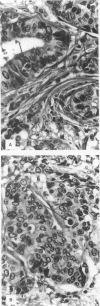
Abstract
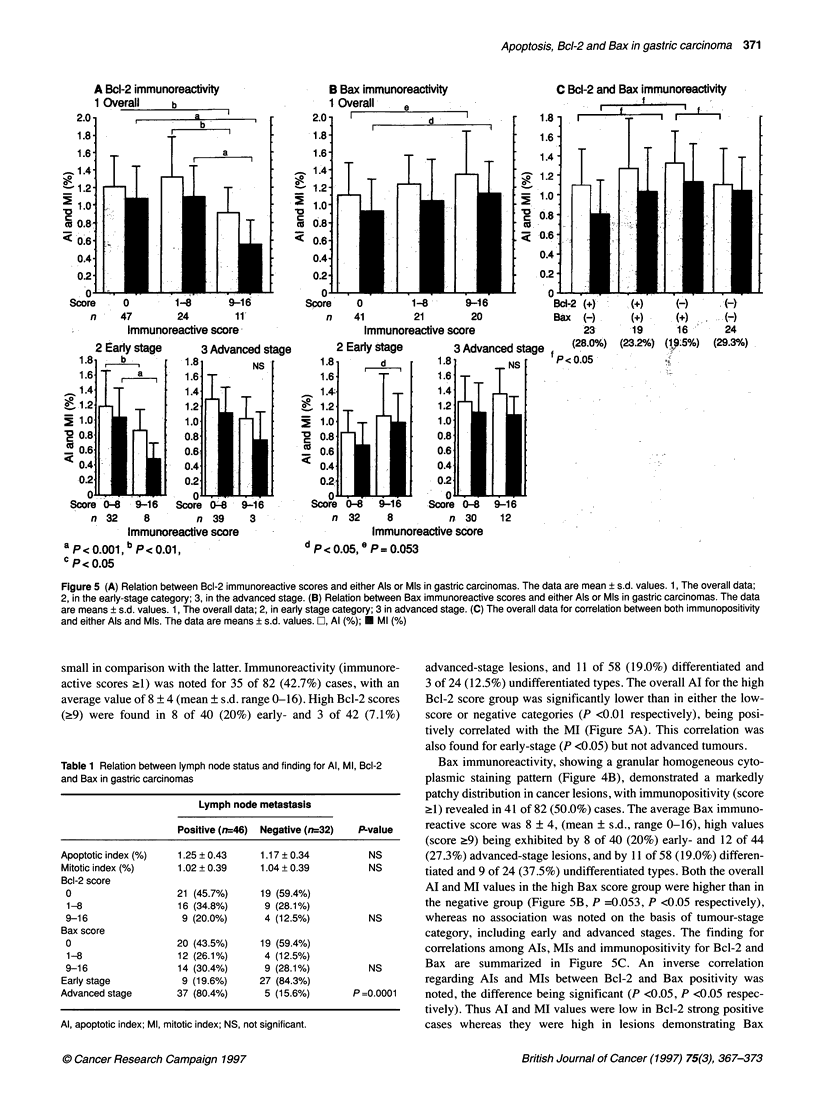
To clarify the relation between bcl-2 and bax protein (Bcl-2 and Bax) expression with regard to apoptosis and cell proliferation, 82 gastric carcinomas were immunohistochemically investigated. The significance of apoptosis for biological behaviour of the tumours was also examined. The apoptotic indices (AIs) were significantly lower in early-stage than in advanced-stage lesions (P<0.05), being positively correlated with the mitotic indices (MIs) (r=0.447, P<0.001). No association between either AIs or MIs and tumour size (diameter of intramural spreading) was noted. The AIs in the high Bcl-2-immunoreactive score group were significantly smaller than in either the low or the negative categories, whereas they were relatively elevated in the high Bax score group. In addition, an inverse correlation between Bcl-2 and Bax expression was revealed for both AIs and MIs. Although depth of tumour invasion and lymph node status were clearly associated with favourable outcome, no relation between survival rates and average values of either AIs or MIs, or immunoreactive scores for Bcl-2 and Bax was observed. These results indicate that in gastric carcinomas, apoptosis is closely associated with cell proliferation and expression of Bcl-2 and Bax, but appears likely to have no particular biological significance as a prognostic factor.
