Abstract
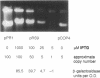
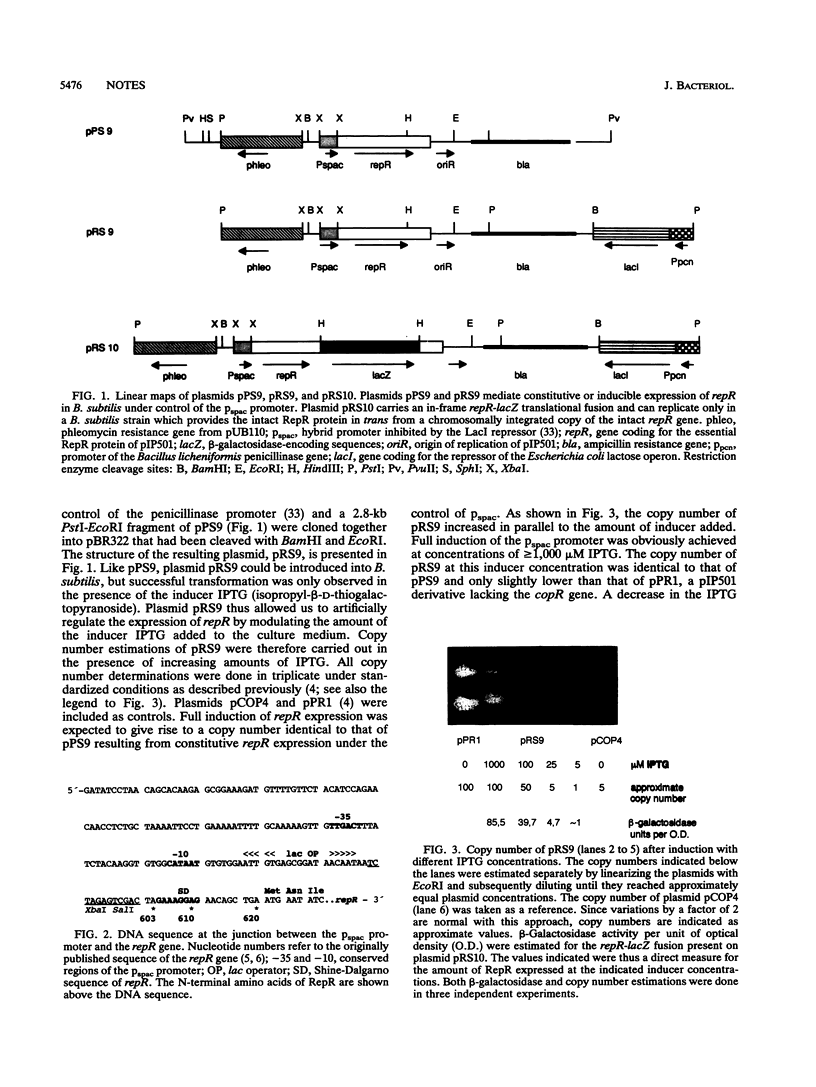
To prove the hypothesis that the amount of RepR protein is the rate-limiting factor for replication of plasmid pIP501 in Bacillus subtilis, the repR gene was placed under control of the inducible promoter pspac. The plasmid copy number of the pIP501 derivative pRS9 could be deliberately adjusted between approximately 1 and 50 to 100 molecules per cell by varying the concentration of the inducer isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside. Construction of a repR-lacZ fusion proved that the increase in copy number was due to a proportional increase in the amount of RepR protein.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso J. C. DNA replication of plasmids from gram-positive bacteria in Bacillus subtilis. Plasmid pUB110 as a model system. Microbiologia. 1989 Jun;5(1):5–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behnke D., Gilmore M. S., Ferretti J. J. Plasmid pGB301, a new multiple resistance streptococcal cloning vehicle and its use in cloning of a gentamicin/kanamycin resistance determinant. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(3):414–421. doi: 10.1007/BF00293929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behnke D., Malke H., Hartmann M., Walter F. Post-transformational rearrangement of an in vitro reconstructed group-A streptococcal erythromycin resistance plasmid. Plasmid. 1979 Oct;2(4):605–616. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90058-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brantl S., Behnke D., Alonso J. C. Molecular analysis of the replication region of the conjugative Streptococcus agalactiae plasmid pIP501 in Bacillus subtilis. Comparison with plasmids pAM beta 1 and pSM19035. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4783–4790. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brantl S., Behnke D. Copy number control of the streptococcal plasmid pIP501 occurs at three levels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 11;20(3):395–400. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.3.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruand C., Ehrlich S. D., Jannière L. Unidirectional theta replication of the structurally stable Enterococcus faecalis plasmid pAM beta 1. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2171–2177. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattoraj D. K., Snyder K. M., Abeles A. L. P1 plasmid replication: multiple functions of RepA protein at the origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2588–2592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Yagi Y., Dunny G. M., Schultz S. K. Characterization of three plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid molecules in a strain of Streptococcus faecalis: identification of a plasmid determining erythromycin resistance. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):283–289. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.283-289.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel H. W., Soedirman N., Rost J. A., van Leeuwen W. J., van Embden J. D. Transferability of macrolide, lincomycin, and streptogramin resistances between group A, B, and D streptococci, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):407–413. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.407-413.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filutowicz M., McEachern M., Greener A., Mukhopadhyay P., Uhlenhopp E., Durland R., Helinski D. Role of the pi initiation protein and direct nucleotide sequence repeats in the regulation of plasmid R6K replication. Basic Life Sci. 1985;30:125–140. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-2447-8_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Givskov M., Stougaard P., Light J., Molin S. Identification and characterization of mutations responsible for a runaway replication phenotype of plasmid R1. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90123-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez C. F., Kunka B. S. Plasmid transfer in Pediococcus spp.: intergeneric and intrageneric transfer of pIP501. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):81–89. