Abstract
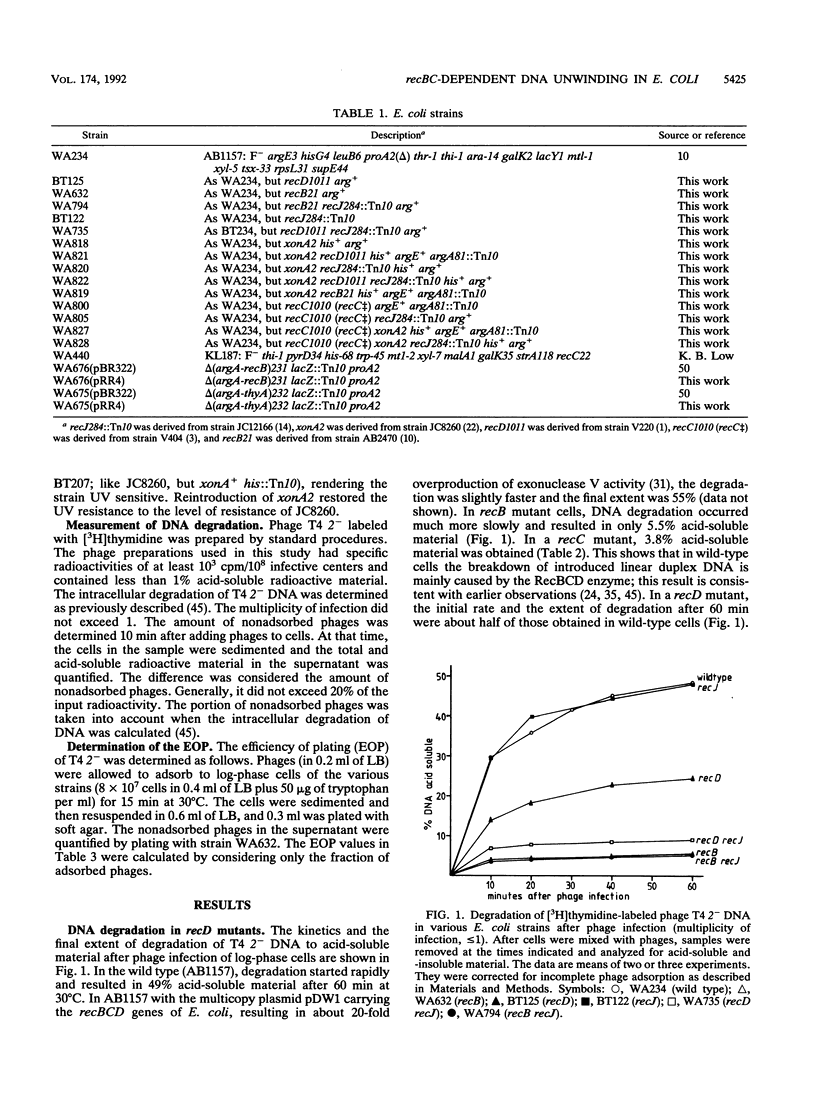
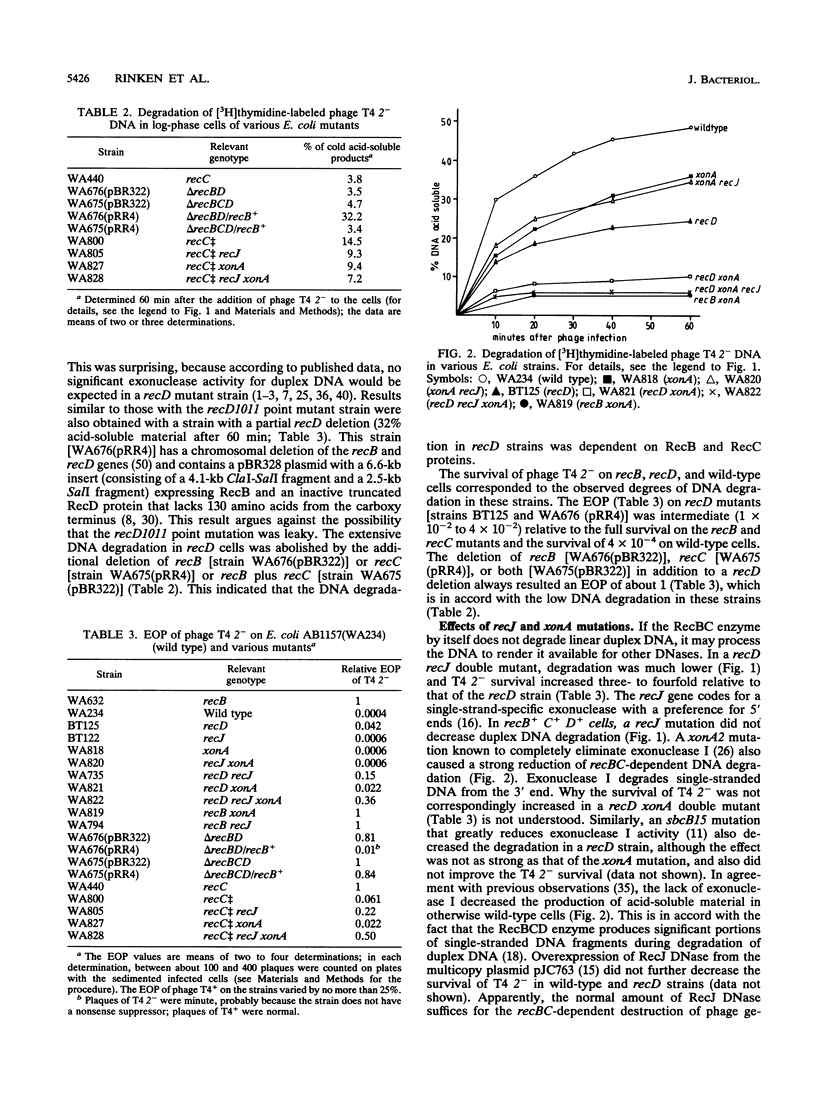
Infection of Escherichia coli with phage T4 gene 2am was used to transport 3H-labeled linear duplex DNA into cells to follow its degradation in relation to the cellular genotype. In wild-type cells, 49% of the DNA was made acid soluble within 60 min; in recB or recC cells, only about 5% of the DNA was made acid soluble. Remarkably, in recD cells about 25% of the DNA was rendered acid soluble. The DNA degradation in recD cells depended on intact recB and recC genes. The degradation in recD cells was largely decreased by mutations in recJ (which eliminates the 5' single-strand-specific exonuclease coded by this gene) or xonA (which abolishes the 3' single-strand-specific exonuclease I). In a recD recJ xonA triple mutant, the degradation of linear duplex DNA was roughly at the level of a recB mutant. Results similar to those with the set of recD strains were also obtained with a recC++ mutant (in which the RecD protein is intact but does not function) and its recJ, xonA, and recJ xonA derivatives. The observations provide evidence for a recBC-dependent DNA-unwinding activity that renders unwound DNA susceptible to exonucleolytic degradation. It is proposed that the DNA-unwinding activity causes the efficient recombination, DNA repair, and SOS induction (after application of nalidixic acid) in recD mutants. The RecBC helicase indirectly detected here may have a central function in Chi-dependent recombination and in the recombinational repair of double-strand breaks by the RecBCD pathway.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amundsen S. K., Taylor A. F., Chaudhury A. M., Smith G. R. recD: the gene for an essential third subunit of exonuclease V. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5558–5562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biek D. P., Cohen S. N. Identification and characterization of recD, a gene affecting plasmid maintenance and recombination in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):594–603. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.594-603.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhury A. M., Smith G. R. A new class of Escherichia coli recBC mutants: implications for the role of RecBC enzyme in homologous recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7850–7854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhury A. M., Smith G. R. Role of Escherichia coli RecBC enzyme in SOS induction. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;201(3):525–528. doi: 10.1007/BF00331350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J. Recombination deficient mutants of E. coli and other bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1973;7:67–86. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.07.120173.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykstra C. C., Prasher D., Kushner S. R. Physical and biochemical analysis of the cloned recB and recC genes of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):21–27. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.21-27.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch P. W., Storey A., Brown K., Hickson I. D., Emmerson P. T. Complete nucleotide sequence of recD, the structural gene for the alpha subunit of Exonuclease V of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8583–8594. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas L. J., Pardee A. B. DNA synthesis inhibition and the induction of protein X in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 15;101(4):459–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90240-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Flanders P., Theriot L. Mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 defective in DNA repair and in genetic recombination. Genetics. 1966 Jun;53(6):1137–1150. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.6.