Abstract
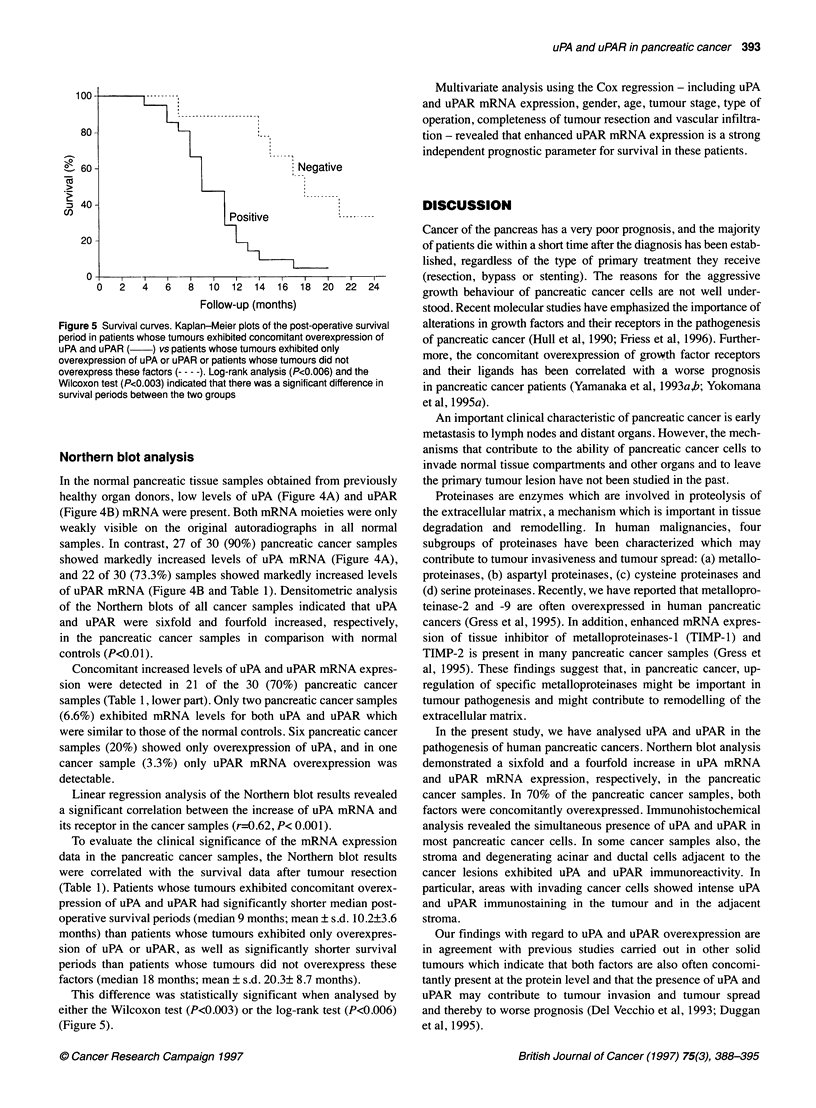
Urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) is a serine proteinase that has been suggested to play an important role in cancer invasion and metastasis. It binds to a specific membrane receptor denominated uPA receptor (uPAR). uPA activates plasminogen to form plasmin, which participates in tissue degradation and proteolysis. Binding of uPA to its receptor accelerates UPA's own activation from pro-uPA, enhancing the activity of the uPA/uPAR cascade. Using immunohistochemistry and Northern blot analysis, we analysed the role of uPA and uPAR in 30 human pancreatic cancers. Immunohistochemical analysis demonstrated moderate to strong immunostaining of both factors in most pancreatic cancers. Cancer lesions with signs of invasion exhibited the strongest immunohistochemical signals for both factors. In addition, in desmoplastic areas adjacent to the cancer cells, moderate uPA and uPAR immunoreactivity was detectable. Northern blot analysis revealed a sixfold and a fourfold increase in uPA and uPAR mRNA levels in pancreatic cancer, respectively, in comparison with normal controls (P<0.01). Correlation of the Northern blot data with the clinical parameters of the patients indicated that patients with concomitant overexpression of uPA and uPAR had a shorter post-operative survival (median 9 months; mean+/-s.d. 10.2+/-3.6 months) than patients in whom only one or none of these factors were overexpressed (median 18 months; mean+/-s.d. 20.3+/-8.7 months) (P<0.002). Our data suggest that uPA and uPAR may serve as prognostic markers in human pancreatic cancer and that the marked overexpression of both factors may create an environment that enables pancreatic cancer cells to invade surrounding tissues.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achbarou A., Kaiser S., Tremblay G., Ste-Marie L. G., Brodt P., Goltzman D., Rabbani S. A. Urokinase overproduction results in increased skeletal metastasis by prostate cancer cells in vivo. Cancer Res. 1994 May 1;54(9):2372–2377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi E., Cohen R. L., Thor A. T., Todd R. F., 3rd, Mizukami I. F., Lawrence D. A., Ljung B. M., Shuman M. A., Smith H. S. The urokinase receptor is expressed in invasive breast cancer but not in normal breast tissue. Cancer Res. 1994 Feb 15;54(4):861–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasi F., Vassalli J. D., Danø K. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator: proenzyme, receptor, and inhibitors. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):801–804. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carriero M. V., Franco P., Del Vecchio S., Massa O., Botti G., D'Aiuto G., Stoppelli M. P., Salvatore M. Tissue distribution of soluble and receptor-bound urokinase in human breast cancer using a panel of monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res. 1994 Oct 15;54(20):5445–5454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D. On the regulation and control of fibrinolysis. Edward Kowalski Memorial Lecture. Thromb Haemost. 1980 Jun 18;43(2):77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:139–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Vecchio S., Stoppelli M. P., Carriero M. V., Fonti R., Massa O., Li P. Y., Botti G., Cerra M., D'Aiuto G., Esposito G. Human urokinase receptor concentration in malignant and benign breast tumors by in vitro quantitative autoradiography: comparison with urokinase levels. Cancer Res. 1993 Jul 1;53(13):3198–3206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan C., Maguire T., McDermott E., O'Higgins N., Fennelly J. J., Duffy M. J. Urokinase plasminogen activator and urokinase plasminogen activator receptor in breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1995 May 29;61(5):597–600. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910610502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert M., Yokoyama M., Friess H., Büchler M. W., Korc M. Coexpression of the c-met proto-oncogene and hepatocyte growth factor in human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 1994 Nov 15;54(22):5775–5778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert M., Yokoyama M., Kobrin M. S., Friess H., Lopez M. E., Büchler M. W., Johnson G. R., Korc M. Induction and expression of amphiregulin in human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 1994 Aug 1;54(15):3959–3962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis V., Scully M. F., Kakkar V. V. Plasminogen activation initiated by single-chain urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Potentiation by U937 monocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2185–2188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estreicher A., Mühlhauser J., Carpentier J. L., Orci L., Vassalli J. D. The receptor for urokinase type plasminogen activator polarizes expression of the protease to the leading edge of migrating monocytes and promotes degradation of enzyme inhibitor complexes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):783–792. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazioli F., Blasi F. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its receptor: new targets for anti-metastatic therapy? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Jan;15(1):25–29. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J., Gersten D. M., Hart I. R. The biology of cancer invasion and metastasis. Adv Cancer Res. 1978;28:149–250. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60648-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friess H., Berberat P., Schilling M., Kunz J., Korc M., Büchler M. W. Pancreatic cancer: the potential clinical relevance of alterations in growth factors and their receptors. J Mol Med (Berl) 1996 Jan;74(1):35–42. doi: 10.1007/BF00202070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friess H., Yamanaka Y., Büchler M., Berger H. G., Kobrin M. S., Baldwin R. L., Korc M. Enhanced expression of the type II transforming growth factor beta receptor in human pancreatic cancer cells without alteration of type III receptor expression. Cancer Res. 1993 Jun 15;53(12):2704–2707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friess H., Yamanaka Y., Büchler M., Ebert M., Beger H. G., Gold L. I., Korc M. Enhanced expression of transforming growth factor beta isoforms in pancreatic cancer correlates with decreased survival. Gastroenterology. 1993 Dec;105(6):1846–1856. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)91084-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friess H., Yamanaka Y., Kobrin M. S., Do D. A., Büchler M. W., Korc M. Enhanced erbB-3 expression in human pancreatic cancer correlates with tumor progression. Clin Cancer Res. 1995 Nov;1(11):1413–1420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gress T. M., Müller-Pillasch F., Lerch M. M., Friess H., Büchler M., Adler G. Expression and in-situ localization of genes coding for extracellular matrix proteins and extracellular matrix degrading proteases in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 1995 Aug 9;62(4):407–413. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910620409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudjonsson B. Cancer of the pancreas. 50 years of surgery. Cancer. 1987 Nov 1;60(9):2284–2303. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19871101)60:9<2284::aid-cncr2820600930>3.0.co;2-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. A., Hughes C. M., Staddon S. L., Richman P. I., Gullick W. J., Lemoine N. R. The c-erb B-2 proto-oncogene in human pancreatic cancer. J Pathol. 1990 Jul;161(3):195–200. doi: 10.1002/path.1711610305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He C. J., Rebibou J. M., Peraldi M. N., Meulders Q., Rondeau E. Growth factor-like effect of urokinase type plasminogen activator in human renal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 15;176(3):1408–1416. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90443-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankun J., Merrick H. W., Goldblatt P. J. Expression and localization of elements of the plasminogen activation system in benign breast disease and breast cancers. J Cell Biochem. 1993 Oct;53(2):135–144. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240530206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobrin M. S., Yamanaka Y., Friess H., Lopez M. E., Korc M. Aberrant expression of type I fibroblast growth factor receptor in human pancreatic adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 1993 Oct 15;53(20):4741–4744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korc M., Chandrasekar B., Yamanaka Y., Friess H., Buchier M., Beger H. G. Overexpression of the epidermal growth factor receptor in human pancreatic cancer is associated with concomitant increases in the levels of epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor alpha. J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1352–1360. doi: 10.1172/JCI116001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Russo-Payne H., Wilson E. L. Inhibition of urokinase-type plasminogen activator by antibodies: the effect on dissemination of a human tumor in the nude mouse. Cancer Res. 1991 Jan 1;51(1):274–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen H., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Francis D., Osterlind K., Hansen H. H., Danø K., Brünner N. Urokinase and plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 1994 Jan 1;54(1):120–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke C., Kristensen P., Ralfkiaer E., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Eriksen J., Blasi F., Danø K. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator is expressed in stromal cells and its receptor in cancer cells at invasive foci in human colon adenocarcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1991 May;138(5):1059–1067. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roldan A. L., Cubellis M. V., Masucci M. T., Behrendt N., Lund L. R., Danø K., Appella E., Blasi F. Cloning and expression of the receptor for human urokinase plasminogen activator, a central molecule in cell surface, plasmin dependent proteolysis. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):467–474. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08132.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saeki T., Stromberg K., Qi C. F., Gullick W. J., Tahara E., Normanno N., Ciardiello F., Kenney N., Johnson G. R., Salomon D. S. Differential immunohistochemical detection of amphiregulin and cripto in human normal colon and colorectal tumors. Cancer Res. 1992 Jun 15;52(12):3467–3473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmalfeldt B., Kuhn W., Reuning U., Pache L., Dettmar P., Schmitt M., Jänicke F., Höfler H., Graeff H. Primary tumor and metastasis in ovarian cancer differ in their content of urokinase-type plasminogen activator, its receptor, and inhibitors types 1 and 2. Cancer Res. 1995 Sep 15;55(18):3958–3963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai S., Yamamura M., Tanaka K., Kawanishi H., Tsuji M., Nakane Y., Hioki K., Yamamoto M. Plasminogen activators in human gastric cancers: correlation with DNA ploidy and immunohistochemical staining. Int J Cancer. 1991 Apr 22;48(1):20–27. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910480105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi Y., Nakao A., Harada A., Nonami T., Fukatsu T., Takagi H. Expression of plasminogen activators and their inhibitors in human pancreatic carcinoma: immunohistochemical study. Am J Gastroenterol. 1993 Nov;88(11):1928–1933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Sappino A. P., Belin D. The plasminogen activator/plasmin system. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1067–1072. doi: 10.1172/JCI115405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verde P., Stoppelli M. P., Galeffi P., Di Nocera P., Blasi F. Identification and primary sequence of an unspliced human urokinase poly(A)+ RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4727–4731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka Y., Friess H., Buchler M., Beger H. G., Uchida E., Onda M., Kobrin M. S., Korc M. Overexpression of acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors in human pancreatic cancer correlates with advanced tumor stage. Cancer Res. 1993 Nov 1;53(21):5289–5296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka Y., Friess H., Kobrin M. S., Buchler M., Beger H. G., Korc M. Coexpression of epidermal growth factor receptor and ligands in human pancreatic cancer is associated with enhanced tumor aggressiveness. Anticancer Res. 1993 May-Jun;13(3):565–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]