Abstract
The Ras family of small GTPases regulates cell proliferation, spreading, migration and apoptosis, and malignant transformation by binding to several protein effectors. One such GTPase, R-Ras, plays distinct roles in each of these processes, but to date, identified R-Ras effectors were shared with other Ras family members (e.g., H-Ras). We utilized a new database of Ras-interacting proteins to identify RLIP76 (RalBP1) as a novel R-Ras effector. RLIP76 binds directly to R-Ras in a GTP-dependent manner, but does not physically associate with the closely related paralogues H-Ras and Rap1A. RLIP76 is required for adhesion-induced Rac activation and the resulting cell spreading and migration, as well as for the ability of R-Ras to enhance these functions. RLIP76 regulates Rac activity through the adhesion-induced activation of Arf6 GTPase and activation of Arf6 bypasses the requirement for RLIP76 in Rac activation and cell spreading. Thus, we identify a novel R-Ras effector, RLIP76, which links R-Ras to adhesion-induced Rac activation through a GTPase cascade that mediates cell spreading and migration.
Introduction
Cell migration is a key component of development, wound healing, and immunological responses (Ridley et al., 2003). It also plays essential roles in pathological processes, e.g., invasion of primary tumor cells and subsequent metastasis to distant sites (Sporn, 1996). Elucidation of the molecular mechanisms involved in the initiation and control of cell migration is therefore essential to understanding these processes (Horwitz and Webb, 2003). Migrating cells extend protrusions in the forward direction, form new attachments to the extracellular matrix, and release attachments at the rear to allow the cell mass to pull forward (Ridley et al., 2003). The newly formed attachments at the cell anterior lead to adhesion-induced activation of Rac1 that causes localized actin polymerization to create broad protrusive structures (lamellipodia; Pollard and Borisy, 2003). When detached cells adhere, adhesion-induced Rac activation leads to unpolarized lamellipodial extension, resulting in cell spreading (Etienne-Manneville and Hall, 2002). Thus, cell spreading and lamellipodial extension are closely related Rac-mediated events.
The Ras family GTPase Related-Ras (R-Ras) can regulate adhesion-mediated Rac activation and cell migration (Holly et al., 2005; Wozniak et al., 2005). R-Ras shares 55% sequence homology with related paralogues in the Ras family of small GTPases, has an almost identical effector-binding region to H-, N-, and K-Ras (Lowe et al., 1987; Self et al., 1993), and couples to common Ras effectors, including Raf1, RalGDS, RapL/NORE1, and PI3-kinase (Oertli et al., 2000). However, R-Ras has distinct cellular functions from other Ras paralogues. In addition to its distinct effects on integrin activation, R-Ras inhibits cell proliferation in endothelial and smooth muscle cells (Komatsu and Ruoslahti, 2005) and promotes cell adhesion (Zhang et al., 1996; Keely et al., 1999), cell spreading, haptotactic migration (Holly et al., 2005; Ada-Nguema et al., 2006), and neurite outgrowth (Ivins et al., 2000; Oinuma et al., 2004). R-Ras mediates these effects on cells through coupling to downstream effectors; however, to date, no bona fide R-Ras effectors have been described to account for its functions distinct from H-Ras and Rap1.
A hindrance to the identification of effectors for small GTPases is the absence of isoprenylation or correct subcellular targeting of Ras GTPases in commonly used methods, such as yeast two-hybrid screens (Gietz et al., 1997). The subcellular localization of these proteins is essential for correct targeting to specific effectors and for resulting biological functions (Hancock, 2003). To facilitate the hunt for isotype-specific effectors of Ras GTPases, we have used tandem affinity purification (TAP) tags (Rigaut et al., 1999; Puig et al., 2001) and high-throughput mass spectroscopy to isolate and characterize proteins that interact with posttranslationally modified Ras GTPases in murine fibroblasts. The results of these studies permitted us to develop and analyze a comparative proteomic database of Ras-interacting proteins that is publicly available (http://www.cellmigration.org/resource/discovery/proteomics/ginsberg_ras_data.shtml). Using this database, we have identified RLIP76 (RalBP1; Cantor et al., 1995; Jullien-Flores et al., 1995) as a novel R-Ras effector. We show that RLIP76 directly binds R-Ras in a GTP-dependent manner, but does not interact with the closely related Ras isotypes H-Ras or Rap1A, confirming that RLIP76 is an authentic effector with relative R-Ras specificity. Furthermore, RLIP76 mediates the effect of R-Ras on cell spreading and migration by functioning as a key link in a cascade of small GTPases in which RLIP76 binding to R-Ras capacitates adhesion-mediated activation of Arf6 GTPase. Activated Arf6 GTPase is then required for adhesion-induced Rac activation and the resulting lamellipodia and cell migration.
Results
An experimental database of Ras-interacting proteins identifies RLIP76 as an R-Ras interactor
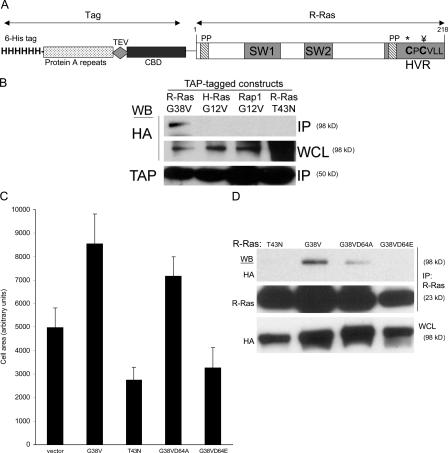
To identify potential effectors of R-Ras, we exploited a comparative proteomic effort (http://www.cellmigration.org/resource/discovery/proteomics/ginsberg_ras_data.shtml) to isolate and characterize Ras-binding proteins. In brief, this database used a modified TAP scheme originally described for yeast proteomics by Rigaut et al. (1999) for a mammalian system (Puig et al., 2001). To do this, we fused the TAP tag-coding region to the N terminus of human Ras cDNAs containing point mutations to render them constitutively active (R-Ras[G38V]) and dominant negative (R-Ras[T43N]); in the case of R-Ras, we used two effector loop mutants, R-Ras(G38VD64A) and R-Ras(G38VD64E), built on the activated background. To assess specificity amongst Ras family members, similar constructs were prepared for activated variants of H-Ras(G12V) or Rap1A(G12V). The Ras constructs were expressed in murine 3T3 cells and purified, and associated proteins were identified by mass spectroscopy (http://www.cellmigration.org/resource/discovery/proteomics/ginsberg_ras_data.shtml).
This unbiased proteomic screen identified RLIP76 (RalBP1) as a protein interacting with activated R-Ras(G38V), but not with dominant-negative R-Ras(T43N). Furthermore, RLIP76 was not identified amongst the proteins co-isolating with activated variants of H-Ras(G12V) or Rap1A(G12V) (http://www.cellmigration.org/resource/discovery/proteomics/ginsberg_ras_data.shtml), suggesting RLIP76 might be involved in R-Ras–specific signaling. To confirm the specificity of RLIP76 interactions with R-Ras, we coexpressed authentic human RLIP76 cDNA with R-Ras variants in murine 3T3 cells. RLIP76 coprecipitated with activated R-Ras(G38V), but not R-Ras(T43N; Fig. 1 B), demonstrating the GTP dependence of the interaction. Furthermore, activated variants of H-Ras(G12V) and Rap1A(G12V) did not interact with RLIP76, establishing the specificity of the interaction amongst Ras family members and confirming a previous report of the failure of RLIP76 to bind H-Ras in a yeast two-hybrid experiment (Fig. 1 B; Jullien-Flores et al., 1995). In contrast to H-Ras, activated R-Ras promotes integrin activation (Zhang et al., 1996; Sethi et al., 1999) and cell spreading (Holly et al., 2005; Ada-Nguema et al., 2006). Mutations in the switch 1 effector-binding region of R-Ras can selectively disrupt its ability to interact with known effectors and can alter its ability to increase integrin activation (Oertli et al., 2000). We examined the effect of such switch 1 mutants of R-Ras on integrin-mediated cell spreading. In confirmation of previous work (Holly et al., 2005), transfection of NIH 3T3 mouse fibroblasts with constitutively active R-Ras(G38V), but not R-Ras(T43N; dominant negative), stimulated cell spreading (Fig. 1 C). The effector loop mutant R-Ras(G38VD64A), which fails to bind or activate PI3-kinase and RalGDS but is competent to activate integrins (Oertli et al., 2000), promoted cell spreading, whereas R-Ras(G38VD64E) failed to do so. Thus, the increase in spreading caused by R-Ras does not require direct activation of PI3-kinase or Ral. In TAP-Ras pulldown experiments we isolated RLIP76 with R-Ras variants that support cell spreading, i.e., R-Ras(G38V) and R-Ras(G38VD64A), but we did not detect RLIP76 in proteins isolated with R-Ras(T43N) or R-Ras(G38VD64E; unpublished data). To directly assess whether RLIP76 was a candidate effector for this R-Ras function, we examined its ability to coprecipitate with each of these variants. RLIP76 coprecipitated with R-Ras(G38V) and the G38VD64A mutant, but not with the dominant-negative T43N variant or the G38VD64E double mutant (Fig. 1 D). Thus, RLIP76 interacts with R-Ras variants that support cell spreading and integrin activation and is a candidate to mediate these activities of R-Ras.
