Abstract
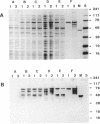
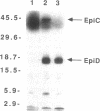
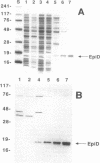
The plasmid-encoded epidermin biosynthesis gene, epiD, of Staphylococcus epidermidis Tü3298 was expressed in Escherichia coli by using both the malE fusion system and the T7 RNA polymerase-promoter system. EpiD was identified by Western blotting (immunoblotting) with anti-maltose-binding protein (MBP)-EpiD antiserum. EpiD and the MBP-EpiD fusion protein, which were mainly present in the soluble protein fraction, were purified from the respective E. coli clones. Purified EpiD showed the typical absorption spectrum of an oxidized flavoprotein with maxima at 274, 382, and 453 nm. The coenzyme released from EpiD by heat treatment was identified as flavin mononucleotide. S. epidermidis Tü3298/EMS11, containing a mutation within epiD, was unable to synthesize active epidermin. This mutated gene, epiD*, was cloned in E. coli and expressed as an MBP-EpiD* fusion protein. DNA sequencing of epiD* identified a point mutation that led to replacement of Gly-93 with Asp. Unlike MBP-EpiD, the fusion protein MBP-EpiD* could not bind flavin mononucleotide. We propose that EpiD catalyzes the removal of two reducing equivalents from the cysteine residue of the C-terminal meso-lanthionine to form a --C==C-- double bond and is therefore involved in formation of the unusual S-[(Z)-2-aminovinyl[-D-cysteine structure in epidermin.
Full text
PDF


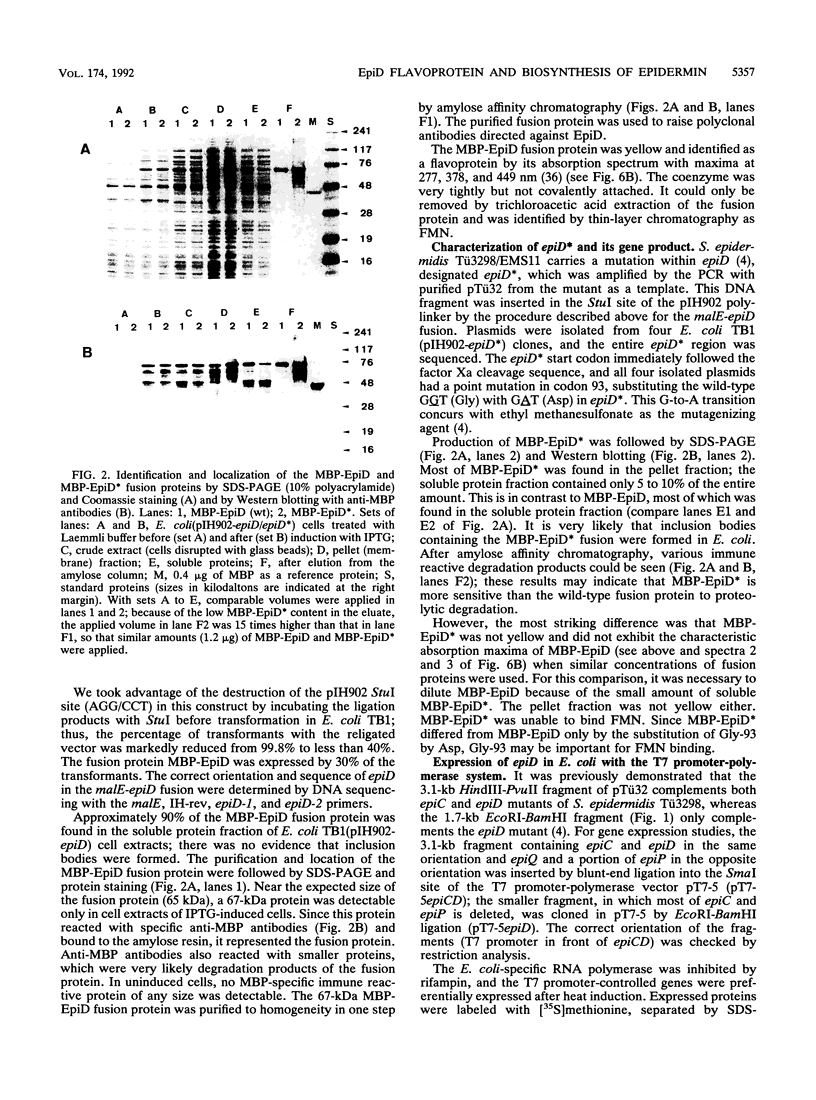
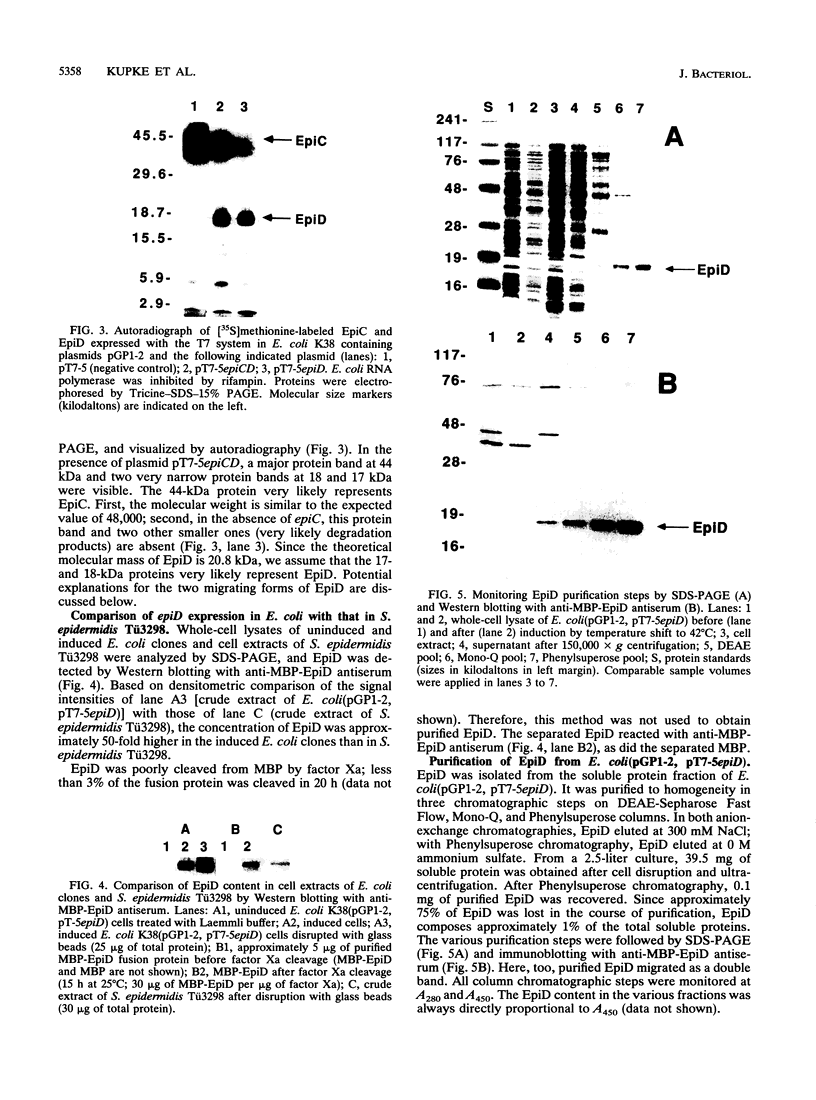
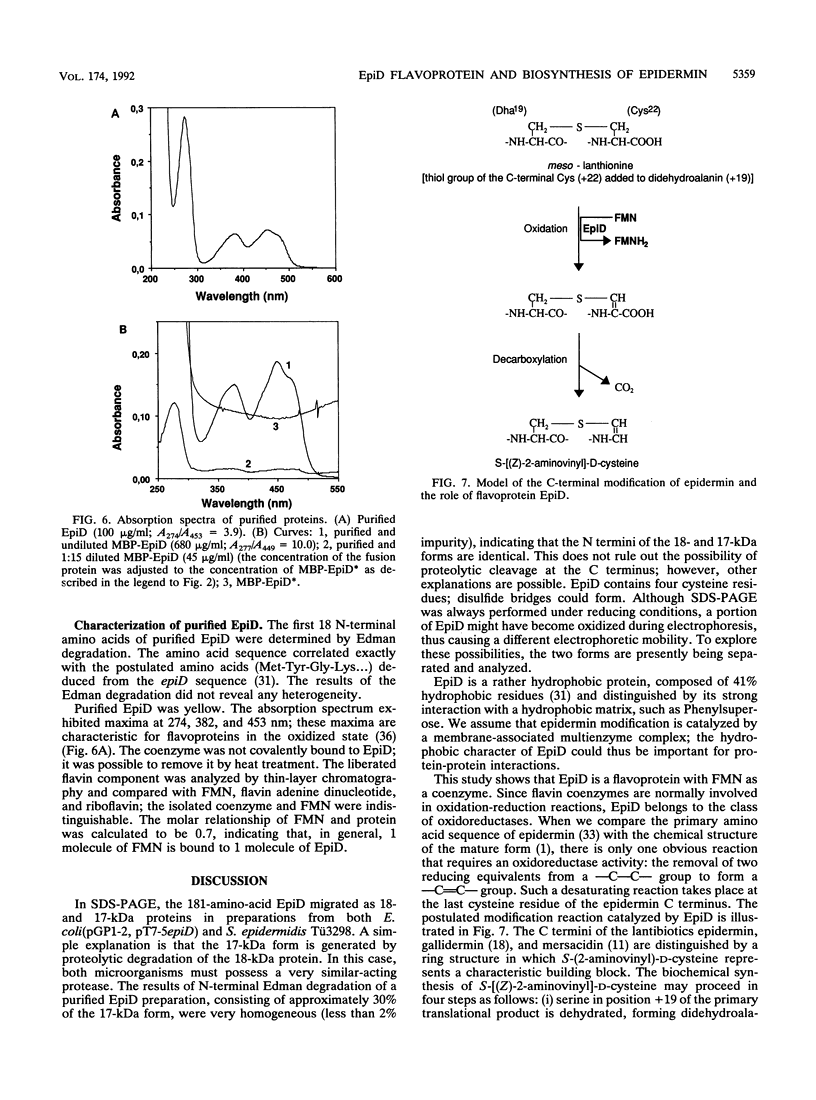