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner S. R., Nagaishi H., Templin A., Clark A. J. Genetic recombination in Escherichia coli: the role of exonuclease I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):824–827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. G., Porton M. C., Buckman C. Effect of recF, recJ, recN, recO and ruv mutations on ultraviolet survival and genetic recombination in a recD strain of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 May;212(2):317–324. doi: 10.1007/BF00334702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett S. T., Clark A. J. Cloning of the Escherichia coli recJ chromosomal region and identification of its encoded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):280–285. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.280-285.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett S. T., Clark A. J. Genetic analysis of the recJ gene of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):190–196. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.190-196.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett S. T., Kolodner R. D. Identification and purification of a single-stranded-DNA-specific exonuclease encoded by the recJ gene of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2627–2631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett S. T., Luisi-DeLuca C., Kolodner R. D. The genetic dependence of recombination in recD mutants of Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1988 Sep;120(1):37–45. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay V., Linn S. The mechanism of degradation of duplex deoxyribonucleic acid by the recBC enzyme of Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4286–4294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinus M. G., Morris N. R. Biological function for 6-methyladenine residues in the DNA of Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1974 May 15;85(2):309–322. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90366-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsić N., Salaj-Smic E., Stojiljković I., Trgovcević Z. Interaction of lambda Gam protein with the RecD subunit of RecBCD enzyme increases radioresistance of the wild-type Escherichia coli. Biochimie. 1991 Apr;73(4):501–503. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90119-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKittrick N. H., Smith G. R. Activation of Chi recombinational hotspots by RecBCD-like enzymes from enteric bacteria. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 5;210(3):485–495. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90125-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk M., Kinross J. Conditional lethality of recA and recB derivatives of a strain of Escherichia coli K-12 with a temperature-sensitive deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase I. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):971–978. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.971-978.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Goldberg E. B. Protection of parental T4 DNA from a restriction exonuclease by the product of gene 2. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov;116(4):877–881. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90276-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palas K. M., Kushner S. R. Biochemical and physical characterization of exonuclease V from Escherichia coli. Comparison of the catalytic activities of the RecBC and RecBCD enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3447–3454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G. J., Prasher D. C., Kushner S. R. Physical and biochemical characterization of cloned sbcB and xonA mutations from Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2089–2094. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2089-2094.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinken R., Wackernagel W. Inhibition of the recBCD-dependent activation of Chi recombinational hot spots in SOS-induced cells of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(4):1172–1178. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.4.1172-1178.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinken R., de Vries J., Weichenhan D., Wackernagel W. The recA-recBCD dependent recombination pathways of Serratia marcescens and Proteus mirabilis in Escherichia coli: functions of hybrid enzymes and hybrid pathways. Biochimie. 1991 Apr;73(4):375–384. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90104-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosamond J., Telander K. M., Linn S. Modulation of the action of the recBC enzyme of Escherichia coli K-12 by Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8646–8652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. M., Hastings P. J. The split-end model for homologous recombination at double-strand breaks and at Chi. Biochimie. 1991 Apr;73(4):385–397. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90105-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargentini N. J., Smith K. C. Quantitation of the involvement of the recA, recB, recC, recF, recJ, recN, lexA, radA, radB, uvrD, and umuC genes in the repair of X-ray-induced DNA double-strand breaks in Escherichia coli. Radiat Res. 1986 Jul;107(1):58–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmon V. F., Lederberg S. Degradation of bacteriophage lambda deoxyribonucleic acid after restriction by Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):161–169. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.161-169.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R. Homologous recombination in procaryotes. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Mar;52(1):1–28. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.1.1-28.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R. Mechanism and control of homologous recombination in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1987;21:179–201. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.21.120187.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl F. W., Thomason L. C., Siddiqi I., Stahl M. M. Further tests of a recombination model in which chi removes the RecD subunit from the RecBCD enzyme of Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1990 Nov;126(3):519–533. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.3.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Orr-Weaver T. L., Rothstein R. J., Stahl F. W. The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A., Smith G. R. Unwinding and rewinding of DNA by the RecBC enzyme. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90355-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thaler D. S., Sampson E., Siddiqi I., Rosenberg S. M., Thomason L. C., Stahl F. W., Stahl M. M. Recombination of bacteriophage lambda in recD mutants of Escherichia coli. Genome. 1989;31(1):53–67. doi: 10.1139/g89-013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoms B., Wackernagel W. Regulatory role of recF in the SOS response of Escherichia coli: impaired induction of SOS genes by UV irradiation and nalidixic acid in a recF mutant. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1731–1736. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1731-1736.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoms B., Wackernagel W. Suppression of the UV-sensitive phenotype of Escherichia coli recF mutants by recA(Srf) and recA(Tif) mutations requires recJ+. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3675–3681. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3675-3681.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoms B., Wackernagel W. UV-induced allevation of lambda restriction in Escherichia coli K-12: kinetics of induction and specificity of this SOS function. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(1):111–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00422921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T. C., Smith K. C. Postreplicational formation and repair of DNA double-strand breaks in UV-irradiated Escherichia coli uvrB cells. Mutat Res. 1986 Jan;165(1):39–44. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(86)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weichenhan D., Wackernagel W. Cloning of the recB, recC, and recD genes from Proteus mirabilis in Escherichia coli: in vivo formation of active hybrid enzymes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1412–1414. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1412-1414.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weichenhan D., Wackernagel W. Functional analyses of Proteus mirabilis wild-type and mutant RecBCD enzymes in Escherichia coli reveal a new mutant phenotype. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1777–1784. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