Figure 1.
Identification of RLIP76 as an R-Ras effector in cell spreading. (A) Schematic representation of the TAP–R-Ras fusion construct. The modified TAP tag consists of an N-terminal poly-histidine tag (6-His tag), a protein A module, the recognition sequence for the TEV protease, and a calmodulin-binding domain (CBD). The following important features of the R-Ras moiety are shown: two proline-rich SH3-binding sequences (PP), one of which is contained within the C-terminal hypervariable region (HVR); the switch 1 effector-binding loop region (SW1), which is important for effector binding; the switch 2 region (SW2), which is involved in binding guanine nucleotide; the Cys213 palmitoylation site (*) and the Cys215 methylation and geranylgeranylation site (¥); and the R-Ras isoprenylation motif. (B) TAP fusions of constitutively active variants of R-Ras, H-Ras, Rap1A, and dominant-negative R-Ras(T43N) were cotransfected with HA-RLIP76 cDNA into NIH 3T3 cells. TAP-Ras proteins were isolated from cell lysates by IgG–Sepharose affinity chromatography, and protein complexes were fractionated by SDS-PAGE and Western blotted with antibodies to the TAP tag (α-MLCKsk) or HA. HA-RLIP76 was detected in R-Ras(G38V) precipitates, but not in precipitates of H-Ras(G12V), Rap1A(G12V), or R-Ras(T43N), indicating that RLIP76 binds in a GTP-dependent manner exclusively to R-Ras among the members of this Ras subfamily. IP, immunoprecipitate; WCL, whole cell lysate. (C) NIH 3T3 cells were cotransfected with cDNA encoding GFP and the following variants of human R-Ras: constitutively active (G38V), dominant-negative (T43N), and effector loop mutants (D64A and D64E) on the activated G38V background. Cells were plated onto fibronectin-coated coverslips, fixed after 45 min, and stained with rhodamine-phalloidin to reveal F-actin. The cell periphery, as delineated by phalloidin labeling, was used to calculate the area of GFP-positive cells. At least 40 cells were counted for each sample. Mean area measurements are representative of at least three independent experiments and are shown ± the SEM. (D) HA-RLIP76 was cotransfected with the indicated R-Ras protein variants in NIH 3T3 cells. R-Ras was immunoprecipitated from each sample with anti–R-Ras antibodies, and the bound proteins were eluted in SDS buffer and separated by SDS-PAGE, and then Western blotted with antibodies to R-Ras or to HA. HA-RLIP76 was detected in R-Ras(G38V) and -G38VD64A precipitates, but not in -T43N or -G38VD64E precipitates.
RLIP76 is required for R-Ras–induced cell spreading
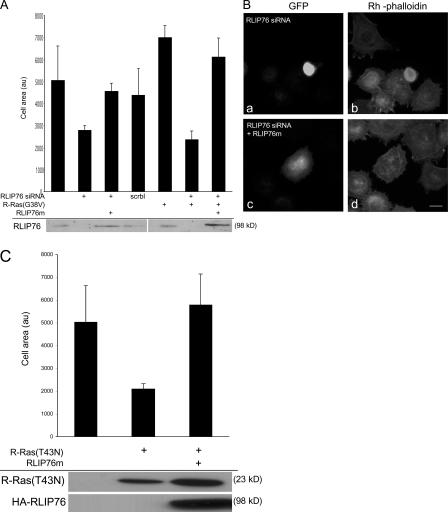
The specificity of the interactions of RLIP76 with the R-Ras variants that promote spreading and integrin activation suggested that RLIP76 may play a role in these processes. We used double-stranded siRNA (Rosse et al., 2003) to inhibit RLIP76 expression in mouse 3T3 cells. This siRNA reduced the expression of endogenous RLIP76 by >90% in mouse 3T3 cells and CHO cells and, as previously reported (Rosse et al., 2003), also suppressed the expression of human RLIP76 (Fig. 2 A and unpublished data).
Figure 2.
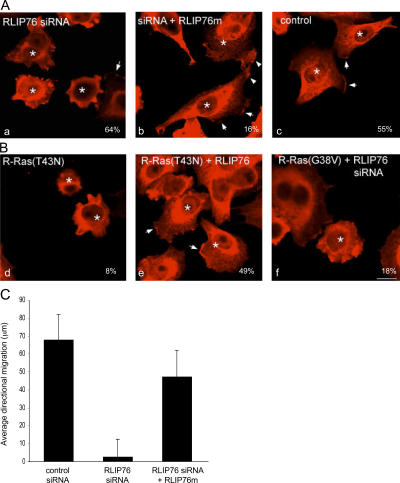
RLIP76 is required for R-Ras–induced cell spreading. (A) NIH 3T3 cells were transfected with R-Ras(G38V) in the presence or absence of 50 pmol of a double-stranded siRNA targeting both human and mouse RLIP76 (RLIP76 siRNA; Rosse et al., 2003) or a sequence-scrambled siRNA (scrbl). Cell lysates were blotted with anti-RLIP76 antibodies. RLIP76 expression was restored in siRNA-transfected cells by coexpression of RLIP76 cDNA containing three silent mutations in the siRNA target site (RLIP76m). Cells were plated on fibronectin-coated coverslips and cell area was measured as described in Materials and methods. Mean area measurements of GFP-positive cells are representative of at least three independent experiments and are shown ± the SEM. (B) Representative micrographs (a and c, GFP to mark transfected cells; b and d, rhodamine-phalloidin to detect F-actin) of cells spreading on fibronectin; cells were transfected with RLIP76 siRNA in the absence (a and b) or presence of the RLIP76m rescue construct (c and d). Bar, 5 μm. (C) NIH 3T3 cells were transfected with dominant-negative R-Ras(T43N), with or without cotransfection with RLIP76, and cell spreading was measured as described in Materials and methods. Mean area measurements of GFP-positive cells are representative of at least three independent experiments and are shown ± the SEM. Expression levels of the transfected proteins were assayed by Western blotting with antibodies to R-Ras (top) or HA (bottom).
To assess a role for RLIP76 in cell spreading, 3T3 cells were transfected with the RLIP76 siRNA, plated onto fibronectin-coated coverslips, and evaluated for spreading. The cells transfected with the RLIP76 siRNA showed markedly reduced cell spreading, and this effect could not be reversed by cotransfection of R-Ras(G38V; Fig. 2, A and B). In contrast, reconstitution of RLIP76 expression with a cDNA encoding three silent mismatches (RLIP76m) in the siRNA target sequence, restored RLIP76 expression and cell spreading (Fig. 2, A and B). R-Ras can regulate integrins' affinity (Zhang et. al. 1996), but siRNA-mediated knockdown of RLIP76 had no effect on the activation state of integrins in CHO cells (Hughes et al., 1997; unpublished data). Furthermore, R-Ras can reverse the suppressive effect of H-Ras on integrin activation (Sethi et al., 1999); however, RLIP76 siRNA had no effect on this activity of R-Ras (unpublished data). Thus, RLIP76 is required for cell spreading and for the increased spreading mediated by activated R-Ras, but did not modulate integrin affinity in CHO cells.
The requirement of RLIP76 expression for spreading suggested that RLIP76 may be downstream of signals from R-Ras in cell spreading. As a test of this hypothesis, we expressed dominant-negative R-Ras(T43N) and found that it inhibited cell spreading (Fig. 1 C and Fig. 2 C) and the defect in cell spreading induced by R-Ras(T43N) was reversed by overexpression of RLIP76 (Fig. 2 C). Thus, RLIP76 is required for R-Ras–mediated cell spreading, and RLIP76 overexpression can bypass a requirement for R-Ras activity in cell spreading. These relationships, in combination with the R-Ras effector loop specificities of the physical interaction of R-Ras with RLIP76, demonstrate that RLIP76 is downstream of R-Ras in promoting cell spreading.
