Abstract
The 97-kDa protein Mtx21, derived from the 100-kDa mosquitocidal protein (Mtx) from Bacillus sphaericus SSII-1 by the deletion of the putative signal sequence, was expressed as a fusion protein with glutathione S-transferase in Escherichia coli, and the fusion protein was purified by affinity chromatography. The fusion protein bound to glutathione agarose was cleaved with thrombin to release the Mtx21 protein. The 97-kDa Mtx21 protein was found to be toxic to Culex quinquefasciatus larvae with a 50% lethal concentration of 15 ng/ml. Treating Mtx21 with crude mosquito larval gut extracts gave rise to two major peptides of 70 and 27 kDa. Treating the 97-kDa Mtx21 protein with trysin also gave rise to a similar proteolytic cleavage pattern. N-terminal sequencing showed that the 27-kDa peptide was derived from the N-terminal region of the 97-kDa protein and that the 70-kDa protein was from the C-terminal region of the 97-kDa protein. The 27-kDa peptide has all the previously identified regions of homology with the catalytic peptides of the ADP-ribosyltransferase toxins, such as pertussis toxin S1 peptide, while the 70-kDa peptide has three internal regions of homology.
Full text
PDF
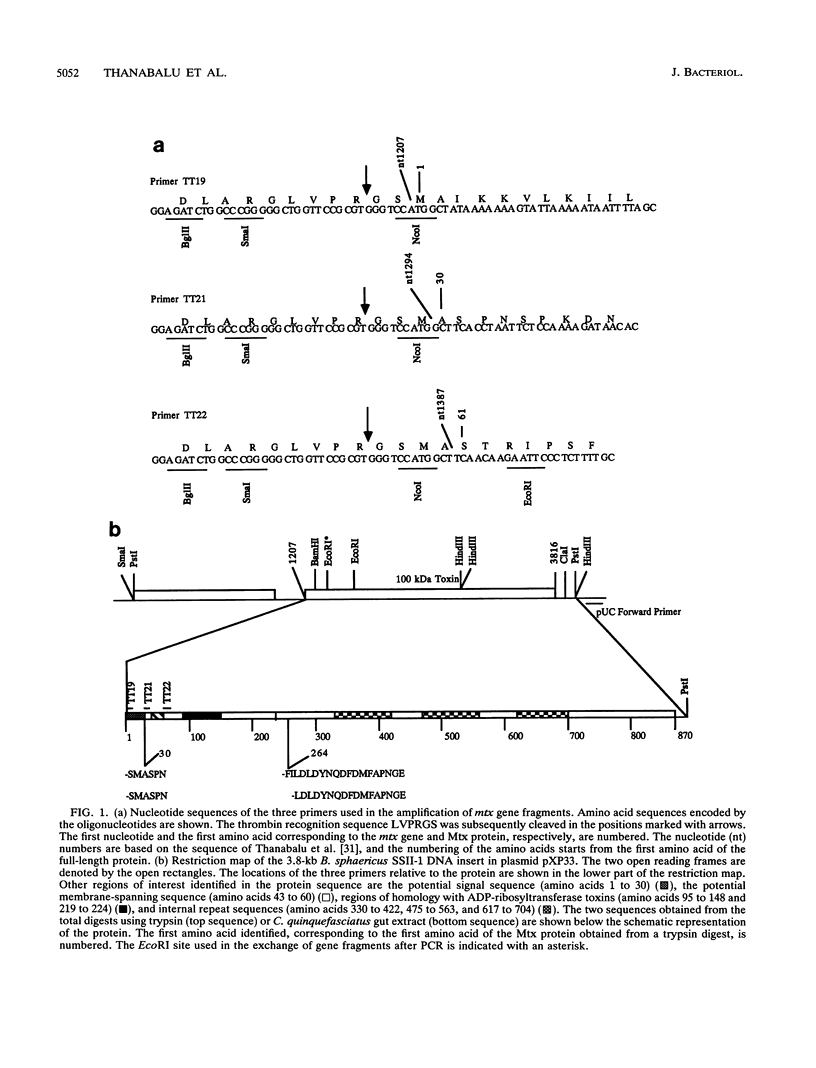




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aly C., Mulla M. S., Federici B. A. Ingestion, dissolution, and proteolysis of the Bacillus sphaericus toxin by mosquito larvae. J Invertebr Pathol. 1989 Jan;53(1):12–20. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(89)90068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann L., Broadwell A. H., Baumann P. Sequence analysis of the mosquitocidal toxin genes encoding 51.4- and 41.9-kilodalton proteins from Bacillus sphaericus 2362 and 2297. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2045–2050. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2045-2050.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Baumann L., Bowditch R. D., Broadwell A. H. Cloning of the gene for the larvicidal toxin of Bacillus sphaericus 2362: evidence for a family of related sequences. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4061–4067. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4061-4067.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Clark M. A., Baumann L., Broadwell A. H. Bacillus sphaericus as a mosquito pathogen: properties of the organism and its toxins. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):425–436. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.425-436.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Unterman B. M., Baumann L., Broadwell A. H., Abbene S. J., Bowditch R. D. Purification of the larvicidal toxin of Bacillus sphaericus and evidence for high-molecular-weight precursors. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):738–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.738-747.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boquet P., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Interaction of diphtheria toxin with mammalian cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5770–5778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadwell A. H., Baumann L., Baumann P. The 42- and 51-kilodalton mosquitocidal proteins of Bacillus sphaericus 2362: construction of recombinants with enhanced expression and in vivo studies of processing and toxicity. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2217–2223. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2217-2223.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadwell A. H., Baumann P. Proteolysis in the gut of mosquito larvae results in further activation of the Bacillus sphaericus toxin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jun;53(6):1333–1337. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.6.1333-1337.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. Engineering for protein secretion in gram-positive bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:507–516. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J., Kandel J. Structure and activity of diphtheria toxin. I. Thiol-dependent dissociation of a fraction of toxin into enzymically active and inactive fragments. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1496–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. W., Bieber A. L., Meyer M., Shellabarger C. Enzymatic activation of the Bacillus sphaericus mosquito larvicidal toxin. J Invertebr Pathol. 