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.81-89.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greener A., Filutowicz M. S., McEachern M. J., Helinski D. R. N-terminal truncated forms of the bifunctional pi initiation protein express negative activity on plasmid R6K replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Oct;224(1):24–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00259447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss A., Ehrlich S. D. The family of highly interrelated single-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid plasmids. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):231–241. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.231-241.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haring V., Scholz P., Scherzinger E., Frey J., Derbyshire K., Hatfull G., Willetts N. S., Bagdasarian M. Protein RepC is involved in copy number control of the broad host range plasmid RSF1010. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6090–6094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horodniceanu T., Bouanchaud D. H., Bieth G., Chabbert Y. A. R plasmids in Streptococcus agalactiae (group B). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Nov;10(5):795–801. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.5.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jannière L., Bruand C., Ehrlich S. D. Structurally stable Bacillus subtilis cloning vectors. Gene. 1990 Mar 1;87(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90495-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K., Meyer R. J. Copy number of the broad host-range plasmid R1162 is determined by the amounts of essential plasmid-encoded proteins. J Mol Biol. 1985 Oct 20;185(4):755–767. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline B. C. A review of mini-F plasmid maintenance. Plasmid. 1985 Jul;14(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline B. C., Sandhu G. S., Eckloff B. W., Aleff R. A. Site-specific proteolysis of mini-F plasmid replication protein RepE destroys initiator function and generates an incompatibility substance. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(9):3004–3010. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.9.3004-3010.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kües U., Stahl U. Replication of plasmids in gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):491–516. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.491-516.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manch-Citron J. N., Gennaro M. L., Majumder S., Novick R. P. RepC is rate limiting for pT181 plasmid replication. Plasmid. 1986 Sep;16(2):108–115. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(86)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Msadek T., Kunst F., Henner D., Klier A., Rapoport G., Dedonder R. Signal transduction pathway controlling synthesis of a class of degradative enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: expression of the regulatory genes and analysis of mutations in degS and degU. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):824–834. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.824-834.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muraiso K., Mukhopadhyay G., Chattoraj D. K. Location of a P1 plasmid replication inhibitor determinant within the initiator gene. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4441–4447. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4441-4447.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P. Plasmid incompatibility. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Dec;51(4):381–395. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.4.381-395.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Díaz J. C., Vicente M. F., Baquero F. Plasmids in Listeria. Plasmid. 1982 Sep;8(2):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terawaki Y., Nozue H., Zeng H., Hayashi T., Kamio Y., Itoh Y. Effects of mutations in the repA gene of plasmid Rts1 on plasmid replication and autorepressor function. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):786–792. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.786-792.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]