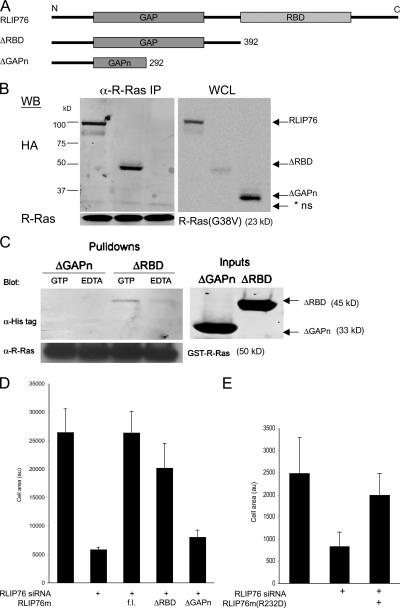
The RhoGAP-binding, but not the Ral-binding, domain of RLIP76 is required for binding to R-Ras and for cell spreading
The association of RLIP76 with activated R-Ras and its role in R-Ras–mediated spreading suggested the possibility that these proteins may interact directly and that RLIP76 might be an authentic R-Ras effector. In prokaryotic expression systems, we were unable to obtain a sufficient quantity of purified full-length RLIP76 protein to analyze its interaction with R-Ras because of low expression levels (unpublished data), and therefore used coimmunoprecipitation studies to initially map the RLIP76-binding domain for R-Ras. The RLIP76 polypeptide consists of an N-terminal coiled coil region, a Rho GTPase-activating protein (RhoGAP) domain, a short connecting segment, a Ral-binding domain (RBD), and a C-terminal region (Fig. 3 A; Cantor et al., 1995; Jullien-Flores et al., 1995; Park and Weinberg, 1995). We constructed N-terminal RLIP76 lacking the RBD and C-terminal region (ΔRBD) or that were further truncated at the C-terminal half of the GAP domain (ΔGAPn; Fig. 3 A). In coimmunoprecipitation experiments, the full-length RLIP76 and the RBD-deleted protein (ΔRBD) coprecipitated with activated R-Ras, whereas the ΔGAPn truncated protein did not (Fig. 3 B). These data suggested that the RBD, responsible for direct interaction of RLIP76 with Ral GTPase, (Jullien-Flores et al., 1995), is not required for RLIP76 interaction with R-Ras. To test whether RLIP76 can interact directly with R-Ras, we generated N-terminal poly-histidine–tagged bacterial expression constructs encoding RLIP76ΔRBD or -ΔGAPn; both were well expressed. An N-terminal glutathione-S-transferase fusion to R-Ras(wt) (GST–R-Ras) protein was coupled to GSH beads and either loaded with 10 μM GTP to generate activated R-Ras or maintained in 10 mM EDTA to produce nucleotide-free R-Ras. Western blotting showed that the ΔRBD fragment protein bound directly to R-Ras in a GTP-dependent manner. In contrast, the ΔGAPn RLIP76 fragment did not detectably interact with R-Ras in either state (Fig. 3 C). Thus, RLIP76 binds directly to R-Ras, in a GTP-dependent manner, and the RLIP76 RhoGAP domain, but not to the RBD, is required for this interaction.
Figure 3.
The RhoGAP, but not the RBD of RLIP76, is required for binding to R-Ras and for cell spreading. (A) Schematic diagram of RLIP76 truncation mutants. Each of the indicated constructs was generated with N-terminal HA tags for mammalian expression and N-terminal His tags for bacterial expression and purification. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of RLIP76 truncation mutants and R-Ras. Full-length RLIP76 and RLIP76ΔRBD coprecipitated with activated R-Ras, but the RLIP76ΔGAPn truncation did not. IP, immunoprecipitates; WCL, whole cell lysate; * ns, nonspecific. (C) In vitro binding of RLIP76ΔRBD to activated R-Ras. GST–R-Ras was coupled to GSH–Sepharose and activated by addition of excess GTP or was kept nucleotide-free in 10 mM EDTA before addition of purified RLIP76 proteins. RLIP76 bound to R-Ras in a GTP-dependent manner, whereas the ΔGAPn mutant was not detected in R-Ras pulldowns. (D) Cell spreading was assessed as before. 3T3 cells were transfected with RLIP76 siRNA, as indicated. HA-RLIP76 mutants were cotransfected to reconstitute RLIP76 expression (fl, full-length RLIP76; au, arbitrary unit). Mean area measurements of GFP-positive cells are representative of at least three independent experiments and are shown ± the SEM. (E) Cell spreading in RLIP76-depleted cells reconstituted with full-length RLIP76 bearing an Arg232Asp point mutation in the GAP domain (R232D).
We next evaluated the abilities of the truncated RLIP76 mutants to reconstitute spreading in RLIP76-depleted cells. The RLIP76 mutants were constructed on the siRNA mismatch RLIP76 mutant background and cotransfected with RLIP76 siRNA. RLIP76mΔRBD, which binds R-Ras, rescued the siRNA-induced spreading defect to a similar extent to the full-length construct (Fig. 3 D). The ΔGAPn truncation mutant, which did not bind R-Ras (Fig. 3, A and B), did not reverse the effect of RLIP76 siRNA. Thus, R-Ras binds the RhoGAP, but not the RBD of RLIP76 in a GTP-dependent manner, and the RhoGAP domain is required for RLIP76-dependent cell spreading.
Cell spreading can be induced by the small GTPase Rac1 (Hall, 1998). The RhoGAP domain of RLIP76 has Rac GAP activity in vitro (Jullien-Flores et al., 1995; Matsubara et al., 1997; Park and Weinberg, 1995). The RLIP76 RhoGAP domain bears strong sequence similarity to the RhoGAP domains of BCR-GAP and n-chimaerin, which are both GAPs for Rac (Jullien-Flores et al., 1995; Park and Weinberg, 1995). Despite sequence divergence among GAP proteins, their mechanism of action is highly conserved, and depends on an “arginine finger,” which is a conserved arginine residue in a loop segment that stabilizes the GTP moiety on the substrate, increasing the substrate's intrinsic GTPase activity (Bourne, 1997). RLIP76, bearing a mutation in the conserved Arg required for GAP function (RLIP76m[R232D]), still supported cell spreading in RLIP76-depleted cells, indicating that GAP activity of RLIP76 is not required for its effects on cell spreading (Fig. 3 E).
RLIP76 regulates R-Ras–induced cell spreading by promoting adhesion-induced Rac activation
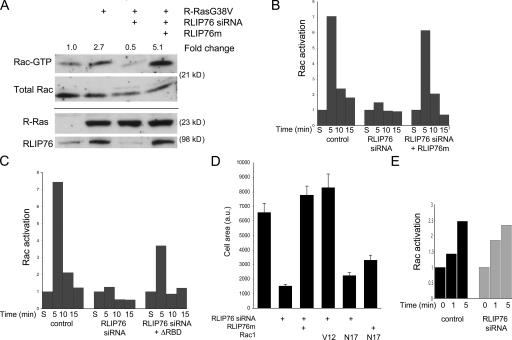
Activated R-Ras stimulates cell spreading and migration by augmenting the activation of the small GTPase Rac1 (Holly et al., 2005), although this effect appears to be cell type specific (Wozniak et al., 2005). In murine 3T3 cells, as reported by Holly et al. (2005), transfection of R-Ras(G38V) resulted in an approximately threefold increase in adhesion-induced activation of Rac1, as measured by its binding to the p21-binding domain of PAK1 (Fig. 4 A; Bagrodia et al., 1998; del Pozo et al., 2000). Cotransfection of RLIP76 siRNA completely blocked this effect of R-Ras(G38V); this decrease could be reversed by reexpression of RLIP76m (Fig. 4 A). Thus, RLIP76 expression is required for R-Ras–induced Rac activation.
Figure 4.
RLIP76 regulates migration and R-Ras–induced cell spreading by controlling adhesion-induced Rac activation. (A) Rac activation induced by adhesion to fibronectin was measured as described in Materials and methods. Expression of R-Ras(G38V) promotes increased Rac activation levels, relative to control in cells adhering to fibronectin, but this function is ablated by depletion of RLIP76. Overexpression of mismatched RLIP76 rescues the defect in Rac activation. (B) Cells were transfected as indicated, kept in suspension for 1 h, and precipitated by centrifugation (S, suspended) or plated on fibronectin for the indicated times, and then adhesion-induced Rac activation was assessed. Rac activation is represented relative to levels in suspended cells (normalized to 1). (C) Adhesion-induced Rac activation in RLIP76-depleted cells reconstituted with RLIP76 truncated N terminal to the RBD. (D) Quantitation of cell spreading in RLIP76-depleted cells expressing activated (V12) or dominant-negative (N17) Rac1. Mean area measurements of GFP-positive cells are representative of at least three independent experiments and are shown ± the SEM. Rac(V12) rescues the spreading defect by RLIP76 depletion, whereas RLIP76 overexpression is not sufficient to restore spreading in Rac(N17)-expressing cells, indicating that Rac is downstream of RLIP76 in cell spreading. (E) Rac activation was measured in serum-starved cells after stimulation with 10 ng/ml EGF for the indicated times.
As noted above, the capacity of dominant-negative (T43N) R-Ras to inhibit spreading and Rac activation suggests that endogenous R-Ras mediates these processes. To determine whether RLIP76 is required for adhesion-dependent activation of Rac, we assessed the effect of siRNA-mediated RLIP76 knockdown on adhesion-induced Rac activation in the absence of exogenous R-Ras. In control siRNA-transfected cells, Rac activation was low in cells maintained in suspension, and increased dramatically after five minutes of adhesion to fibronectin (Fig. 4 B). This increase in Rac activation was followed by a diminution over the next 10 min. In contrast, cells with reduced RLIP76 expression failed to increase Rac activation in response to cell adhesion. This defect in Rac activation was reversed by expression of mismatched RLIP76 (Fig. 4 B). Defective Rac activation in RLIP76-deficient cells was also partially restored by reconstitution with RLIP76ΔRBD (Fig. 4 C), which also restored spreading (Fig. 3 D). The spreading defect induced by RLIP76 knockdown was reversed by expression of an activated variant of Rac (Rac1A[G12V]; Fig. 4 D). Furthermore, overexpression of RLIP76 failed to complement the spreading defect induced by dominant-negative Rac(T17N). Thus, Rac1 activation is downstream of RLIP76. The requirement for RLIP76 is specific to adhesion-induced Rac activation because RLIP76 depletion had little effect on Rac activation stimulated by EGF (Fig. 4 E). Thus, RLIP76 mediates cell spreading by regulating adhesion-induced activation of Rac.
