha H. S., Waxman J., Gullick W. J. Expression of the type 1 tyrosine kinase growth factor receptors EGF receptor, c-erbB2 and c-erbB3 in bladder cancer. J Pathol. 1996 Aug;179(4):381–385. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199608)179:4<381::AID-PATH603>3.0.CO;2-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sainsbury J. R., Farndon J. R., Needham G. K., Malcolm A. J., Harris A. L. Epidermal-growth-factor receptor status as predictor of early recurrence of and death from breast cancer. Lancet. 1987 Jun 20;1(8547):1398–1402. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90593-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanidas E. E., Filipe M. I., Linehan J., Lemoine N. R., Gullick W. J., Rajkumar T., Levison D. A. Expression of the c-erbB-3 gene product in gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 1993 Jul 30;54(6):935–940. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910540612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson B. J., Weatherill J., Miller E. P., Lessells A. M., Langdon S. P., Miller W. R. c-erbB-3 protein expression in ovarian tumours. Br J Cancer. 1995 Apr;71(4):758–762. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sliwkowski M. X., Schaefer G., Akita R. W., Lofgren J. A., Fitzpatrick V. D., Nuijens A., Fendly B. M., Cerione R. A., Vandlen R. L., Carraway K. L., 3rd Coexpression of erbB2 and erbB3 proteins reconstitutes a high affinity receptor for heregulin. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 20;269(20):14661–14665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr N. K., Solomon E., Jansson M., Sheer D., Goodfellow P. N., Bodmer W. F., Vennstrom B. Chromosomal localisation of the human homologues to the oncogenes erbA and B. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):159–163. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01777.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tandon A. K., Clark G. M., Chamness G. C., Chirgwin J. M., McGuire W. L. Cathepsin D and prognosis in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1990 Feb 1;322(5):297–302. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199002013220504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis A., Pinder S. E., Robertson J. F., Bell J. A., Wencyk P., Gullick W. J., Nicholson R. I., Poller D. N., Blamey R. W., Elston C. W. C-erbB-3 in human breast carcinoma: expression and relation to prognosis and established prognostic indicators. Br J Cancer. 1996 Jul;74(2):229–233. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1996.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winstanley J. H., Leinster S. J., Cooke T. G., Westley B. R., Platt-Higgins A. M., Rudland P. S. Prognostic significance of cathepsin-D in patients with breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1993 Apr;67(4):767–772. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]