Full text
PDF
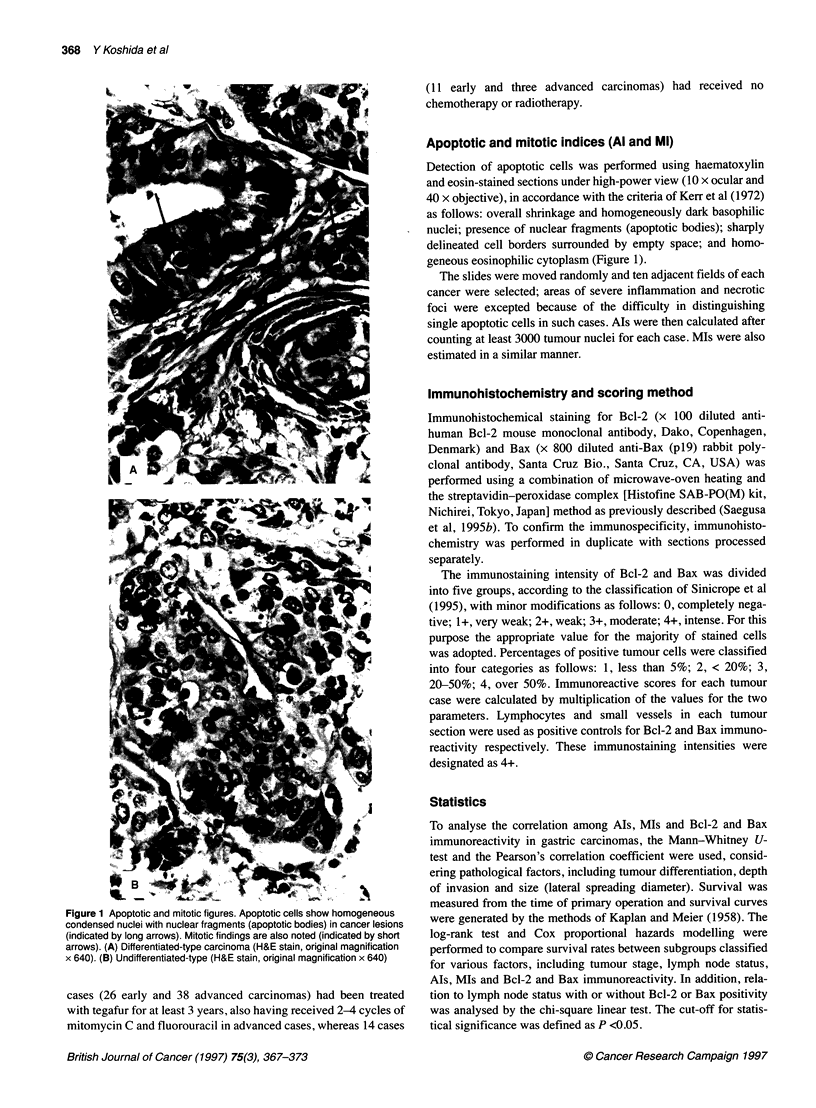
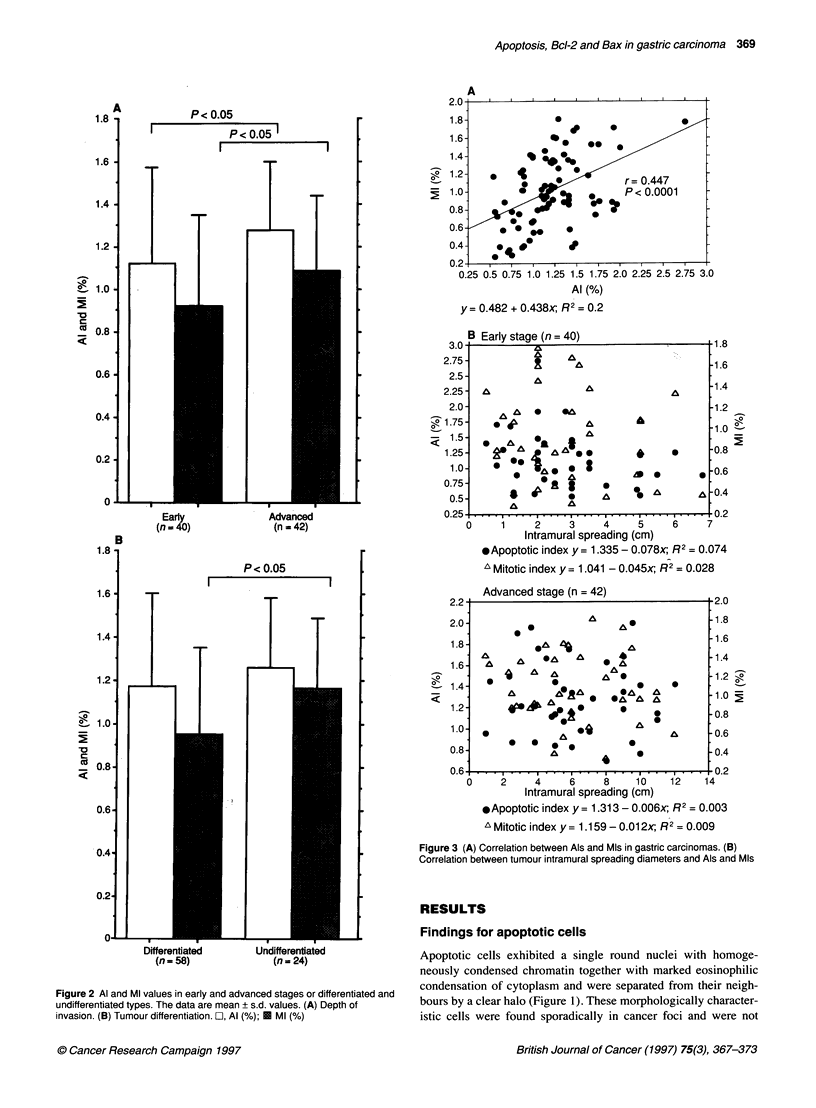
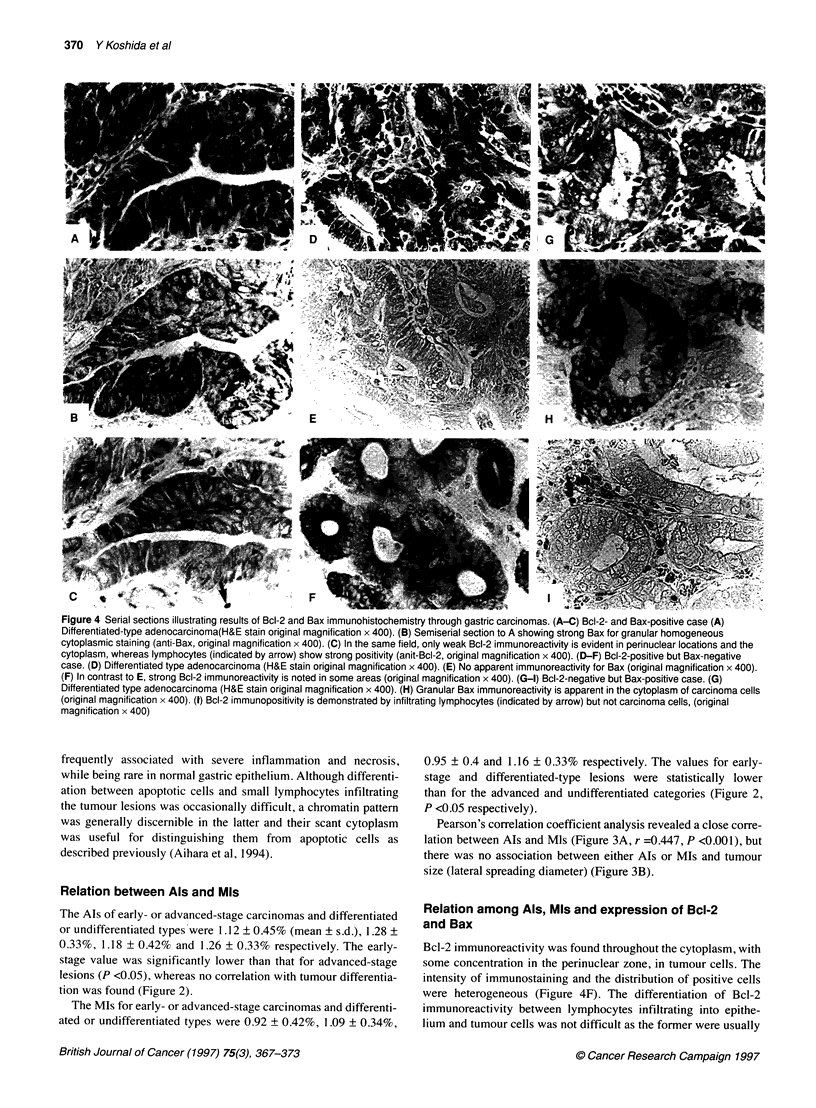


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aihara M., Truong L. D., Dunn J. K., Wheeler T. M., Scardino P. T., Thompson T. C. Frequency of apoptotic bodies positively correlates with Gleason grade in prostate cancer. Hum Pathol. 1994 Aug;25(8):797–801. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90249-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai T., Kino I. Role of apoptosis in modulation of the growth of human colorectal tubular and villous adenomas. J Pathol. 1995 May;176(1):37–44. doi: 10.1002/path.1711760107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikenaga M., Takano Y., Saegusa M., Ohtani Y., Hiki Y., Kakita A., Okayasu I. Apoptosis of colon cancers assessed by in situ DNA nick end-labeling method. Pathol Int. 1996 Jan;46(1):33–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1996.tb03530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama Y., Inokuchi K., Soejima K., Matsusaka T., Okamura T. Growth patterns and prognosis in early gastric carcinoma. Superficially spreading and penetrating growth types. Cancer. 1983 Jan 15;51(2):320–326. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19830115)51:2<320::aid-cncr2820510226>3.0.co;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 initiates a new category of oncogenes: regulators of cell death. Blood. 1992 Aug 15;80(4):879–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krajewski S., Krajewska M., Shabaik A., Miyashita T., Wang H. G., Reed J. C. Immunohistochemical determination of in vivo distribution of Bax, a dominant inhibitor of Bcl-2. Am J Pathol. 1994 Dec;145(6):1323–1336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauwers G. Y., Scott G. V., Karpeh M. S. Immunohistochemical evaluation of bcl-2 protein expression in gastric adenocarcinomas. Cancer. 1995 May 1;75(9):2209–2213. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19950501)75:9<2209::aid-cncr2820750904>3.0.co;2-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijerink J. P., Smetsers T. F., Slöetjes A. W., Linders E. H., Mensink E. J. Bax mutations in cell lines derived from hematological malignancies. Leukemia. 1995 Nov;9(11):1828–1832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohbu M., Saegusa M., Okayasu I. Apoptosis and cellular proliferation in oesophageal squamous cell carcinomas: differences between keratinizing and nonkeratinizing types. Virchows Arch. 1995;427(3):271–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00203394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oltvai Z. N., Milliman C. L., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):609–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90509-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita H., Matsusaka T., Wakasugi K., Kume K., Fujinaga Y., Fuchigami T., Iwashita A. Clinicopathologic evaluation of recurrence in early gastric cancer. Surg Today. 1992;22(1):19–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00326120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezzella F., Turley H., Kuzu I., Tungekar M. F., Dunnill M. S., Pierce C. B., Harris A., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. bcl-2 protein in non-small-cell lung carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1993 Sep 2;329(10):690–694. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199309023291003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietenpol J. A., Papadopoulos N., Markowitz S., Willson J. K., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Paradoxical inhibition of solid tumor cell growth by bcl2. Cancer Res. 1994 Jul 15;54(14):3714–3717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranaldi R., Santinelli A., Verdolini R., Rezai B., Mannello B., Bearzi I. Long-term follow-up in early gastric cancer: evaluation of prognostic factors. J Pathol. 1995 Dec;177(4):343–351. doi: 10.1002/path.1711770404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs L., Lotem J. Control of programmed cell death in normal and leukemic cells: new implications for therapy. Blood. 