Rac1 activation is associated with its localization to the plasma membrane and concentration in nascent lamellipodia (Kraynov et al., 2000; Kurokawa et al., 2004). Depletion of RLIP76 led to diminished lamellipodial extensions and loss of Rac localization at the peripheral membrane. This phenotype was rescued by reexpression of RLIP76m (Fig. 5 A). Furthermore, depletion of RLIP76 blocked lamellipodia and Rac membrane localization even in the presence of activated R-Ras(G38V) (Fig. 5 B). In contrast, RLIP76 overexpression rescued the loss of lamellipodia and peripheral Rac localization in R-Ras(T43N)–transfected cells (Fig. 5 B). Thus, RLIP76 regulates the localization and the activation of Rac GTPase.
Figure 5.
RLIP76 is required for Rac membrane localization and lamellipodia. (A) Cells were transfected with GFP and control siRNA (a), RLIP76 siRNA (b), or RLIP76 siRNA and RLIP76m (c), and peripheral membrane Rac localization was assessed in cells spread on fibronectin by immunostaining with antibodies to Rac1. Arrows point to areas of Rac enrichment in lamellipodia. GFP-positive cells are indicated by asterisks. Percentages of GFP-positive cells showing Rac membrane localization are shown. Bar, 10 μm. (B) Cells were transfected with GFP and R-Ras(T43N) (a), R-Ras(T43N) and RLIP76m (b), or R-Ras(G38V) and RLIP76 siRNA (c). Percentages of cells showing Rac membrane localization are shown. (C) Directional migration of RLIP76-depleted cells into a scratch wound. Cells were plated on fibronectin-coated substrates, a single scratch was made in confluent cell monolayers 48 h after transfection, and GFP-positive cells were tracked microscopically over 4 h. The mean distances traveled into the wound space by GFP-positive cells at the wound edge (at least 25 cells/sample) are shown ± the SEM.
The requirement for RLIP76 in adhesion-induced Rac activation suggested that RLIP76 is important for cell migration. To test this idea, we wounded monolayers of GFP-transfected murine 3T3 cells and measured the migration of GFP-positive cells into the wound. Cells cotransfected with RLIP76 siRNA exhibited markedly impaired migration relative to control vector-transfected cells or cells cotransfected with the rescue construct RLIP76m in combination with the siRNA (Fig. 5 C). Thus, RLIP76 is required for directional cell migration into a wound.
RLIP76 regulates Rac activity via Arf6
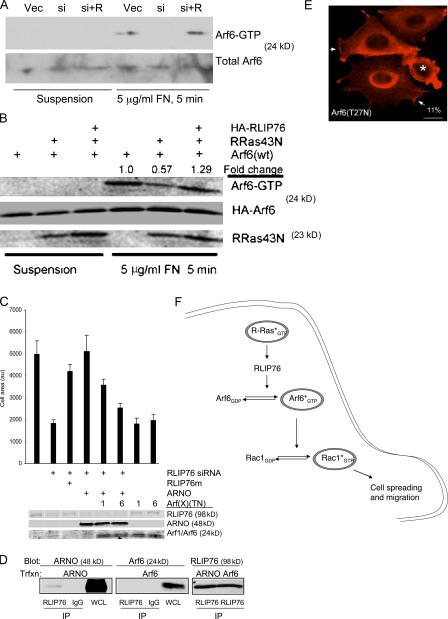
Arf6 GTPase, which is a class III ADP-ribosylation factor, regulates endosomal trafficking of Rac1 (Radhakrishna et al., 1999; Santy and Casanova, 2001) and mediates adhesion-dependent DOCK180/Elmo-induced Rac activation (Santy et al., 2005). Therefore, we asked if RLIP76 effects on Rac localization and activation are mediated by Arf6. Cell adhesion activates Arf6 and we found that siRNA-mediated knockdown of RLIP76 blocked adhesion-induced Arf6 activation (Fig. 6 A). We had previously observed (Fig. 2 C) that RLIP76 overexpression can bypass a requirement for R-Ras activity in cell spreading, suggesting that RLIP76 might render adhesion-induced Arf6 activation independent of R-Ras. Dominant-negative R-Ras(T43N) inhibited adhesion-induced activation of Arf6 (Fig. 6 B); however, ectopic RLIP76 restored Arf6 activation in R-Ras(T43N)–expressing cells (Fig. 6 B).
Figure 6.
RLIP76 regulates spreading through the activation of Arf6. (A) Loss of adhesion-induced Arf6 activation in the absence of RLIP76. NIH 3T3 cells were transfected with vector and control siRNA (Vec), RLIP76 siRNA (si), or siRNA and RLIP76m (si + R), and after 24 h were detached and either kept in suspension or plated on fibronectin. Arf6 activation was measured as described in Materials and methods. (B) RLIP76 bypasses the requirement for R-Ras activity in adhesion-induced Arf6 activation. NIH 3T3 cells were transfected as indicated, and Arf6 activation was measured as in A. (C) The Arf-GEF ARNO rescues the spreading defect in RLIP76-depleted cells. 3T3 cells were transfected as indicated and plated on fibronectin-coated coverslips for spreading assays. Arf(TN) mutants are indicated as 1 (Arf1[T31N]) or 6 (Arf6[T27N]). Mean area measurements of GFP-positive cells are representative of at least three independent experiments and are shown ± the SEM. (D) Association of ARNO with RLIP76. Cells were cotransfected with either FLAG-ARNO or HA-Arf6, and RLIP76 was precipitated from cell lysates with anti-RLIP76 antibodies. ARNO was present in RLIP76 precipitates and not detected in an irrelevant IgG control, whereas Arf6 was not detected in either immunoprecipitate. Images of the Arf6 and ARNO immunoblots are derived from the same exposure of one gel that was cut to remove an intervening marker lane. IP, immunoprecipitates; WCL, whole cell lysate. (E) Cells were transfected with Arf6(T27N), and peripheral membrane Rac localization was assessed in cells spread on fibronectin by immunostaining with antibodies to Rac1. Arrows point to areas of Rac enrichment in lamellipodia. GFP-positive cells are indicated by asterisks. 11% of GFP-positive cells showed peripheral membrane Rac localization in Arf6(T27N)-transfected cells, compared with 72% of GFP-positive control-transfected cells. Bar, 10 μm. (F) RLIP76 is a central component of a GTPase cascade linking Ras to Arf and Rho family GTPases. Activated R-Ras couples to RLIP76, leading to Arf6 activation, which promotes adhesion-induced GTP loading of Rac1 leading to cell spreading and migration.
We next evaluated the contribution of Arf-GEFs to RLIP76-dependent cell spreading. Transfection of ARF nucleotide-binding site opener (ARNO), which is a Sec7 domain–containing GEF for Arf6 (Chardin et al., 1996; Frank et al., 1998; Santy and Casanova, 2001), overcame the effect of siRNA knockdown of RLIP76 on cell spreading (Fig. 6 C), and this rescue could be fully reversed by expression of a dominant-negative Arf6(T27N) and partially reversed by Arf1(T31N) (Fig. 6 C). Moreover, transfection of either dominant-negative Arf1 or Arf6 alone inhibited cell spreading, indicating that sequestration of Arf-GEFs was sufficient to block cell spreading. Furthermore, Arf6(T27N) blocked lamellipodia formation and peripheral localization of Rac1 (Fig. 6 D). These two results suggested that RLIP76 might interact with an Arf-GEF; indeed, we found that RLIP76 and ARNO physically associate in vivo (Fig. 6 E). Thus, RLIP76 links R-Ras to adhesion-induced Arf6 activation with consequent enhancement of the activation of Rac1 GTPase. Therefore, RLIP76 is a critical R-Ras effector in a cascade of GTPases leading to cell spreading and migration (Fig. 6 F).
Discussion
R-Ras has pleiotropic cellular effects, enhancing cell spreading, migration, and neurite outgrowth, and inhibiting cell proliferation; frequently, R-Ras effects differ from those of closely related paralogues such as H-Ras and Rap1A (Cox et al., 1994; Kinbara et al., 2003; Oinuma et al., 2004; Self et al., 2001). We used a recently developed experimental database of Ras GTPase–interacting proteins to identify RLIP76 (RalBP1) as an effector protein for R-Ras, but not for the closely related paralogues H-Ras and Rap1. We find that RLIP76 binds directly to R-Ras in a GTP-dependent manner and that the R-Ras–binding site is distinct from that of Ral. Furthermore, RLIP76 is required for adhesion-mediated Rac activation and cell spreading and migration, and for the stimulation of these processes by R-Ras. Arf6 GTPase is a mediator of adhesion-induced Rac activation, and RLIP76 is needed for adhesion-induced activation of Arf6. Reconstitution of Arf6 activity by transfection with an Arf6–guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF), ARNO restored Rac activation and cell spreading in RLIP76-depleted cells. Thus, we identify a new R-Ras effector, RLIP76, which is a critical link in a cascade of three GTPases that regulates cell spreading and migration.