1987 Jul;50(1):40–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(87)90143-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. W., Oei C., Meyer M., Bieber A. L., Hindley J., Berry C. Interaction of the Bacillus sphaericus mosquito larvicidal proteins. Can J Microbiol. 1990 Dec;36(12):870–878. doi: 10.1139/m90-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Dinius L. L. Observations on the structure of diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1485–1491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Structure-activity relationships in diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1492–1495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindley J., Berry C. Identification, cloning and sequence analysis of the Bacillus sphaericus 1593 41.9 kD larvicidal toxin gene. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Sep;1(2):187–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00511.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Nishizuka Y., Hayaishi O. Diphtheria toxin-dependent adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of aminoacyl transferase II and inhibition of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3553–3555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellen W. R., Clark T. B., Lindegren J. E., Ho B. C., Rogoff M. H., Singer S. Bacillus sphaericus Neide as a pathogen of mosquitoes. J Invertebr Pathol. 1965 Dec;7(4):442–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(65)90120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lory S., Carroll S. F., Bernard P. D., Collier R. J. Ligand interactions of diphtheria toxin. I. Binding and hydrolysis of NAD. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):12011–12015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel A., Zanen J., Monier C., Crispeels C., Dirkx J. Partial characterization of diphtheria toxin and its subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 29;257(2):249–256. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90276-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers P., Yousten A. A., Davidson E. W. Comparative studies of the mosquito-larval toxin of Bacillus sphaericus SSII-1 and 1593. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Nov;25(11):1227–1231. doi: 10.1139/m79-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers P., Yousten A. A. Toxic activity of Bacillus sphaericus SSII-1 for mosquito larvae. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1047–1053. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1047-1053.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Perugini M., Franzini C., Casagli M. C., Borri M. G., Antoni G., Almoni M., Neri P., Ratti G., Rappuoli R. Cloning and sequencing of the pertussis toxin genes: operon structure and gene duplication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4631–4635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfannenstiel M. A., Couche G. A., Ross E. J., Nickerson K. W. Immunological relationships among proteins making up the Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis crystalline toxin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):644–649. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.644-649.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. Insecticidal activity of recent bacterial isolates and their toxins against mosquito larvae. Nature. 1973 Jul 13;244(5411):110–111. doi: 10.1038/244110a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanabalu T., Hindley J., Jackson-Yap J., Berry C. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of a gene encoding a 100-kilodalton mosquitocidal toxin from Bacillus sphaericus SSII-1. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):2776–2785. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.2776-2785.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinelli R., Bourgouin C. Larvicidal toxin from Bacillus sphaericus spores: isolation of toxic components. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jun 1;142(1):155–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser J. A mosquito-virulent Bacillus sphaericus in adult Simulium damnosum from northern Nigeria. Zentralbl Mikrobiol. 1984;139(1):57–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Barjac H., Thiery I., Cosmao-Dumanoir V., Frachon E., Laurent P., Charles J. F., Hamon S., Ofori J. Another Bacillus sphaericus serotype harbouring strains very toxic to mosquito larvae: serotype H6. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1988 May-Jun;139(3):363–377. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(88)90028-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



