Abstract
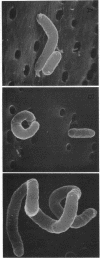
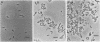
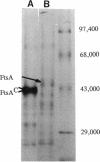
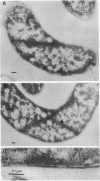
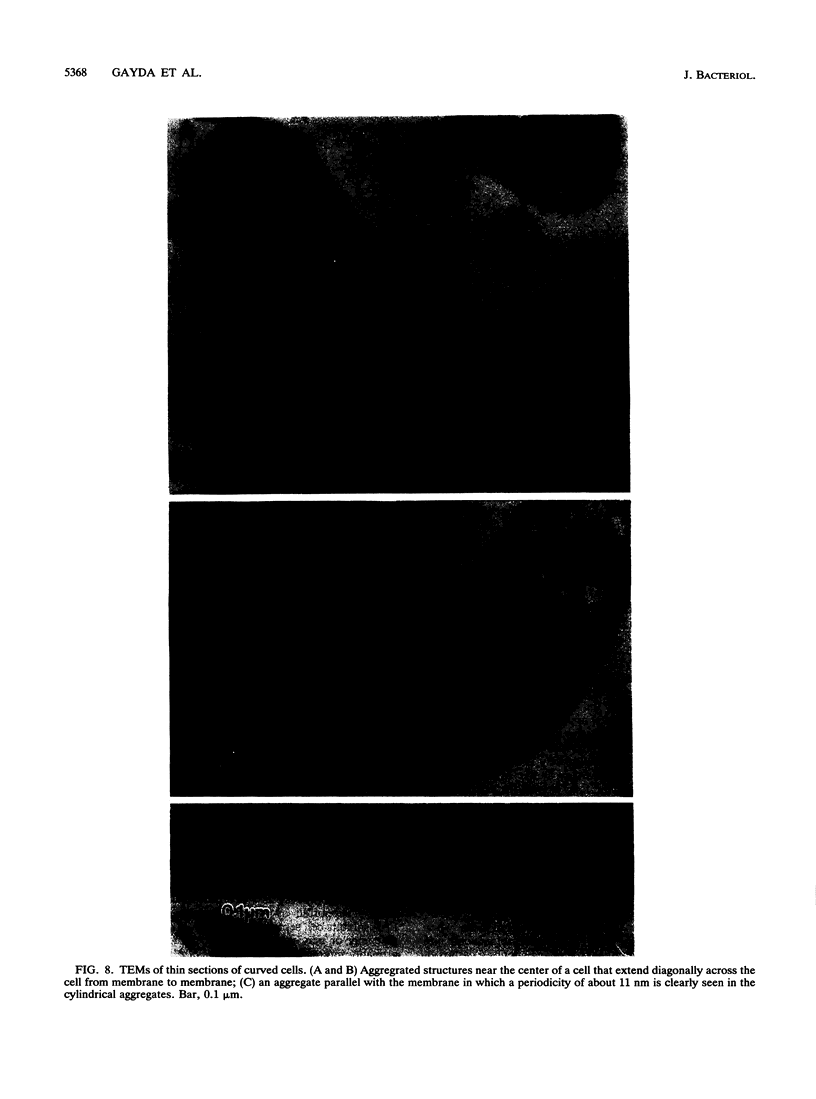
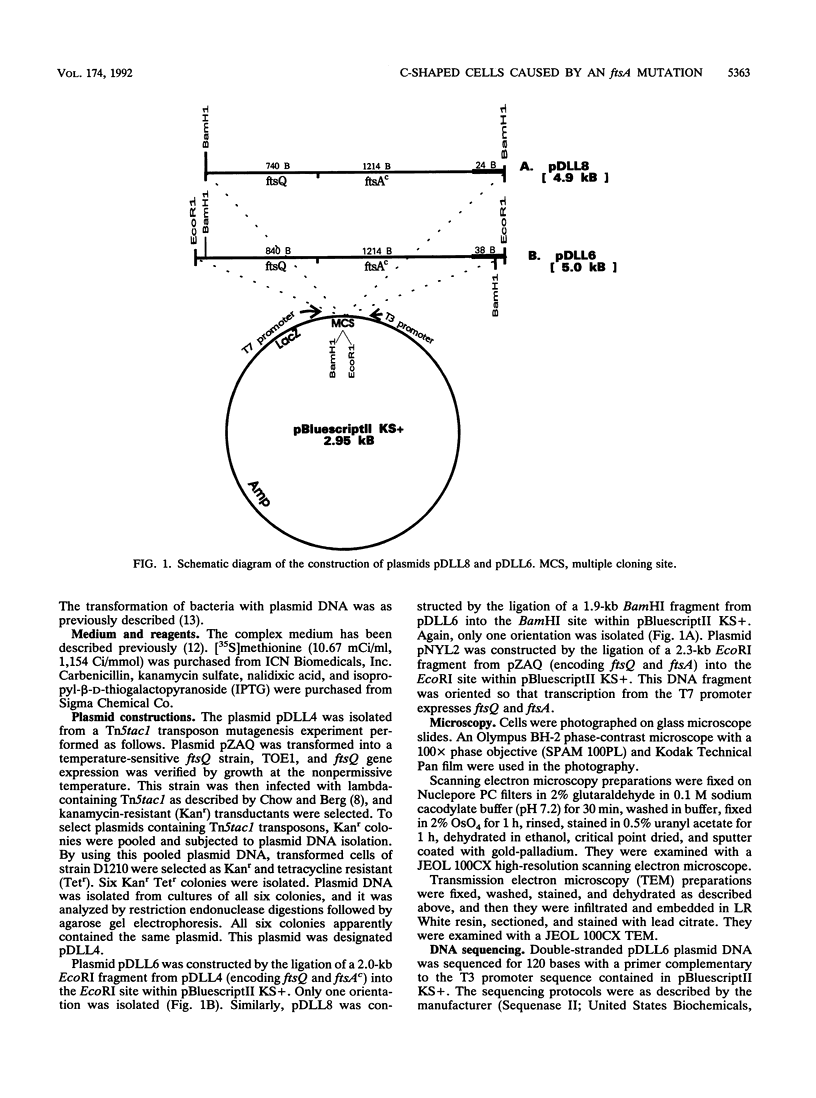
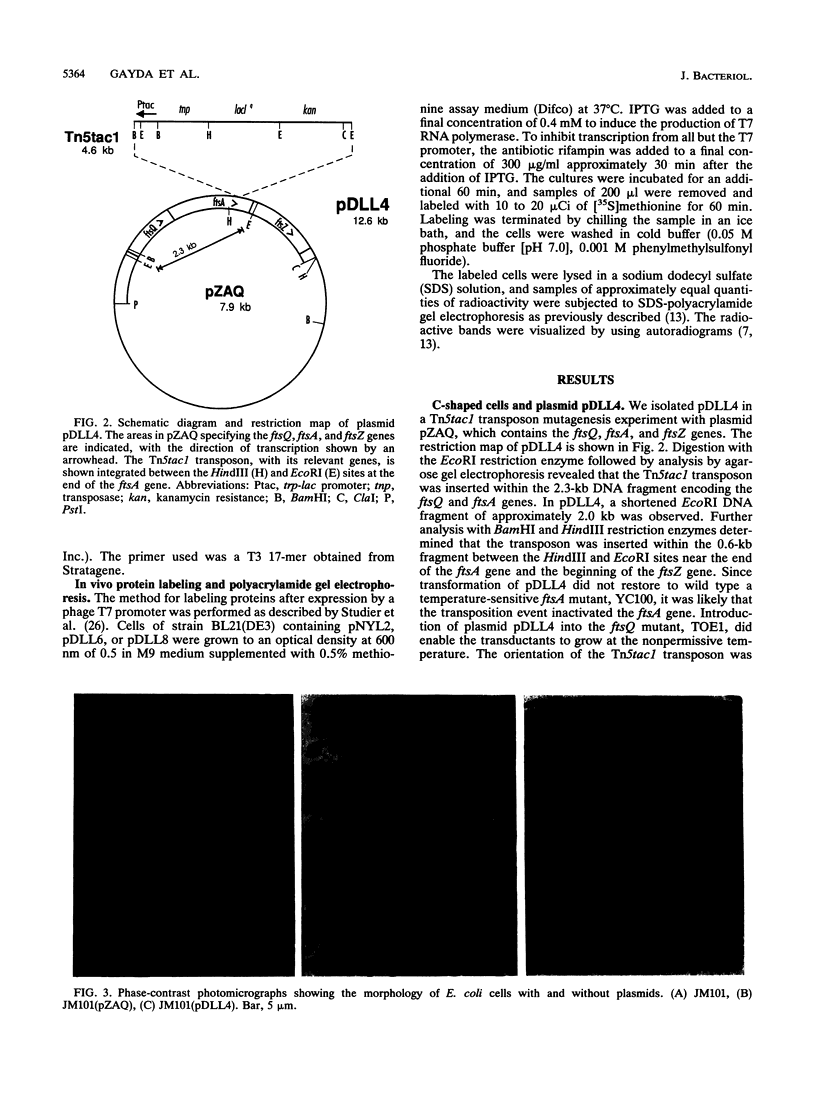
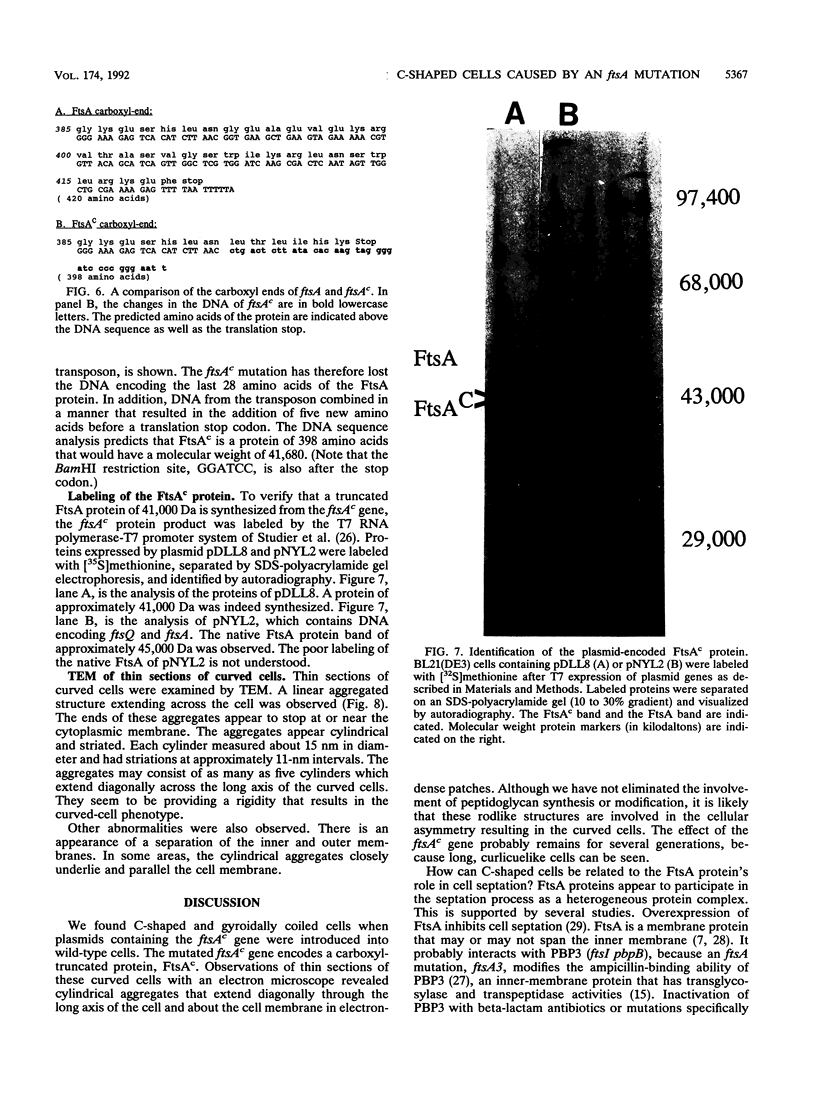
A plasmid, pDLL4, was isolated from a Tn5tac1 mutagenesis experiment with plasmid pZAQ. When pDLL4 was transformed into wild-type rod-shaped cells, it caused cells in the population to become curved (C-shaped or convoluted). The Tn5tac1 transposon was integrated within the carboxyl end of the ftsA gene in pDLL4. This mutation was designated ftsAc. Subcloning ftsAc DNA into another plasmid vector verified that the curved-cell phenotype was caused by the expression of this altered gene. DNA sequence analysis of the ftsAc mutation revealed that the transposition event changed the DNA so that the last 28 amino acids of the FtsA protein were lost and 5 new amino acids were added. A radioactive peptide band corresponding to this truncated FtsAc protein was identified by a T7 promoter-T7 polymerase protein labeling system. Observations of thin sections of these curved cells with an electron microscope revealed aggregates of striated cylindrical structures traversing the cytoplasm. The ends of these aggregates appear to be at or near the cell membrane. The linear periodicity of the cylinders was approximately 11 nm, and the diameter of a cylinder was about 15 nm. Aggregates of as many as five cylinders were arrayed diagonally to the long axis of the curved cells, a finding that suggests that some type of internal organization may be causing the curved cell shape.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Begg K. J., Donachie W. D. Cell shape and division in Escherichia coli: experiments with shape and division mutants. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):615–622. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.615-622.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begg K. J., Hatfull G. F., Donachie W. D. Identification of new genes in a cell envelope-cell division gene cluster of Escherichia coli: cell division gene ftsQ. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):435–437. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.435-437.