The proteomic strategy used in this study identified RLIP76 as a candidate R-Ras effector, and subsequent studies established that it is an authentic effector that mediates the activities of R-Ras in cell spreading. In particular, RLIP76 binding to R-Ras was direct and specific for the GTP-bound form of R-Ras. Moreover, we previously identified a switch 1 domain mutation (D64A) that perturbs R-Ras interaction with effectors such as RalGDS, Raf1, NORE1, and PI3-kinase (Oertli et al., 2000). This mutation did not block interaction with RLIP76, nor did it block the effect of R-Ras on cell spreading, thus, implicating RLIP76 as a previously proposed (Kinashi et al., 2000; Oertli et al., 2000) novel R-Ras effector. In contrast, the R-Ras(D64E) mutant was deficient in binding to RLIP76 and did not promote spreading, suggesting that the R-Ras–RLIP76 interaction involves the effector-binding region of R-Ras. Collectively, these data indicate that RLIP76 is an authentic R-Ras effector that mediates R-Ras stimulation of cell spreading; suppression of cell spreading by siRNA-induced RLIP76 depletion confirmed this conclusion.
RLIP76 binds R-Ras, but not the closely related Ras proteins H-Ras or Rap-1. This distinguishes RLIP76 from effectors such as Raf-1, RalGDS, PI3-kinase, and NORE1 that bind to multiple Ras family members (Marshall, 1996; Campbell et al., 1998; Oertli et al., 2000). Recently, Ada-Nguema et al. (2006) showed that PLCɛ interacts with activated R-Ras(G38V) better than wild-type R-Ras, although a direct interaction was not demonstrated. However, PLCɛ can also bind to other Ras isotypes through its Ras-association domain (Bunney et al., 2006). It seems likely that our success in identifying the RLIP76 interaction may be attributable to the use of prenylated R-Ras in mammalian cells. Most previous studies have used yeast two-hybrid approaches in which the Ras protein is neither posttranslationally modified nor appropriately localized (Gietz et al., 1997). The posttranslational modification and localization of Ras proteins has a critical effect on their interactions and resulting biological functions (Hancock, 2003); indeed, this principle has been experimentally demonstrated for R-Ras (Oertli et al., 2000; Hughes et al., 2001; Hansen et al., 2003). RLIP76 binds the small GTPase, RalA (Cantor et al., 1995; Jullien-Flores et al., 1995; Park and Weinberg, 1995; Matsubara et al., 1997; Lebreton et al., 2004); however, RalA is not involved in R-Ras–RLIP76–mediated cell spreading. An activated R-Ras effector loop mutant that does not bind RalGDS (G38VD64A; Oertli et al., 2000) still promoted cell spreading. In addition, the RBD of RLIP76 was not required for direct binding to R-Ras. This finding is consistent with earlier structure–function studies in which the RLIP76 RBD did not bind to Ras (Bauer et al., 1999). Indeed, the RBD is predicted to form a coiled coil, unlike the ubiquitin fold common to RBDs, suggesting that RLIP76 interacts with R-Ras through a structural mechanism that is distinct from the canonical interactions of Ras proteins with effectors (Bauer et al., 1999). The RLIP76 RBD was also not required for Rac activation or cell spreading. Thus, RLIP76 is a bona fide R-Ras–specific effector that mediates R-Ras–stimulated cell spreading.
RLIP76 promotes cell spreading by mediating adhesion-dependent activation of Rac GTPase. Specifically, adhesion-dependent spreading and Rac activation required RLIP76. Furthermore, activated Rac1(G12V) rescued the spreading defect in RLIP76-depleted cells, and RLIP76 overexpression did not restore spreading in cells expressing dominant-negative Rac1(T17N); hence, RLIP76 is upstream of adhesion-mediated Rac activation. The RhoGAP domain of RLIP76 was important in its ability to mediate adhesion-dependent Rac activation. This domain, which is similar to the GAP domains of Bcr-GAP and n-chimaerin (Jullien-Flores et al., 1995; Park and Weinberg, 1995), has been reported to act as a Rac and Cdc42 GAP in vitro (Jullien-Flores et al., 1995; Park and Weinberg, 1995; Matsubara et al., 1997). Nevertheless, our studies show that in vivo, RLIP76 is required for adhesion-induced activation of Rac, and this function is insensitive to a mutation of the arginine finger of the RhoGAP domain that is predicted to disrupt GAP activity (Bourne, 1997). Furthermore, forced targeting of RLIP76 to the plasma membrane causes extensive membrane ruffling and protrusive activity, which are Rac-dependent processes (Lebreton et al., 2004), which is consistent with a positive role in Rac activation. Thus, these data show that RLIP76 is upstream of adhesion-dependent Rac activation that leads to cell spreading.
RLIP76 mediates adhesion-dependent Rac activation and cell spreading by regulating Arf6 GTPase. Cell adhesion activated Arf6, which is a small GTPase known to participate in adhesion-mediated Rac activation (Santy and Casanova, 2001) and cell spreading. Furthermore, enforced activation of Arf GTPases by an Arf-GEF (ARNO) rescued spreading in RLIP76-depleted cells, establishing that Arf6 activation can bypass the requirement for RLIP76. ARNO activates both Arf1 and Arf6; however, only Arf6 can act at the plasma membrane to promote Rac activation (Al-Awar et al., 2000; Santy and Casanova, 2001), implicating Arf6 as the major target of ARNO in cell spreading (Santy et al., 2005). However, ARNO is an exchange factor for both Arf1 and Arf6, and we found that dominant-negative Arf6(T27N) and Arf1(T31N) both reduced the ability of ARNO to rescue spreading in RLIP76-depleted cells. Previous studies implicated Arf6 in adhesion-dependent Rac activation (Santy and Casanova, 2001; Nishiya et al., 2005), possibly because Arf6 activity is necessary for delivery of Rac to the plasma membrane (Radhakrishna et al., 1999; Al-Awar et al., 2000; Boshans et al., 2000) and Arf6 is implicated in ARNO-mediated recruitment of the Rac-GEF, DOCK180/Elmo (Santy et al., 2005). Furthermore, we found that RLIP76 interacts with ARNO in cells, suggesting a physical as well as a functional connection between RLIP76 and Arf-GEF activity. RLIP76 has been shown to mediate glutathione conjugate transport activity and to be localized to the cell surface (Yadav et al., 2004). Our results describe an additional signaling function for RLIP76 in the cytosol. Thus, Arf6 acts between RLIP76 and Rac in adhesion-mediated cell spreading; moreover, the capacity of Arf6 to regulate Rac localization and activity provides a plausible mechanism for its role in RLIP76-dependent cell spreading.
In sum, our data establish that RLIP76 is a new R-Ras effector that connects R-Ras to the activation of Arf6 and, consequently, to Rac1 leading to adhesion-dependent cell spreading and migration (Fig. 6 F). Furthermore, the multiple functions of RLIP76 may account for the pleiotropic effects of R-Ras. For example, the RLIP76-dependent activation of Rac GTPase may contribute to the ability of R-Ras to promote cell migration and neurite outgrowth, which are processes that are known to depend on Rac (Keely et al., 1999; Ivins et al., 2000; Holly et al., 2005). Also, RLIP76 mediates the adhesion-induced activation of Arf6 GTPase, which is a regulator of vesicle trafficking (Radhakrishna and Donaldson, 1997); hence, regulation of Arf6 may contribute to the ability of RLIP76 to control endocytosis (Jullien-Flores et al., 2000). Indeed, RLIP76 physically associates with the μ2 chain of AP-2, which is an adaptor whose membrane recruitment is controlled by Arf6, suggesting that these two proteins can coordinately regulate clathrin-mediated endocytosis (Jullien-Flores et al., 2000; Paleotti et al., 2005). Endocytosis of growth factor receptors can limit their ability to stimulate cell proliferation (Ceresa and Schmid, 2000); therefore, the interaction of RLIP76 with R-Ras may explain the capacity of R-Ras to limit the proliferation of endothelial and smooth muscle cells (Komatsu and Ruoslahti, 2005). R-Ras can have complex and differing effects on apoptosis, cell adhesion, and migration, depending on cellular context (Wang et al., 1995; Zhang et al., 1996; Keely et al., 1999; Ohba et al., 2001; Kinbara et al., 2003; Kwong et al., 2003; Holly et al., 2005; Wozniak et al., 2005). The capacity of R-Ras to interact with RLIP76, and thereby regulate Arf6, links R-Ras to the regulation of vesicle trafficking and helps to explain its wide-ranging effects on cell growth, apoptosis, cell adhesion, and cell migration.
