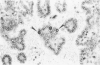
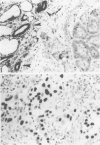
Abstract
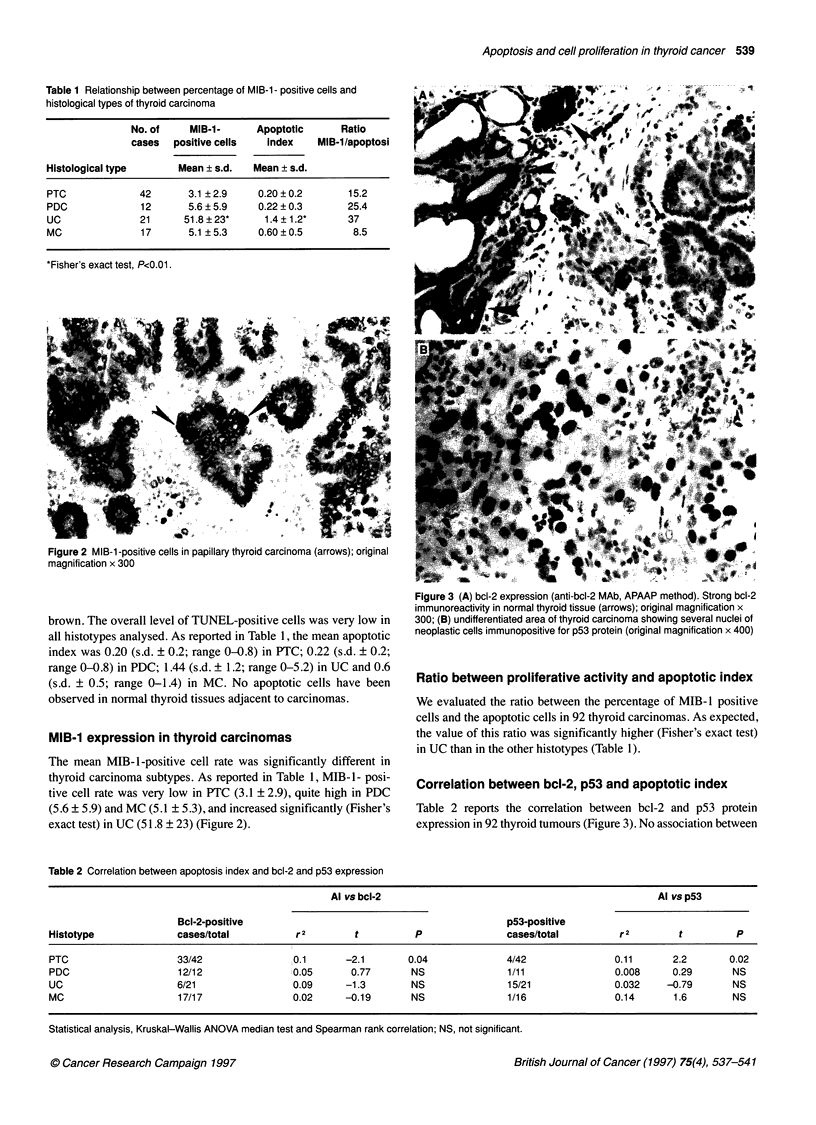
The aim of this study was to determine the apoptotic cell death in 92 thyroid carcinomas of different histotypes (42 papillary, PTC; 12 poorly differentiated, PDC: 21 undifferentiated, UC; and 17 medullary, MC) by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)-mediated dUTP-digoxigenin nick end labelling (TUNEL). Apoptotic index (Al, evaluated as a percentage of TUNEL-positive cells of neoplastic cells) was calculated in each tumour. The AI was very low in all subtypes of thyroid carcinoma, ranging from a median value of 0.2 in PTC to 1.4 in UC. The proliferative activity was determined by immunohistochemistry using monoclonal antibody, MIB-1. The percentage of proliferating cells was significantly different among the histotypes, increasing with tumour aggressiveness (from the mean value of 3.1 for PTC to 5.6 for PDC and 51.8 for UC). In addition, the ratio between proliferative activity and apoptosis was significantly higher in UC than in the other histotypes. The expression of bcl-2 and p53 protein (important in the modulation of cell death) was correlated (bcl-2, inverse correlation, r2 = 0.1, P = 0.04; p53, direct correlation, r2 = 0.11, P = 0.02) with apoptotic index in PTC.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barr P. J., Tomei L. D. Apoptosis and its role in human disease. Biotechnology (N Y) 1994 May;12(5):487–493. doi: 10.1038/nbt0594-487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedi A., Pasricha P. J., Akhtar A. J., Barber J. P., Bedi G. C., Giardiello F. M., Zehnbauer B. A., Hamilton S. R., Jones R. J. Inhibition of apoptosis during development of colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 1995 May 1;55(9):1811–1816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canman C. E., Kastan M. B. Induction of apoptosis by tumor suppressor genes and oncogenes. Semin Cancer Biol. 1995 Feb;6(1):17–25. doi: 10.1006/scbi.1995.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canman C. E., Kastan M. B. Induction of apoptosis by tumor suppressor genes and oncogenes. Semin Cancer Biol. 1995 Feb;6(1):17–25. doi: 10.1006/scbi.1995.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattoretti G., Becker M. H., Key G., Duchrow M., Schlüter C., Galle J., Gerdes J. Monoclonal antibodies against recombinant parts of the Ki-67 antigen (MIB 1 and MIB 3) detect proliferating cells in microwave-processed formalin-fixed paraffin sections. J Pathol. 1992 Dec;168(4):357–363. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler D., el-Naggar A. K., Brisbay S., Redline R. W., McDonnell T. J. Apoptosis and expression of the bcl-2 proto-oncogene in the fetal and adult human kidney: evidence for the contribution of bcl-2 expression to renal carcinogenesis. Hum Pathol. 1994 Aug;25(8):789–796. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell J. L., Falini B., Erber W. N., Ghosh A. K., Abdulaziz Z., MacDonald S., Pulford K. A., Stein H., Mason D. Y. Immunoenzymatic labeling of monoclonal antibodies using immune complexes of alkaline phosphatase and monoclonal anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP complexes). J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Feb;32(2):219–229. doi: 10.1177/32.2.6198355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig R. W. The bcl-2 gene family. Semin Cancer Biol. 1995 Feb;6(1):35–43. doi: 10.1006/scbi.1995.0005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavrieli Y., Sherman Y., Ben-Sasson S. A. Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):493–501. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gestblom C., Hoehner J. C., Påhlman S. Proliferation and apoptosis in neuroblastoma: subdividing the mitosis-karyorrhexis index. Eur J Cancer. 1995;31A(4):458–463. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(95)00006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heatley M. K. Association between the apoptotic index and established prognostic parameters in endometrial adenocarcinoma. Histopathology. 