Abstract
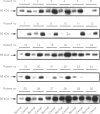
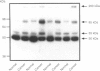
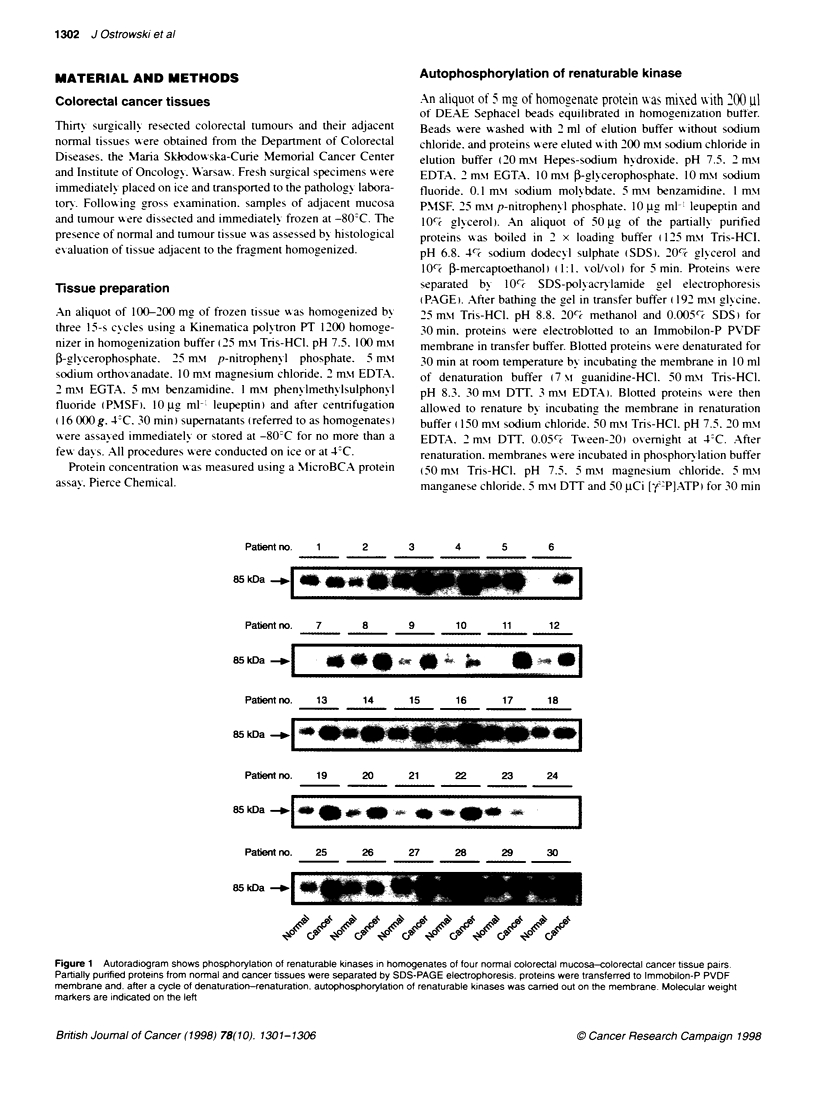
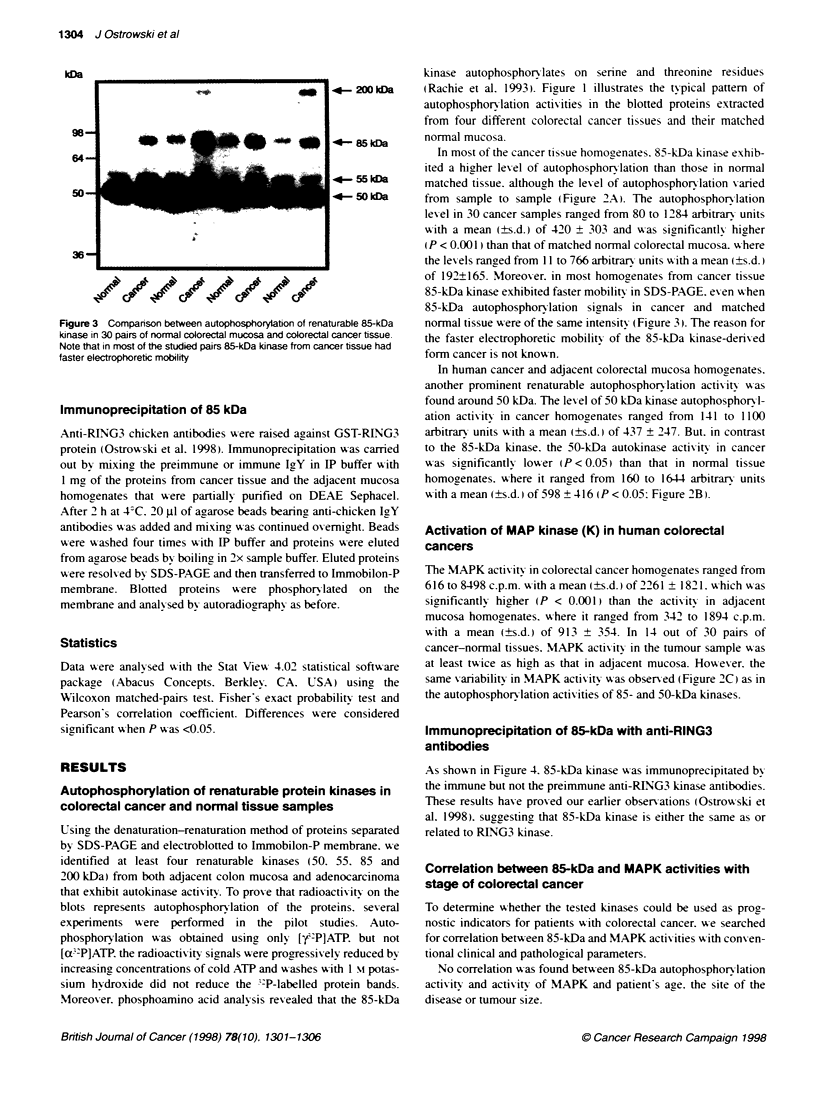
Protein kinases play a key role in intracellular signalling, participating at multiple levels along the transduction cascades that trigger mitogenic response. Because protein kinases are involved in mitogenic pathways, they are likely to play a role in the abnormal proliferation of malignant cells. In this study we compared activity of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase and several renaturable kinases in homogenates of 30 surgically resected colorectal cancers and their adjacent normal tissues. Using sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and membrane autophosphorylation assay on homogenates obtained from normal colon mucosa and adenocarcinoma, we identified at least four renaturable kinases (50, 55, 85, 200 kDa). Compared with adjacent tissue, in most of the cancer samples only the 85-kDa kinase exhibited a higher level of autophosphorylation activity than those in normal matched tissue (P < 0.001). Moreover, the 85-kDa kinase from nearly all cancer homogenates showed faster electrophoretic mobility than the 85-kDa kinase from normal tissue homogenates. Interestingly, the 50-kDa kinase had significantly lower autophosphorylation activity in cancer tissues than those of normal tissue (P< 0.05). To assess p42-p44 MAP kinase activity, proteins were immunoprecipitated from adjacent colon mucosa and adenocarcinoma with anti-extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) 1/2 antibodies, and MAP kinase activity was measured using MBP as a substrate. These studies revealed that MAP kinase activity in colorectal cancer was significantly higher (P < 0.001) than that in adjacent mucosa. Thus, the constitutive activity of MAP kinase and autophosphorylation activity of 85-kDa kinase are increased, whereas the autophosphorylation activity of another kinase, 50 kDa, is decreased in colorectal adenocarcinoma. However, although signal transduction pathways are markedly altered in this cancer, neither p42/p44 MAP kinase activity nor 85-kDa autokinase activity could be correlated with the established prognostic indicators.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTLER V. B., COLLER F. A. The prognostic significance of direct extension of carcinoma of the colon and rectum. Ann Surg. 1954 Jun;139(6):846–852. doi: 10.1097/00000658-195406000-00015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boring C. C., Squires T. S., Tong T. Cancer statistics, 1991. CA Cancer J Clin. 1991 Jan-Feb;41(1):19–36. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.41.1.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cance W. G., Liu E. T. Protein kinases in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1995 Jul;35(1):105–114. doi: 10.1007/BF00694751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Lin J. K., Lee P. H., Hsieh Y. S., Cheng C. K., Liu J. Y. The altered activity of membrane-bound protein kinase C in human liver cancer. Cancer Lett. 1996 Aug 2;105(2):211–215. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(96)04283-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. Signal-transducing protein phosphorylation cascades mediated by Ras/Rho proteins in the mammalian cell: the potential for multiplex signalling. Biochem J. 1996 Sep 15;318(Pt 3):729–747. doi: 10.1042/bj3180729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis G. V., Green M. R. A novel, mitogen-activated nuclear kinase is related to a Drosophila developmental regulator. Genes Dev. 1996 Feb 1;10(3):261–271. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.3.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Jiang Y., Li Z., Kravchenko V. V., Ulevitch R. J. Activation of the transcription factor MEF2C by the MAP kinase p38 in inflammation. Nature. 1997 Mar 20;386(6622):296–299. doi: 10.1038/386296a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. S., Treisman R. Transcriptional regulation by extracellular signals: mechanisms and specificity. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):199–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90403-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. Protein kinases and phosphatases: the yin and yang of protein phosphorylation and signaling. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):225–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90405-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusunoki M., Sakanoue Y., Hatada T., Yanagi H., Yamamura T., Utsunomiya J. Protein kinase C activity in human colonic adenoma and colorectal carcinoma. Cancer. 1992 Jan 1;69(1):24–30. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19920101)69:1<24::aid-cncr2820690107>3.0.co;2-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitzki A. Targeting signal transduction for disease therapy. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996 Apr;8(2):239–244. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(96)80071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden K., Sheu Y. J., Baetz K., Andrews B., Snyder M. SBF cell cycle regulator as a target of the yeast PKC-MAP kinase pathway. Science. 1997 Mar 21;275(5307):1781–1784. doi: 10.1126/science.275.5307.1781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magi-Galluzzi C., Mishra R., Fiorentino M., Montironi R., Yao H., Capodieci P., Wishnow K., Kaplan I., Stork P. J., Loda M. Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 1 is overexpressed in prostate cancers and is inversely related to apoptosis. Lab Invest. 1997 Jan;76(1):37–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marais R., Wynne J., Treisman R. The SRF accessory protein Elk-1 contains a growth factor-regulated transcriptional activation domain. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):381–393. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90237-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. J. MAP kinase kinase kinase, MAP kinase kinase and MAP kinase. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Feb;4(1):82–89. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida E., Gotoh Y. The MAP kinase cascade is essential for diverse signal transduction pathways. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Apr;18(4):128–131. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90019-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka H., Chatani Y., Hoshino R., Ogawa O., Kakehi Y., Terachi T., Okada Y., Kawaichi M., Kohno M., Yoshida O. Constitutive activation of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases in human renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1995 Sep 15;55(18):4182–4187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski J., Florio S. K., Denis G. V., Suzuki H., Bomsztyk K. Stimulation of p85/RING3 kinase in multiple organs after systemic administration of mitogens into mice. Oncogene. 1998 Mar 5;16(9):1223–1227. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Sanghera J. S. Mitogen-activated protein kinases: versatile transducers for cell signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jun;17(6):233–238. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)80005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Nikolakaki E., Woodgett J. R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):670–674. doi: 10.1038/353670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachie N. A., Seger R., Valentine M. A., Ostrowski J., Bomsztyk K. Identification of an inducible 85-kDa nuclear protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):22143–22149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter C. W., Catling A. D., Weber M. J. Immune complex kinase assays for mitogen-activated protein kinase and MEK. Methods Enzymol. 1995;255:245–256. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(95)55027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues G. A., Park M. Oncogenic activation of tyrosine kinases. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Feb;4(1):15–24. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Krebs E. G. The MAPK signaling cascade. FASEB J. 1995 Jun;9(9):726–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towatari M., Iida H., Tanimoto M., Iwata H., Hamaguchi M., Saito H. Constitutive activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in acute leukemia cells. Leukemia. 1997 Apr;11(4):479–484. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2400617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Regulation of transcription by MAP kinase cascades. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996 Apr;8(2):205–215. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(96)80067-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitmarsh A. J., Davis R. J. Transcription factor AP-1 regulation by mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways. J Mol Med (Berl) 1996 Oct;74(10):589–607. doi: 10.1007/s001090050063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]