Materials and methods
Antibodies and reagents
Monoclonal anti-Rac1 antibody (23A8) was obtained from Millipore. Goat anti–human RalBP1 (RLIP76), rabbit anti–R-Ras, goat anti-MLCKsk, mouse monoclonal anti-Arf6, and rabbit H-15 anti–His tag antibodies were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. Monoclonal anti-HA antibody was obtained from Covance. Restriction endonucleases were obtained from New England Biolabs.
Cell lines and transfections
NIH 3T3 cells (American Type Culture Collection) were maintained in DME (Cellgro) supplemented with 10% FBS, 2 mM l-glutamine, 50 U/ml penicillin, 50 μg/ml streptomycin sulfate, and 1% nonessential amino acids (Sigma-Aldrich) at 37°C in 5% CO2. Cells were transfected with plasmids using Lipofectamine reagent (Invitrogen) following the manufacturer's instructions. Cells were analyzed 48 h after transfection. For cotransfection with siRNA after plasmid transfection, the medium was changed to complete DME without antibiotics after plasmid transfection and the cells were cultured for 24 h. Cells were subsequently transfected with siRNA as described below and cultured for an additional 24 h before analysis. For siRNA-mediated RLIP76 knockdown, complementary single-strand RNAs (GUAGAGAGGACCAUGAUGdTdT and ACAUCAUGGUCCUCUCUACdTdT) targeting human and mouse RLIP76 were purchased from Invitrogen and dissolved in TE (10 mM Tris-Cl, pH 7.5, 0.1 mM EDTA). Sequence-scrambled complementary single-strand RNAs were also obtained (GAAGAAGAUCGUCAGUGGdTdT and CCACUGACGAUCUUCUUCdTdT). Double-stranded RNA was generated by annealing the RNAs in annealing buffer (100 mM KOAc, 30 mM Hepes-KOH, pH 7.4, and 2 mM MgOAc). Formation of double-stranded RNA was confirmed by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. For siRNA-mediated knockdown of RLIP76, 3T3 cells were maintained overnight in complete DME with 10% FBS, but without antibiotics. Cells were transfected with Lipofectamine 2000 in Opti-MEM (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Cells were analyzed 24 h after transfection.
Complementary DNAs
pEGFP-C1 was obtained from CLONTECH Laboratories, Inc. pEGFP-C1-Rac1 WT was a gift from M. del Pozo (Fundación Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares, Madrid, Spain). N-terminal TAP-tag fusions of human Ras isotype variants were made by subcloning human cDNAs of R-Ras, H-Ras, and Rap1A containing the indicated mutations (Oertli et al., 2000) into the N-terminal TAP vector (a gift from B. Séraphin, European Molecular Biology Laboratory, Heidelberg, Germany) using BamH1–Xba1 sites. J. Han provided the nTAP-H-Ras and –Rap1A plasmids. The human RLIP76 cDNA was obtained from the American Type Culture Collection. An oligodeoxyribonucleotide encoding a 5′ influenza HA tag joined to six bases from the 5′ end and another oligodeoxyribonucleotide complementary to the 3′ end of RLIP76 (5′-RLIP76: 5′-GGAGATATCGGCGTCATGTACCCATACGATGTTCCAGATTACGCTCTCGAGATGACTTGCTTCCTGCCCCCCACCAGC-3′ and 3′-RLIP76: 5′-CGCAACCTTGCTCAGATGGACGTCTCCTTCCTATCCCTGCTGGG-3′) were obtained from GenBase. The oligodeoxyribonucleotides were used in a PCR reaction to amplify HA-tagged RLIP76 from the RLIP76 cDNA. The PCR product was sequenced and cloned into pcDNA3.1(−) (Invitrogen) using EcoRV and HindIII sites. HA-tagged RLIP76 truncation and deletion plasmids were generated by PCR from the HA-RLIP761/pcDNA3.1(−) template using the following primer sets: ΔRBD (truncated at amino acid 392): 5′-RLIP76 and 5′-GGCTGATGGATCCTTGATGCCCGCCTAGGTCTCTGGCAGCGTGGG-3′; and ΔGAP-n (truncated at amino acid 292): 5′-RLIP76 and 5′-CGCAAGCTTTTACTGCTTCAGCAAACTGGA-3′. HA-RLIP76/3.1(−) mismatch construct was produced by QuikChange mutagenesis (Stratagene) according to the manufacturer's instructions, using the primers: 5′-GGCTGATGCAGTCGAAGAACTATGATGTATGATGGCATTCGGCTGCCAGCC-3′ and 5′-CCTTAAGGAAACCGACTACGTCAGCTTTCTTGATACTACATACTACCGTAAGCC-3′. HA-RLIP76-RD/3.1(−) Arg232Asp mutant was also produced by QuikChange mutagenesis, using the primers: 5′-GGCATGAAGTGTGAAGGCATCTACGACGTATCAGGAATTAAATCAAAG-3′ and 5′-CCTTGATTTAATTCCTGATACGTCGTAGATGCCTTCACACTTCATGCC-3′. 6-His-tagged RLIP76 constructs were made by Xba1–HindIII digestion of the appropriate constructs in pcDNA3.1(−) and ligation into Xba1–HindIII–digested pRSET(A) vector (Invitrogen). The GST–R-Ras(wt) plasmid was as previously described (Oertli et al., 2000). HA-tagged Arf expression constructs were a gift from J. Casanova (University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA).
TAP of R-Ras protein complexes and identification of binding proteins
TAP of TAP–R-Ras protein complexes was performed as described at the National Cell Migration Consortium website (http://demo.cellmigration.org/resource/discovery/ginsberg_tap_appr.shtml).
Solution-based digestion: The TAP-purified protein samples were treated with 10 μl of 200 mM CaCl2 and 20 μl of 100 mM ammonium bicarbonate. Reduction of the disulfide bonds in the proteins was accomplished by treatment of the samples with 1 μl DTT (20 mM final) for 1 h at 52°C, followed by carboxyamidation by treatment with 1 μl iodoacetamide (40 mM final) for 1 h at RT in the dark. Proteolytic digestion of the reduced and alkylated sample was conducted by addition of 1 μl of modified trypsin (0.5 μg; Promega) and incubating the mixture at 37°C for 9 h. The digestion was quenched by acidification with 2 μl of glacial acetic acid and frozen at −35°C until further analysis.
Analysis by mass spectrometry: For the identification of interacting proteins, the digested samples were loaded onto a C18 column. Peptides were analyzed by nanoflow reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography microelectrospray tandem mass spectrometry (RP-HPLC/μESI/MS/MS) interfaced with a Finnigan LCQ ion trap mass spectrometer (Thermo Electron Corp.). Peptides were gradient-eluted using a linear gradient of 0–60% B in 120 min (A, 0.1 M acetic acid in NANOpure water; B, 70% acetonitrile in 0.1 M acetic acid). The LTQ spectrometer was operated in a data-dependent top 10 MS/MS mode. The data was then searched against a human, rat, and mouse GenBank protein database compiled by National Center for Biotechnology Information (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Sitemap/ResourceGuide.html#FTPSite), using the SEQUEST search algorithm (version 27; Link et al., 1999). Peptide sequence assignments were verified by manual interpretation of MS/MS spectra.
Recombinant proteins
To produce 6-His-tagged RLIP76 proteins and GST–R-Ras(wt), 1 mM IPTG was added to a suspension containing BL21/pLys(s)-DE3 (Stratagene) bacteria (OD = 0.5) bearing the appropriate plasmid, and the bacteria were incubated with continuous shaking at 37°C for 4 h. Bacteria were lysed by sonication in lysis buffer (GST–R-Ras: 20 mM Tris-Cl, pH 7.0, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 1% Triton X-100, 1 mM DTT, 5 mg/ml lysozyme, and protease inhibitors; His-tagged proteins: 20 mM Tris-Cl, pH 7.9, 5 mM imidazole, 500 mM NaCl, 0.1% NP-40, 5 mg/ml lysozyme, and protease inhibitors) and centrifuged at 39,000 g for 20 min, and the soluble proteins were purified on Ni2+-coupled Sepharose (His-tagged proteins; Novagen) or GSH-Sepharose (R-Ras; Roche), according to the manufacturer's instructions. GST-PBD protein was generated and purified as in del Pozo et al. (2000). GST-GGA3VHS-GAT was generated and purified as in Santy and Casanova (2001).
Cell-spreading assays and microscopy
Glass coverslips were incubated with 5 μg/ml plasma fibronectin in 0.1 M NaHCO3 at 4°C overnight; after washing, the coverslips were incubated for 30 min with 1% BSA/PBS that had been heat inactivated by incubation at 80°C for 30 min to block unreacted sites. Cells were detached with 0.1% trypsin and kept in suspension for 1 h at RT in DME containing 0.2% BSA, and then plated on the coated coverslips for 45 min at 37°C. Nonadherent cells were removed by washing two times with PBS, and the adherent cells were fixed in 3.7% formaldehyde/PBS for 20 min at RT. Fixed cells were washed and permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100/PBS for 5 min, washed with PBS, and incubated with 5 μg/ml rhodamine-phalloidin (Invitrogen) in PBS at 37°C for 1 h. Coverslips were washed and mounted on slides with ProLong Gold antifade reagent (Invitrogen) and imaged on an epifluorescence microscope (DMLS; Leica) fitted with a SPOT charge-coupled device camera (Diagnostic Instruments). The area of GFP-positive cells was measured using ImageJ software (National Institutes of Health).
