Abstract
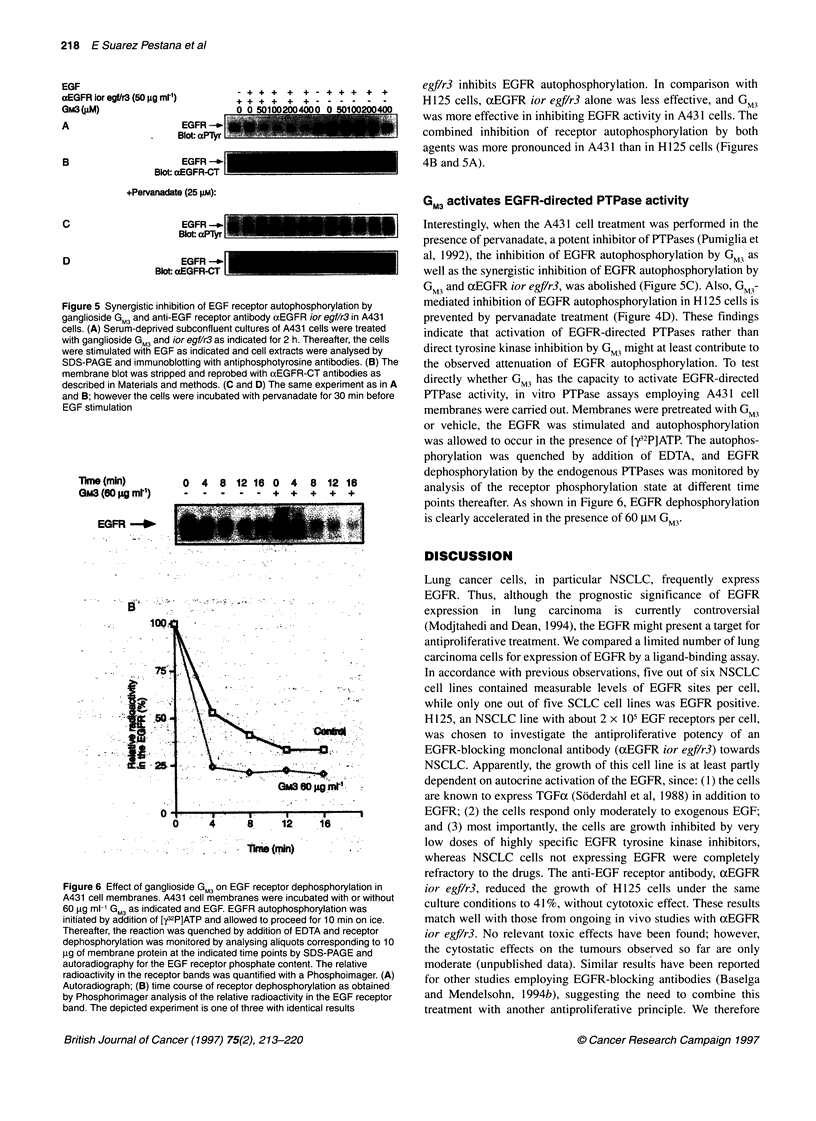
Growth of the EGF receptor-expressing non-small-cell lung carcinoma cell line H125 seems to be at least partially driven by autocrine activation of the resident EGF receptors. Thus, the possibility of an EGF receptor-directed antiproliferative treatment was investigated in vitro using a monoclonal antibody (alpha EGFR ior egf/r3) against the human EGF receptor and gangliosides which are known to possess antiproliferative and anti-tyrosine kinase activity. The moderate growth-inhibitory effect of alpha EGFR ior egf/r3 was strongly potentiated by the addition of monosialoganglioside GM3. Likewise, the combination of alpha EGFR ior egf/r3 and GM3 inhibited EGF receptor autophosphorylation activity in H125 cells more strongly than either agent alone. A synergistic inhibition of EGF receptor autophosphorylation by alpha EGFR ior egf/r3 and GM3 was also observed in the human epidermoid carcinoma cell line A431. In both cell lines, the inhibition of EGF receptor autophosphorylation by GM3 was prevented by pretreatment of the cells with pervanadate, a potent inhibitor of protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPases). Also, GM3 accelerated EGF receptor dephosphorylation in isolated A431 cell membranes. These findings indicate that GM3 has the capacity to activate EGF receptor-directed PTPase activity and suggest a novel possible mechanism for the regulation of cellular PTPases.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes D. W. Epidermal growth factor inhibits growth of A431 human epidermoid carcinoma in serum-free cell culture. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):1–4. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baselga J., Mendelsohn J. Receptor blockade with monoclonal antibodies as anti-cancer therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 1994 Oct;64(1):127–154. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(94)90036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baselga J., Mendelsohn J. The epidermal growth factor receptor as a target for therapy in breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1994 Jan;29(1):127–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00666188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergh J., Larsson E., Zech L., Nilsson K. Establishment and characterization of two neoplastic cell lines (U-1285 and U-1568) derived from small cell carcinoma of the lung. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand A. 1982 May;90(3):149–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1982.tb00076_90a.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergh J., Nilsson K., Zech L., Giovanella B. Establishment and characterization of a continuous lung squamous cell carcinoma cell line (U-1752). Anticancer Res. 1981;1(6):317–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremer E. G., Schlessinger J., Hakomori S. Ganglioside-mediated modulation of cell growth. Specific effects of GM3 on tyrosine phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2434–2440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhmer F. D., Böhmer A., Obermeier A., Ullrich A. Use of selective tyrosine kinase blockers to monitor growth factor receptor dephosphorylation in intact cells. Anal Biochem. 1995 Jul 1;228(2):267–273. doi: 10.1006/abio.1995.1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhmer F. D., Böhmer S. A., Heldin C. H. The dephosphorylation characteristics of the receptors for epidermal growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor in Swiss 3T3 cell membranes suggest differential regulation of receptor signalling by endogenous protein-tyrosine phosphatases. FEBS Lett. 1993 Oct 4;331(3):276–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80352-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney D. N., Gazdar A. F., Bepler G., Guccion J. G., Marangos P. J., Moody T. W., Zweig M. H., Minna J. D. Establishment and identification of small cell lung cancer cell lines having classic and variant features. Cancer Res. 1985 Jun;45(6):2913–2923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K. 1002 protein phosphatases? Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:463–493. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Carpenter G. Human epidermal growth factor: isolation and chemical and biological properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1317–1321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Goeddel D. V., Ullrich A., Gutterman J. U., Williams R. D., Bringman T. S., Berger W. H. Synthesis of messenger RNAs for transforming growth factors alpha and beta and the epidermal growth factor receptor by human tumors. Cancer Res. 1987 Feb 1;47(3):707–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Yarden Y., Mayes E., Scrace G., Totty N., Stockwell P., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):521–527. doi: 10.1038/307521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faure R., Baquiran G., Bergeron J. J., Posner B. I. The dephosphorylation of insulin and epidermal growth factor receptors. Role of endosome-associated phosphotyrosine phosphatase(s). J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11215–11221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez A., Spitzer E., Perez R., Boehmer F. D., Eckert K., Zschiesche W., Grosse R. A new monoclonal antibody for detection of EGF-receptors in western blots and paraffin-embedded tissue sections. J Cell Biochem. 1992 Jun;49(2):157–165. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240490208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong C. J., Sherwood E. R., Mendelsohn J., Lee C., Kozlowski J. M. Epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody inhibits constitutive receptor phosphorylation, reduces autonomous growth, and sensitizes androgen-independent prostatic carcinoma cells to tumor necrosis factor alpha. Cancer Res. 1992 Nov 1;52(21):5887–5892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontanini G., Vignati S., Bigini D., Mussi A., Lucchi H., Angeletti C. A., Pingitore R., Pepe S., Basolo F., Bevilacqua G. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFr) expression in non-small cell lung carcinomas correlates with metastatic involvement of hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes in the squamous subtype. Eur J Cancer. 1995;31A(2):178–183. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(93)00421-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry D. W., Kraker A. J., McMichael A., Ambroso L. A., Nelson J. M., Leopold W. R., Connors R. W., Bridges A. J. A specific inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. Science. 1994 Aug 19;265(5175):1093–1095. doi: 10.1126/science.8066447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F., Carney D. N., Russell E. K., Sims H. L., Baylin S. B., Bunn P. A., Jr, Guccion J. G., Minna J. D. Establishment of continuous, clonable cultures of small-cell carcinoma of lung which have amine precursor uptake and decarboxylation cell properties. Cancer Res. 1980 Oct;40(10):3502–3507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B., Oliff A. Pharmaceutical research in molecular oncology. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90189-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groenen L. C., Nice E. C., Burgess A. W. Structure-function relationships for the EGF/TGF-alpha family of mitogens. Growth Factors. 1994;11(4):235–257. doi: 10.3109/08977199409010997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanai N., Nores G. A., MacLeod C., Torres-Mendez C. R., Hakomori S. Ganglioside-mediated modulation of cell growth. Specific effects of GM3 and lyso-GM3 in tyrosine phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10915–10921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto N., Zhang W. R., Goldstein B. J. Insulin receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor dephosphorylation by three major rat liver protein-tyrosine phosphatases expressed in a recombinant bacterial system. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 1;284(Pt 2):569–576. doi: 10.1042/bj2840569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman M. J., Kitchener G., Vogt P. K., Beug H. The putative transforming protein of S13 avian erythroblastosis virus is a transmembrane glycoprotein with an associated protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8237–8241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata N., Chida K., Rikimaru K., Horikoshi M., Enomoto S., Kuroki T. Growth-inhibitory effects of epidermal growth factor and overexpression of its receptors on human squamous cell carcinomas in culture. Cancer Res. 1986 Apr;46(4 Pt 1):1648–1653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khazaie K., Schirrmacher V., Lichtner R. B. EGF receptor in neoplasia and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1993 Sep;12(3-4):255–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00665957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klijn J. G., Berns P. M., Schmitz P. I., Foekens J. A. The clinical significance of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF-R) in human breast cancer: a review on 5232 patients. Endocr Rev. 1992 Feb;13(1):3–17. doi: 10.1210/edrv-13-1-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammers R., Bossenmaier B., Cool D. E., Tonks N. K., Schlessinger J., Fischer E. H., Ullrich A. Differential activities of protein tyrosine phosphatases in intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22456–22462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitzki A., Gazit A. Tyrosine kinase inhibition: an approach to drug development. Science. 1995 Mar 24;267(5205):1782–1788. doi: 10.1126/science.7892601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardero J., Pérez R., Lage A. Epidermal growth factor inhibits thymidine incorporation in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells in vivo. Neoplasma. 1986;33(4):423–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macias A., Azavedo E., Hägerström T., Klintenberg C., Pérez R., Skoog L. Prognostic significance of the receptor for epidermal growth factor in human mammary carcinomas. Anticancer Res. 1987 May-Jun;7(3 Pt B):459–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macias A., Azavedo E., Perez R., Rutqvist L. E., Skoog L. Receptors for epidermal growth factor in human mammary carcinomas and their metastases. Anticancer Res. 1986 Jul-Aug;6(4):849–851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macias A., Perez R., Hägerström T., Skoog L. Identification of transforming growth factor alpha in human primary breast carcinomas. Anticancer Res. 1987 Nov-Dec;7(6):1271–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modjtahedi H., Eccles S., Box G., Styles J., Dean C. Immunotherapy of human tumour xenografts overexpressing the EGF receptor with rat antibodies that block growth factor-receptor interaction. Br J Cancer. 1993 Feb;67(2):254–261. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller B. M., Romerdahl C. A., Trent J. M., Reisfeld R. A. Suppression of spontaneous melanoma metastasis in scid mice with an antibody to the epidermal growth factor receptor. Cancer Res. 1991 Apr 15;51(8):2193–2198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nores G. A., Hanai N., Levery S. B., Eaton H. L., Salyan M. E., Hakomori S. Synthesis and characterization of ganglioside GM3 derivatives: lyso-GM3, de-N-acetyl-GM3, and other compounds. Methods Enzymol. 1989;179:242–253. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)79124-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osherov N., Levitzki A. Epidermal-growth-factor-dependent activation of the src-family kinases. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Nov 1;225(3):1047–1053. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.1047b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pot D. A., Dixon J. E. A thousand and two protein tyrosine phosphatases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jul 22;1136(1):35–43. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90082-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pumiglia K. M., Lau L. F., Huang C. K., Burroughs S., Feinstein M. B. Activation of signal transduction in platelets by the tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor pervanadate (vanadyl hydroperoxide). Biochem J. 1992 Sep 1;286(Pt 2):441–449. doi: 10.1042/bj2860441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez R., Pascual M., Macías A., Lage A. Epidermal growth factor receptors in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1984;4(3):189–193. doi: 10.1007/BF01806484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reins H. A., Steinhilber G., Freiberg B., Anderer F. A. Anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibodies affecting signal transduction. J Cell Biochem. 1993 Feb;51(2):236–248. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240510215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodeck U., Herlyn M., Herlyn D., Molthoff C., Atkinson B., Varello M., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H. Tumor growth modulation by a monoclonal antibody to the epidermal growth factor receptor: immunologically mediated and effector cell-independent effects. Cancer Res. 1987 Jul 15;47(14):3692–3696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sainsbury J. R., Farndon J. R., Sherbet G. V., Harris A. L. Epidermal-growth-factor receptors and oestrogen receptors in human breast cancer. Lancet. 1985 Feb 16;1(8425):364–366. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91385-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm L. Gangliosides--a new therapeutic agent against stroke and Alzheimer's disease. Life Sci. 1994;55(25-26):2125–2134. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(94)00393-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarup G., Cohen S., Garbers D. L. Inhibition of membrane phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatase activity by vanadate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):1104–1109. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90635-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderdahl G., Betsholtz C., Johansson A., Nilsson K., Bergh J. Differential expression of platelet-derived growth factor and transforming growth factor genes in small- and non-small-cell human lung carcinoma lines. Int J Cancer. 1988 Apr 15;41(4):636–641. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomic S., Greiser U., Lammers R., Kharitonenkov A., Imyanitov E., Ullrich A., Böhmer F. D. Association of SH2 domain protein tyrosine phosphatases with the epidermal growth factor receptor in human tumor cells. Phosphatidic acid activates receptor dephosphorylation by PTP1C. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 8;270(36):21277–21284. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.36.21277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velu T. J., Beguinot L., Vass W. C., Willingham M. C., Merlino G. T., Pastan I., Lowy D. R. Epidermal-growth-factor-dependent transformation by a human EGF receptor proto-oncogene. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1408–1410. doi: 10.1126/science.3500513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis F. M., Davis R. J. Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signal transduction. Role of gangliosides. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):12059–12066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda T., Lyall R. M., Alsina M. M., Persons P. E., Spada A. P., Levitzki A., Zilberstein A., Mundy G. R. The antiproliferative effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitors tyrphostins on a human squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in nude mice. Cancer Res. 1991 Aug 15;51(16):4430–4435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q., Hakomori S., Kitamura K., Igarashi Y. GM3 directly inhibits tyrosine phosphorylation and de-N-acetyl-GM3 directly enhances serine phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor, independently of receptor-receptor interaction. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):1959–1965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]