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amann E., Brosius J. "ATG vectors' for regulated high-level expression of cloned genes in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;40(2-3):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augustin J., Götz F. Transformation of Staphylococcus epidermidis and other staphylococcal species with plasmid DNA by electroporation. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Jan 1;54(1-3):203–207. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90283-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augustin J., Rosenstein R., Wieland B., Schneider U., Schnell N., Engelke G., Entian K. D., Götz F. Genetic analysis of epidermin biosynthetic genes and epidermin-negative mutants of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Mar 15;204(3):1149–1154. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower W. J., Miller J. F., Ragsdale C. W. High efficiency transformation of E. coli by high voltage electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6127–6145. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston T. C., Thompson R. B., Baldwin T. O. Nucleotide sequence of the luxB gene of Vibrio harveyi and the complete amino acid sequence of the beta subunit of bacterial luciferase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4805–4811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaletta C., Entian K. D., Kellner R., Jung G., Reis M., Sahl H. G. Pep5, a new lantibiotic: structural gene isolation and prepeptide sequence. Arch Microbiol. 1989;152(1):16–19. doi: 10.1007/BF00447005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellner R., Jung G., Hörner T., Zähner H., Schnell N., Entian K. D., Götz F. Gallidermin: a new lanthionine-containing polypeptide antibiotic. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 15;177(1):53–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14344.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordel M., Benz R., Sahl H. G. Mode of action of the staphylococcinlike peptide Pep 5: voltage-dependent depolarization of bacterial and artificial membranes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):84–88. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.84-88.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhew S. G., Massey V. Purification and characterization of flavodoxin from Peptostreptococcus elsdenii. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):794–802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Bouanchaud D. The problems of drug-resistant pathogenic bacteria. Extrachromosomal nature of drug resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 11;182:279–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb30664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russel M., Model P. Replacement of the fip gene of Escherichia coli by an inactive gene cloned on a plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):1034–1039. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.1034-1039.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell N., Engelke G., Augustin J., Rosenstein R., Ungermann V., Götz F., Entian K. D. Analysis of genes involved in the biosynthesis of lantibiotic epidermin. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Feb 15;204(1):57–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16605.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell N., Entian K. D., Götz F., Hörner T., Kellner R., Jung G. Structural gene isolation and prepeptide sequence of gallidermin, a new lanthionine containing antibiotic. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Apr;49(2-3):263–267. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell N., Entian K. D., Schneider U., Götz F., Zähner H., Kellner R., Jung G. Prepeptide sequence of epidermin, a ribosomally synthesized antibiotic with four sulphide-rings. Nature. 1988 May 19;333(6170):276–278. doi: 10.1038/333276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]