Migration assays
Cells were transfected and plated on fibronectin-coated dishes as described in the previous section. 48 h after transfection, cell monolayers were scratched with a pipette tip. Cells were maintained in complete medium at 37°C in 6% CO2, and images were taken at 30 min intervals for 4 h. Cell centroid movements of GFP-positive cells were tracked in successive images using ImageJ software.
Rac activation assays
Adhesion-dependent Rac activation was measured following the method of del Pozo et al. (2000). Cells were transfected as indicated, and cultured in MEM/0.2% FBS overnight. Cells were detached and maintained in suspension for 1 h at RT. The cells were plated on prewarmed, fibronectin-coated dishes, incubated at 37°C with 6% CO2 for the indicated times, rinsed briefly with ice-cold PBS, and scraped into Rac assay lysis buffer (50 mM Tris-Cl, pH 7.0, 0.5% NP-40, 500 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA, 100 mM Na3VO4, and protease inhibitors) containing 5 μg/ sample GST-PBD protein. Cell lysates were cleared of insoluble material by centrifugation and incubated with GSH–Sepharose for 30 min. The Sepharose beads were pelleted, washed three times with ice-cold lysis buffer (without GST-PBD), and resuspended in SDS gel-loading buffer. Bead-bound proteins were extracted by boiling, and the protein samples were separated by SDS-PAGE. Proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose membrane, and Rac was detected by Western blotting with 23A8 anti-Rac antibody (Millipore).
Arf6 activation assays
Cells were detached and kept in suspension for 1 h in serum-free DME containing 0.2% BSA. Cells were then plated on dishes coated with 5 μg/ml fibronectin. After 5 min, cells were lysed and GTP-bound Arf6 was assayed by its binding to a GST-fusion protein containing the VHS domain to the GAT region of an Arf effector, GGA3 (Golgi-localized, γ-ear-containing Arf-binding protein 3; GST-GGA3VHS-GAT; Dell'Angelica et al., 2000), as previously described (Santy and Casanova, 2001).
Immunoprecipitation and in vitro binding experiments
Coprecipitations: Cells were plated and transfected as in Cell lines and transfections, and maintained in complete DME. After 48 h, cell lysates were harvested by scraping in TEV protease cell lysis buffer (TEVCB). Lysates were maintained at 4°C and insoluble material was removed by centrifugation at 14,000 rpm for 10 min. For coprecipitations with TAP-tagged constructs, supernatants containing soluble material were incubated with IgG-coupled Sepharose (Roche) for 1 h at 4°C. The Sepharose beads were pelleted by centrifugation and washed three times in TEVCB; then the bead-bound material was extracted in SDS buffer and separated by SDS-PAGE, followed by Western blotting with the appropriate antibodies. For coimmunoprecipitation experiments, cell lysates were precleared by incubation with protein G–Sepharose for 1 h at 4°C. Cleared lysates were incubated for an additional hour with 1 μg of the appropriate antibody, followed by antibody capture on protein G–Sepharose beads for 1 h. Antibody-bound complexes were precipitated by centrifugation, washed, and separated by SDS-PAGE, followed by Western blotting with relevant antibodies.
In vitro binding assays: GST–R-Ras was bound to glutathione–Sepharose beads (Roche) by incubation for 1 h at 4°C and coupled to GTP by an additional hour with 10 μM GTP, or kept inactive by addition of 10 mM EDTA. Recombinant RLIP76 proteins were added at 300 nM each in 1 ml of TEVCB for 1 h at 4°C. Beads were washed with buffer three times, and the bound proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and detected with anti-His or anti–R-Ras antibodies.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grants U54 GM064346 (Cell Migration Consortium), HL078784 and HL57900 (to M.H. Ginsberg), and GM37537 (to D.F. Hunt), and by American Heart Association grant SDG 0435295N (to L.E. Goldfinger).
C. Ptak's present address is Advion BioSciences, Inc., Ithaca, NY 14850.
Abbreviations used in this paper: GAP, GTPase-activating protein; GEF, guanine nucleotide exchange factor; RBD, Ral- or Ras-binding domain; TAP, tandem affinity purification; TEVCB, TEV protease cell lysis buffer.
References
- Ada-Nguema, A.S., H. Xenias, M.P. Sheetz, and P.J. Keely. 2006. The small GTPase R-Ras regulates organization of actin and drives membrane protrusions through the activity of PLC{epsilon}. J. Cell Sci. 119:1307–1319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Awar, O., H. Radhakrishna, N.N. Powell, and J.G. Donaldson. 2000. Separation of membrane trafficking and actin remodeling functions of ARF6 with an effector domain mutant. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20:5998–6007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagrodia, S., S.J. Taylor, K.A. Jordon, A.L. Van, and R.A. Cerione. 1998. A novel regulator of p21-activated kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 273:23633–23636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, B., G. Mirey, I.R. Vetter, J.A. Garcia-Ranea, A. Valencia, A. Wittinghofer, J.H. Camonis, and R.H. Cool. 1999. Effector recognition by the small GTP-binding proteins Ras and Ral. J. Biol. Chem. 274:17763–17770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshans, R.L., S. Szanto, A.L. Van, and C. Souza-Schorey. 2000. ADP-ribosylation factor 6 regulates actin cytoskeleton remodeling in coordination with Rac1 and RhoA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20:3685–3694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne, H.R. 1997. G proteins. The arginine finger strikes again. Nature. 389:673–674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunney, T.D., R. Harris, N.L. Gandarillas, M.B. Josephs, S.M. Roe, S.C. Sorli, H.F. Paterson, F. Rodrigeus-Lima, D. Esposito, C.P. Ponting, et al. 2006. Structural and mechanistic insight into ras association domains of phospholipase C epsilon. Mol. Cell. 21:495–507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, S.L., R. Khosravi-Far, K.L. Rossman, G.J. Clark, and C.J. Der. 1998. Increasing complexity of Ras signaling. Oncogene. 17:1395–1413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor, S.B., T. Urano, and L.A. Feig. 1995. Identification and characterization of Ral-binding protein 1, a potential downstream target of Ral GTPases. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15:4578–4584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceresa, B.P., and S.L. Schmid. 2000. Regulation of signal transduction by endocytosis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 12:204–210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardin, P., S. Paris, B. Antonny, S. Robineau, S. Beraud-Dufour, C.L. Jackson, and M. Chabre. 1996. A human exchange factor for ARF contains Sec7- and pleckstrin-homology domains. Nature. 384:481–484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox, A.D., T.R. Brtva, D.G. Lowe, and C.J. Der. 1994. R-Ras induces malignant, but not morphologic, transformation of NIH3T3 cells. Oncogene. 9:3281–3288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Pozo, M.A., L.S. Price, N.B. Alderson, X.D. Ren, and M.A. Schwartz. 2000. Adhesion to the extracellular matrix regulates the coupling of the small GTPase Rac to its effector PAK. EMBO J. 19:2008–2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dell'Angelica, E.C., R. Puertollano, C. Mullins, R.C. Aguilar, J.D. Vargas, L.M. Hartnell, and J.S. Bonifacino. 2000. GGAs: a family of ADP ribosylation factor–binding proteins related to adaptors and associated with the Golgi complex. J. Cell Biol. 149:81–94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etienne-Manneville, S., and A. Hall. 2002. Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature. 420:629–635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank, S., S. Upender, S.H. Hansen, and J.E. Casanova. 1998. ARNO is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for ADP-ribosylation factor 6. J. Biol. Chem. 273:23–27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz, R.D., B. Triggs-Raine, A. Robbins, K.C. Graham, and R.A. Woods. 1997. Identification of proteins that interact with a protein of interest: applications of the yeast two-hybrid system. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 172:67–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall, A. 1998. Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton. Science. 23:509–514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock, J.F. 2003. Ras proteins: different signals from different locations. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4:373–384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, M., I.A. Prior, P.E. Hughes, B. Oertli, F.L. Chou, B.M. Willumsen, J.F. Hancock, and M.H. Ginsberg. 2003. C-terminal sequences in R-Ras are involved in integrin regulation and in plasma membrane microdomain distribution. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 311:829–838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holly, S.P., M.K. Larson, and L.V. Parise. 2005. The unique N-terminus of R-ras is required for Rac activation and precise regulation of cell migration. Mol. Biol. Cell. 16:2458–2469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz, R., and D. Webb. 2003. Cell migration. Curr. Biol. 13:R756–R759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, P.E., M.W. Renshaw, M. Pfaff, J. Forsyth, V.M. Keivens, M.A. Schwartz, and M.H. Ginsberg. 