1993 Jul 1;82(1):15–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saegusa M., Takano Y., Hashimura M., Shoji Y., Okayasu I. The possible role of bcl-2 expression in the progression of tumors of the uterine cervix. Cancer. 1995 Dec 1;76(11):2297–2303. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19951201)76:11<2297::aid-cncr2820761118>3.0.co;2-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saegusa M., Takano Y., Kamata Y., Okayasu J. Bcl-2 expression and allelic loss of the p53 gene in gastric carcinomas. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1996;122(7):427–432. doi: 10.1007/BF01212883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saegusa M., Takano Y., Okayasu I. Bcl-2 expression and its association with cell kinetics in human gastric carcinomas and intestinal metaplasia. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1995;121(6):357–363. doi: 10.1007/BF01225688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd N. A., Richman P. I., England J. Ki-67 derived proliferative activity in colorectal adenocarcinoma with prognostic correlations. J Pathol. 1988 Jul;155(3):213–219. doi: 10.1002/path.1711550306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y. F., Sahai B. M., Green D. R. Cyclosporin A inhibits activation-induced cell death in T-cell hybridomas and thymocytes. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):625–626. doi: 10.1038/339625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji Y., Saegusa M., Takano Y., Ohbu M., Okayasu I. Correlation of apoptosis with tumour cell differentiation, progression, and HPV infection in cervical carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 1996 Feb;49(2):134–138. doi: 10.1136/jcp.49.2.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvestrini R., Veneroni S., Daidone M. G., Benini E., Boracchi P., Mezzetti M., Di Fronzo G., Rilke F., Veronesi U. The Bcl-2 protein: a prognostic indicator strongly related to p53 protein in lymph node-negative breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994 Apr 6;86(7):499–504. doi: 10.1093/jnci/86.7.