1995 Nov;27(5):469–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1995.tb00312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstädter F., Knüchel R., Rüschoff J. Cell proliferation assessment in oncology. Virchows Arch. 1995;427(3):323–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00203402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isner J. M., Kearney M., Bortman S., Passeri J. Apoptosis in human atherosclerosis and restenosis. Circulation. 1995 Jun 1;91(11):2703–2711. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.91.11.2703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh R., Bray C. E., Suzuki K., Komiyama A., Hemmi A., Kawaoi A., Oyama T., Sugai T., Sasou S. Growth activity in hyperplastic and neoplastic human thyroid determined by an immunohistochemical staining procedure using monoclonal antibody MIB-1. Hum Pathol. 1995 Feb;26(2):139–146. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(95)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsikis P. D., Leben W. R. Apoptosis. Nature. 1995 Apr 20;374(6524):670–670. doi: 10.1038/374670b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlo G. R., Basolo F., Fiore L., Duboc L., Hynes N. E. p53-dependent and p53-independent activation of apoptosis in mammary epithelial cells reveals a survival function of EGF and insulin. J Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;128(6):1185–1196. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.6.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohbu M., Saegusa M., Okayasu I. Apoptosis and cellular proliferation in oesophageal squamous cell carcinomas: differences between keratinizing and nonkeratinizing types. Virchows Arch. 1995;427(3):271–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00203394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilotti S., Collini P., Rilke F., Cattoretti G., Del Bo R., Pierotti M. A. Bcl-2 protein expression in carcinomas originating from the follicular epithelium of the thyroid gland. J Pathol. 1994 Apr;172(4):337–342. doi: 10.1002/path.1711720408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollina L., Pacini F., Fontanini G., Vignati S., Bevilacqua G., Basolo F. bcl-2, p53 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression is related to the degree of differentiation in thyroid carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 1996 Jan;73(2):139–143. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1996.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto A., Kasai N., Sugano H. Poorly differentiated carcinoma of the thyroid. A clinicopathologic entity for a high-risk group of papillary and follicular carcinomas. Cancer. 1983 Nov 15;52(10):1849–1855. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19831115)52:10<1849::aid-cncr2820521015>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon R. N., Diaz-Cano S. Introduction to apoptosis. Diagn Mol Pathol. 1995 Dec;4(4):235–238. doi: 10.1097/00019606-199512000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton M. J., Gaffney E. F. Tumor type is a determinant of susceptibility to apoptosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1995 Mar;103(3):300–307. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/103.3.300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanimoto C., Hirakawa S., Kawasaki H., Hayakawa N., Ota Z. Apoptosis in thyroid diseases: a histochemical study. Endocr J. 1995 Apr;42(2):193–201. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.42.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatebe S., Ishida M., Kasagi N., Tsujitani S., Kaibara N., Ito H. Apoptosis occurs more frequently in metastatic foci than in primary lesions of human colorectal carcinomas: analysis by terminal-deoxynucleotidyl-transferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling. Int J Cancer. 1996 Jan 17;65(2):173–177. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19960117)65:2<173::AID-IJC8>3.0.CO;2-W. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. T. Programmed cell death: apoptosis and oncogenesis. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1097–1098. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90002-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]