1997. Suppression of integrin activation: a novel function of a Ras/Raf-initiated MAP kinase pathway. Cell. 88:521–530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, P.E., B. Oertli, J. Han, and M.H. Ginsberg. 2001. R-Ras regulation of integrin function. Methods Enzymol. 333:163–171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivins, J.K., P.D. Yurchenco, and A.D. Lander. 2000. Regulation of neurite outgrowth by integrin activation. J. Neurosci. 20:6551–6560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jullien-Flores, V., O. Dorseuil, F. Romero, F. Letourneur, S. Saragosti, R. Berger, A. Tavitian, G. Gacon, and J.H. Camonis. 1995. Bridging Ral GTPase to Rho pathways. RLIP76, a Ral effector with CDC42/Rac GTPase-activating protein activity. J. Biol. Chem. 270:22473–22477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jullien-Flores, V., Y. Mahe, G. Mirey, C. Leprince, B. Meunier-Bisceuil, A. Sorkin, and J.H. Camonis. 2000. RLIP76, an effector of the GTPase Ral, interacts with the AP2 complex: involvement of the Ral pathway in receptor endocytosis. J. Cell Sci. 113(Pt 16):2837–2844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keely, P.J., E.V. Rusyn, A.D. Cox, and L.V. Parise. 1999. R-Ras signals through specific integrin α cytoplasmic domains to promote migration and invasion of breast epithelial cells. J. Cell Biol. 145:1077–1088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinashi, T., K. Katagiri, S. Watanabe, B. Vanhaesebroeck, J. Downward, and K. Takatsu. 2000. Distinct mechanisms of alpha 5beta 1 integrin activation by Ha-Ras and R-Ras. J. Biol. Chem. 275:22590–22596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinbara, K., L.E. Goldfinger, M. Hansen, F.L. Chou, and M.H. Ginsberg. 2003. Ras GTPases: integrins' friends or foes? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4:767–776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu, M., and E. Ruoslahti. 2005. R-Ras is a global regulator of vascular regeneration that suppresses intimal hyperplasia and tumor angiogenesis. Nat. Med. 11:1346–1350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraynov, V.S., C. Chamberlain, G.M. Bokoch, M.A. Schwartz, S. Slabaugh, and K.M. Hahn. 2000. Localized Rac activation dynamics visualized in living cells. Science. 290:333–337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa, K., R.E. Itoh, H. Yoshizaki, Y.O. Nakamura, and M. Matsuda. 2004. Coactivation of Rac1 and Cdc42 at lamellipodia and membrane ruffles induced by epidermal growth factor. Mol. Biol. Cell. 15:1003–1010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwong, L., M.A. Wozniak, A.S. Collins, S.D. Wilson, and P.J. Keely. 2003. R-Ras promotes focal adhesion formation through focal adhesion kinase and p130(Cas) by a novel mechanism that differs from integrins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23:933–949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebreton, S., L. Boissel, N. Iouzalen, and J. Moreau. 2004. RLIP mediates downstream signalling from RalB to the actin cytoskeleton during Xenopus early development. Mech. Dev. 121:1481–1494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link, A.J., J. Eng, D.M. Schieltz, E. Carmack, G.J. Mize, D.R. Morris, B.M. Garvik, and J.R. Yates III. 1999. Direct analysis of protein complexes using mass spectrometry. Nat. Biotechnol. 17:676–682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D.G., D.J. Capon, E. Delwart, A.Y. Sakaguchi, S.L. Naylor, and D.V. Goeddel. 1987. Structure of the human and murine R-ras genes, novel genes closely related to ras proto-oncogenes. Cell. 48:137–146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, C.J. 1996. Ras effectors. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 8:197–204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara, K., T. Hinoi, S. Koyama, and A. Kikuchi. 1997. The post-translational modifications of Ral and Rac1 are important for the action of Ral-binding protein 1, a putative effector protein of Ral. FEBS Lett. 410:169–174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiya, N., W.B. Kiosses, J. Han, and M.H. Ginsberg. 2005. An alpha4 integrin-paxillin-Arf-GAP complex restricts Rac activation to the leading edge of migrating cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 7:343–352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oertli, B., J. Han, B.M. Marte, T. Sethi, J. Downward, M. Ginsberg, and P.E. Hughes. 2000. The effector loop and prenylation site of R-Ras are involved in the regulation of integrin function. Oncogene. 19:4961–4969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohba, Y., K. Ikuta, A. Ogura, J. Matsuda, N. Mochizuki, K. Nagashima, K. Kurokawa, B.J. Mayer, K. Maki, J. Miyazaki, and M. Matsuda. 2001. Requirement for C3G-dependent Rap1 activation for cell adhesion and embryogenesis. EMBO J. 20:3333–3341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oinuma, I., Y. Ishikawa, H. Katoh, and M. Negishi. 2004. The Semaphorin 4D receptor Plexin-B1 is a GTPase activating protein for R-Ras. Science. 305:862–865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paleotti, O., E. Macia, F. Luton, S. Klein, M. Partisani, P. Chardin, T. Kirchhausen, and M. Franco. 2005. The small G-protein Arf6GTP recruits the AP-2 adaptor complex to membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 280:21661–21666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.H., and R.A. Weinberg. 1995. A putative effector of Ral has homology to Rho/Rac GTPase activating proteins. Oncogene. 11:2349–2355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard, T.D., and G.G. Borisy. 2003. Cellular motility driven by assembly and disassembly of actin filaments. Cell. 112:453–465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puig, O., F. Caspary, G. Rigaut, B. Rutz, E. Bouveret, E. Bragado-Nilsson, M. Wilm, and B. Seraphin. 2001. The tandem affinity purification (TAP) method: a general procedure of protein complex purification. Methods. 24:218–229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radhakrishna, H., and J.G. Donaldson. 1997. ADP-ribosylation factor 6 regulates a novel plasma membrane recycling pathway. J. Cell Biol. 139:49–61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radhakrishna, H., O. Al-Awar, Z. Khachikian, and J.G. Donaldson. 1999. ARF6 requirement for Rac ruffling suggests a role for membrane trafficking in cortical actin rearrangements. J. Cell Sci. 112(Pt 6):855–866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley, A.J., M.A. Schwartz, K. Burridge, R.A. Firtel, M.H. Ginsberg, G. Borisy, J.T. Parsons, and A.R. Horwitz. 2003. Cell migration: integrating signals from front to back. Science. 302:1704–1709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigaut, G., A. Shevchenko, B. Rutz, M. Wilm, M. Mann, and B. Seraphin. 1999. A generic protein purification method for protein complex characterization and proteome exploration. Nat. Biotechnol. 17:1030–1032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosse, C., S. L'Hoste, N. Offner, A. Picard, and J. Camonis. 2003. RLIP, an effector of the Ral GTPases, is a platform for Cdk1 to phosphorylate epsin during the switch off of endocytosis in mitosis. J. Biol. Chem. 278:30597–30604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santy, L.C., and J.E. Casanova. 2001. Activation of ARF6 by ARNO stimulates epithelial cell migration through downstream activation of both Rac1 and phospholipase D. J. Cell Biol. 154:599–610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santy, L.C., K.S. Ravichandran, and J.E. Casanova. 2005. The DOCK180/Elmo complex couples ARNO-mediated Arf6 activation to the downstream activation of Rac1. Curr. Biol. 15:1749–1754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Self, A.J., H.F. Paterson, and A. Hall. 1993. Different structural organization of Ras and Rho effector domains. Oncogene. 8:655–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Self, A.J., E. Caron, H.F. Paterson, and A. Hall. 2001. Analysis of R-Ras signalling pathways. J. Cell Sci. 114:1357–1366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi, T., M.H. Ginsberg, J. Downward, and P.E. Hughes. 1999. The small GTP-binding protein R-Ras can influence integrin activation by antagonizing a Ras/Raf initiated integrin suppression pathway. Mol. Biol. Cell. 10:1799–1809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn, M.B. 1996. The war on cancer. Lancet. 347:1377–1381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.G., J.A. Millan, A.D. Cox, C.J. Der, U.R. Rapp, T. Beck, H. Zha, and J.C. Reed. 1995. R-Ras promotes apoptosis caused by growth factor deprivation via a Bcl-2 suppressible mechanism. J. Cell Biol. 129:1103–1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozniak, M.A., L. Kwong, D. Chodniewicz, R.L. Klemke, and P.J. Keely. 2005. R-Ras controls membrane protrusion and cell migration through the spatial regulation of Rac and Rho. Mol. Biol. Cell. 16:84–96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, S., S.S. Singhal, J. Singhal, D. Wickramarachchi, E. Knutson, T.B. Albrecht, Y.C. Awasthi, and S. Awasthi. 2004. Identification of membrane-anchoring domains of RLIP76 using deletion mutant analyses. Biochemistry. 43:16243–16253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z., K. Vuori, H.-G. Wang, J.C. Reed, and E. Ruosiahti. 1996. Integrin activation by R-ras. Cell. 85:61–69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]