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinicrope F. A., Ruan S. B., Cleary K. R., Stephens L. C., Lee J. J., Levin B. bcl-2 and p53 oncoprotein expression during colorectal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 1995 Jan 15;55(2):237–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Williams G. T., Kingston R., Jenkinson E. J., Owen J. J. Antibodies to CD3/T-cell receptor complex induce death by apoptosis in immature T cells in thymic cultures. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):181–184. doi: 10.1038/337181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sträter J., Koretz K., Günthert A. R., Möller P. In situ detection of enterocytic apoptosis in normal colonic mucosa and in familial adenomatous polyposis. Gut. 1995 Dec;37(6):819–825. doi: 10.1136/gut.37.6.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugano H., Nakamura K., Kato Y. Pathological studies of human gastric cancer. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1982;32 (Suppl 2):329–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira C., Reed J. C., Pratt M. A. Estrogen promotes chemotherapeutic drug resistance by a mechanism involving Bcl-2 proto-oncogene expression in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1995 Sep 1;55(17):3902–3907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Finger L. R., Yunis J., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Cloning of the chromosome breakpoint of neoplastic B cells with the t(14;18) chromosome translocation. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1097–1099. doi: 10.1126/science.6093263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker N. I., Bennett R. E., Kerr J. F. Cell death by apoptosis during involution of the lactating breast in mice and rats. Am J Anat. 1989 May;185(1):19–32. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001850104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H. Apoptosis and the regulation of cell numbers in normal and neoplastic tissues: an overview. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1992 Sep;11(2):95–103. doi: 10.1007/BF00048057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]