Abstract
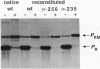
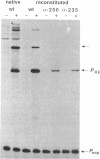
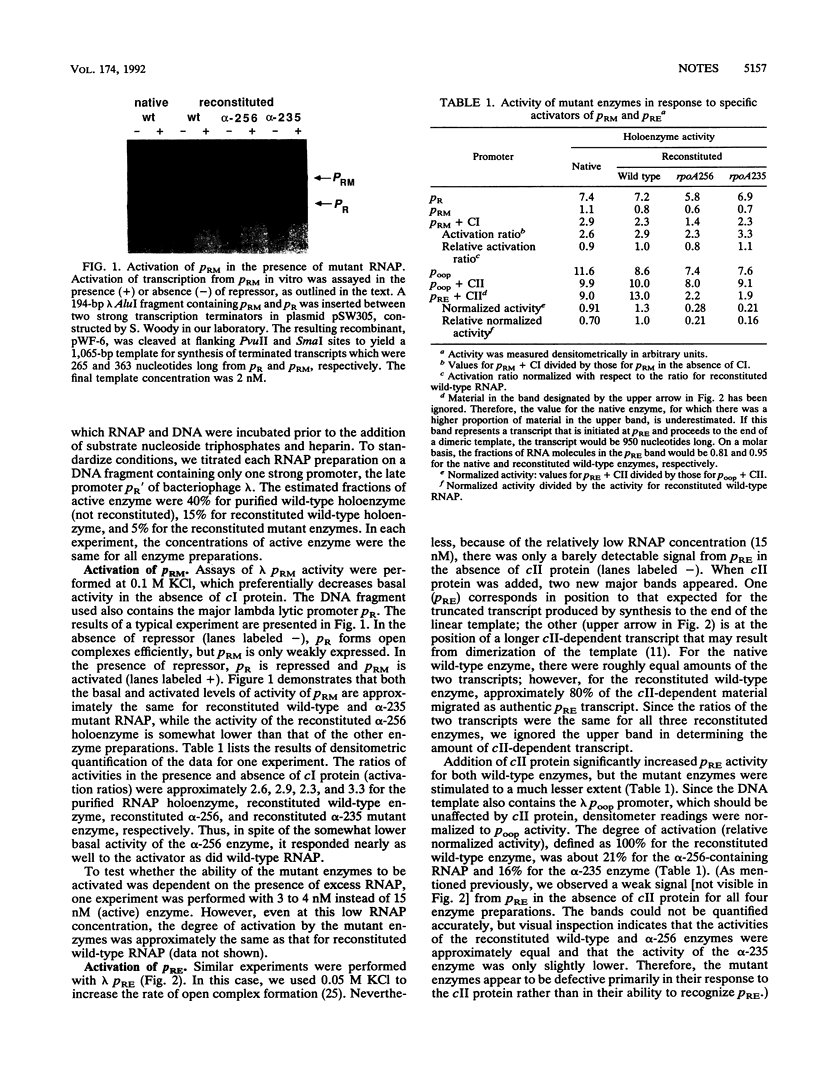
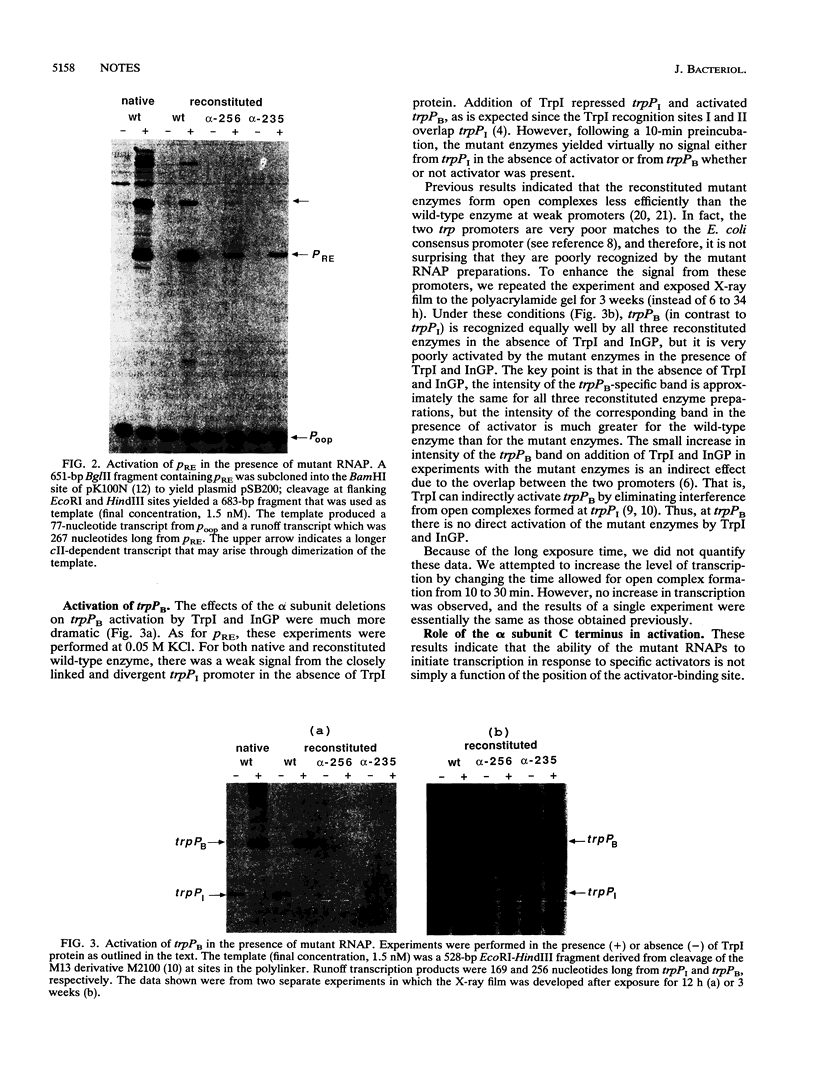
Escherichia coli RNA polymerases containing mutated alpha subunits were tested for their ability to respond to three different positive regulators (activators) in vitro. The two alpha (rpoA) mutants, alpha-256 and alpha-235, have deletions of the C-terminal 73 and 94 amino acids, respectively. In runoff transcription assays catalyzed by reconstituted holoenzyme, the effects of the mutations on each of three promoters tested were different: activation of the lambda pRM promoter by cI protein (repressor) was nearly normal, activation of the lambda pRE promoter by cII protein was reduced approximately fivefold, and direct activation of the trpPB promoter of Pseudomonas aeruginosa was completely inhibited. We also found that the reconstituted mutant enzyme was defective in recognition of trpPI in the absence of activator. The differential responses of the three promoters to their activators in the presence of the mutant enzymes indicate that the location of an activator-binding site does not by itself determine the region of RNA polymerase with which the activator interacts.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell A., Gaston K., Williams R., Chapman K., Kolb A., Buc H., Minchin S., Williams J., Busby S. Mutations that alter the ability of the Escherichia coli cyclic AMP receptor protein to activate transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7243–7250. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracco L., Kotlarz D., Kolb A., Diekmann S., Buc H. Synthetic curved DNA sequences can act as transcriptional activators in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4289–4296. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08615.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Jendrisak J. J. A procedure for the rapid, large-scall purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4634–4638. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M., Crawford I. P. In vitro determination of the effect of indoleglycerol phosphate on the interaction of purified TrpI protein with its DNA-binding sites. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1590–1597. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1590-1597.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M., Crawford I. P. The roles of indoleglycerol phosphate and the TrpI protein in the expression of trpBA from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):979–988. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M., Hadero A., Crawford I. P. Sequence of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa trpI activator gene and relatedness of trpI to other procaryotic regulatory genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):172–183. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.172-183.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eschenlauer A. C., Reznikoff W. S. Escherichia coli catabolite gene activator protein mutants defective in positive control of lac operon transcription. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5024–5029. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5024-5029.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao J. G., Gussin G. N. Activation of the trpBA promoter of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by TrpI protein in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3763–3769. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3763-3769.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao J., Gussin G. N. Mutations in TrpI binding site II that differentially affect activation of the trpBA promoter of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4137–4144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04991.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayhack E. J., Yang X. J., Lau L. F., Roberts J. W. Phage lambda gene Q antiterminator recognizes RNA polymerase near the promoter and accelerates it through a pause site. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):259–269. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gussin G. N., Temple E., Brown S. E., Court D. Repression of a mutant derivative of the pRE promoter of bacteriophage lambda by its activator, CII. Gene. 1986;46(2-3):171–180. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90401-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halling C., Sunshine M. G., Lane K. B., Six E. W., Calendar R. A mutation of the transactivation gene of satellite bacteriophage P4 that suppresses the rpoA109 mutation of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3541–3548. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3541-3548.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B., Reynolds R. P. Analysis of E. coli promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2343–2361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward R. S., Igarashi K., Ishihama A. Functional specialization within the alpha-subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 5;221(1):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80197-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. S., Mahoney M. E., Wulff D. L., Rosenberg M. Identification of the DNA binding domain of the phage lambda cII transcriptional activator and the direct correlation of cII protein stability with its oligomeric forms. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):184–195. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. S., Rosenberg M. Characterization of a third, cII-dependent, coordinately activated promoter on phage lambda involved in lysogenic development. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11838–11844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochschild A., Irwin N., Ptashne M. Repressor structure and the mechanism of positive control. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90451-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang J. J., Gussin G. N. Interactions between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and lambda repressor. Mutations in PRM affect repression of PR. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 20;200(4):735–739. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90484-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Hanamura A., Makino K., Aiba H., Aiba H., Mizuno T., Nakata A., Ishihama A. Functional map of the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: two modes of transcription activation by positive factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8958–8962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Ishihama A. Bipartite functional map of the E. coli RNA polymerase alpha subunit: involvement of the C-terminal region in transcription activation by cAMP-CRP. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1015–1022. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90553-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo M. J., Bagga D., Miller C. G. Mutations in rpoA affect expression of anaerobically regulated genes in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7511–7518. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7511-7518.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih M. C., Gussin G. N. Role of cII protein in stimulating transcription initiation at the lambda PRE promoter. Enhanced formation and stabilization of open complexes. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 5;172(4):489–506. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slauch J. M., Russo F. D., Silhavy T. J. Suppressor mutations in rpoA suggest that OmpR controls transcription by direct interaction with the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7501–7510. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7501-7510.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su W., Porter S., Kustu S., Echols H. DNA-looping and enhancer activity: association between DNA-bound NtrC activator and RNA polymerase at the bacterial glnA promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5504–5508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]