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J. The bacterial surface: general considerations towards design and function. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Apr;34(4):363–372. doi: 10.1139/m88-067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bi E. F., Lutkenhaus J. FtsZ ring structure associated with division in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1991 Nov 14;354(6349):161–164. doi: 10.1038/354161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson M. J., Barondess J., Beckwith J. The FtsQ protein of Escherichia coli: membrane topology, abundance, and cell division phenotypes due to overproduction and insertion mutations. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(7):2187–2195. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.7.2187-2195.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chon Y., Gayda R. Studies with FtsA-LacZ protein fusions reveal FtsA located inner-outer membrane junctions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 16;152(3):1023–1030. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80386-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow W. Y., Berg D. E. Tn5tac1, a derivative of transposon Tn5 that generates conditional mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6468–6472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descoteaux A., Drapeau G. R. Regulation of cell division in Escherichia coli K-12: probable interactions among proteins FtsQ, FtsA, and FtsZ. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):1938–1942. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.1938-1942.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gayda R. C., Markovitz A. Cloned DNA fragment specifying major outer membrane protein a in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):369–380. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.369-380.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gayda R. C., Yamamoto L. T., Markovitz A. Second-site mutations in capR (lon) strains of Escherichia coli K-12 that prevent radiation sensitivity and allow bacteriophage lambda to lysogenize. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1208–1216. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1208-1216.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedge P. J., Spratt B. G. Amino acid substitutions that reduce the affinity of penicillin-binding protein 3 of Escherichia coli for cephalexin. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Aug 15;151(1):111–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09075.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishino F., Matsuhashi M. Peptidoglycan synthetic enzyme activities of highly purified penicillin-binding protein 3 in Escherichia coli: a septum-forming reaction sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Aug 14;101(3):905–911. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91835-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C., Holland I. B. Role of the SulB (FtsZ) protein in division inhibition during the SOS response in Escherichia coli: FtsZ stabilizes the inhibitor SulA in maxicells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6045–6049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. L. Biophysics of bacterial walls viewed as stress-bearing fabric. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Sep;52(3):337–353. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.3.337-353.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutkenhaus J. F., Donachie W. D. Identification of the ftsA gene product. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1088–1094. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1088-1094.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pla J., Dopazo A., Vicente M. The native form of FtsA, a septal protein of Escherichia coli, is located in the cytoplasmic membrane. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5097–5102. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5097-5102.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. C., Begg K. J., Sweeney J., Condie A., Donachie W. D. Mapping and characterization of mutants of the Escherichia coli cell division gene, ftsA. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Sep;2(5):581–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. C., Collins J. F., Donachie W. D. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell-cycle proteins. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):766–766. doi: 10.1038/328766a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. C., Kenan D. J., Hatfull G. F., Sullivan N. F., Spiegelberg R., Donachie W. D. DNA sequence and transcriptional organization of essential cell division genes ftsQ and ftsA of Escherichia coli: evidence for overlapping transcriptional units. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):546–555. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.546-555.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Distinct penicillin binding proteins involved in the division, elongation, and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Temperature-sensitive cell division mutants of Escherichia coli with thermolabile penicillin-binding proteins. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):293–305. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.293-305.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tormo A., Ayala J. A., de Pedro M. A., Aldea M., Vicente M. Interaction of FtsA and PBP3 proteins in the Escherichia coli septum. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):985–992. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.985-992.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tormo A., Vicente M. The ftsA gene product participates in formation of the Escherichia coli septum structure. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):779–784. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.779-784.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. C., Gayda R. C. High-level expression of the FtsA protein inhibits cell septation in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4736–4740. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4736-4740.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. E., Jr, Lutkenhaus J. Overproduction of FtsZ induces minicell formation in E. coli. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):941–949. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90290-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wientjes F. B., Woldringh C. L., Nanninga N. Amount of peptidoglycan in cell walls of gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7684–7691. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7684-7691.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi Q. M., Rockenbach S., Ward J. E., Jr, Lutkenhaus J. Structure and expression of the cell division genes ftsQ, ftsA and ftsZ. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 5;184(3):399–412. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90290-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]