Abstract
A monospecific antibody recognizing two membrane proteins in Acholeplasma laidlawii identified a plasmid clone from a genomic library. The nucleotide sequence of the 4.6-kbp insert contained four sequential genes coding for proteins of 39 kDa (E1 alpha, N terminus not cloned), 36 kDa (E1 beta), 57 kDa (E2), and 36 kDa (E3; C terminus not cloned). The N termini of the cloned E2, E1 beta, and native A. laidlawii E2 proteins were verified by amino acid sequencing. Computer-aided searches showed that the translated DNA sequences were homologous to the four subenzymes of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes from gram-positive bacteria and humans. The plasmid-encoded 57-kDa (E2) protein was recognized by antibodies against the E2 subenzymes of the pyruvate and oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complexes from Bacillus subtilis. A substantial fraction of the E2 protein as well as part of the pyruvate dehydrogenase enzymatic activity was associated with the cytoplasmic membrane in A. laidlawii. In vivo complementation with three different Escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenase-defective mutants showed that the four plasmid-encoded proteins were able to restore pyruvate dehydrogenase enzyme activity in E. coli. Since A. laidlawii lacks oxoglutarate dehydrogenase and most likely branched-chain dehydrogenase enzyme complex activities, these results strongly suggest that the sequenced genes code for the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.
Full text
PDF

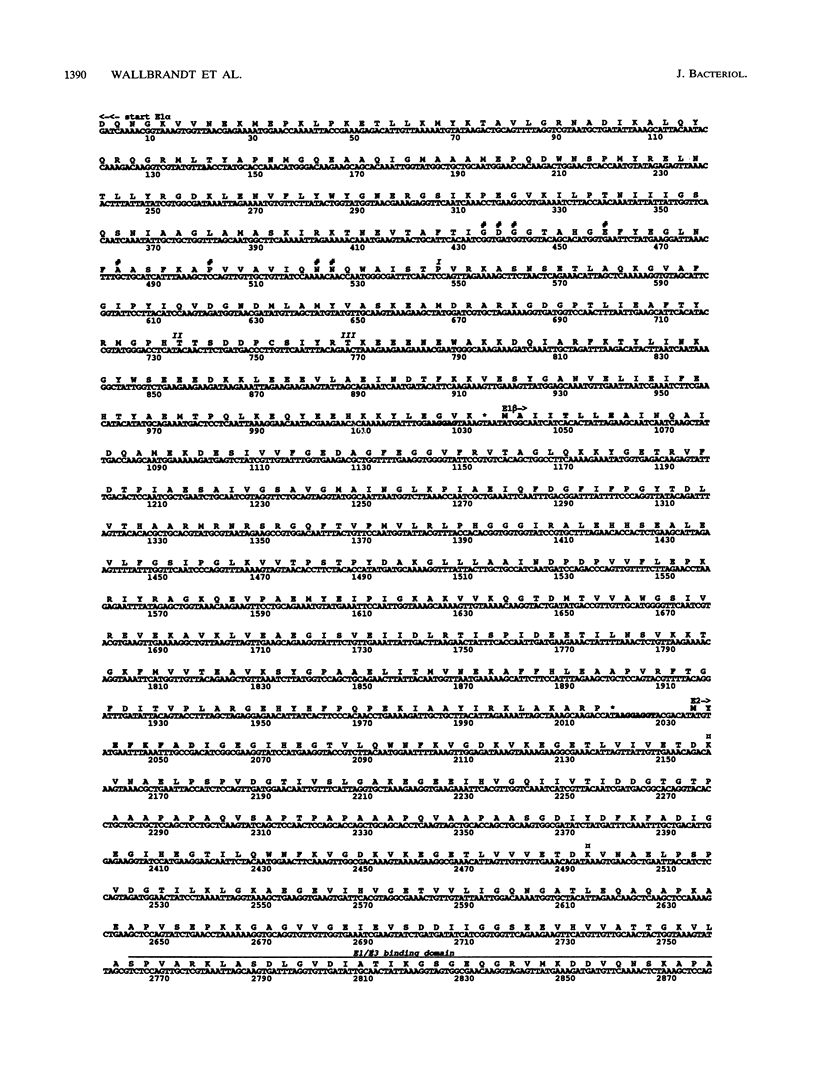

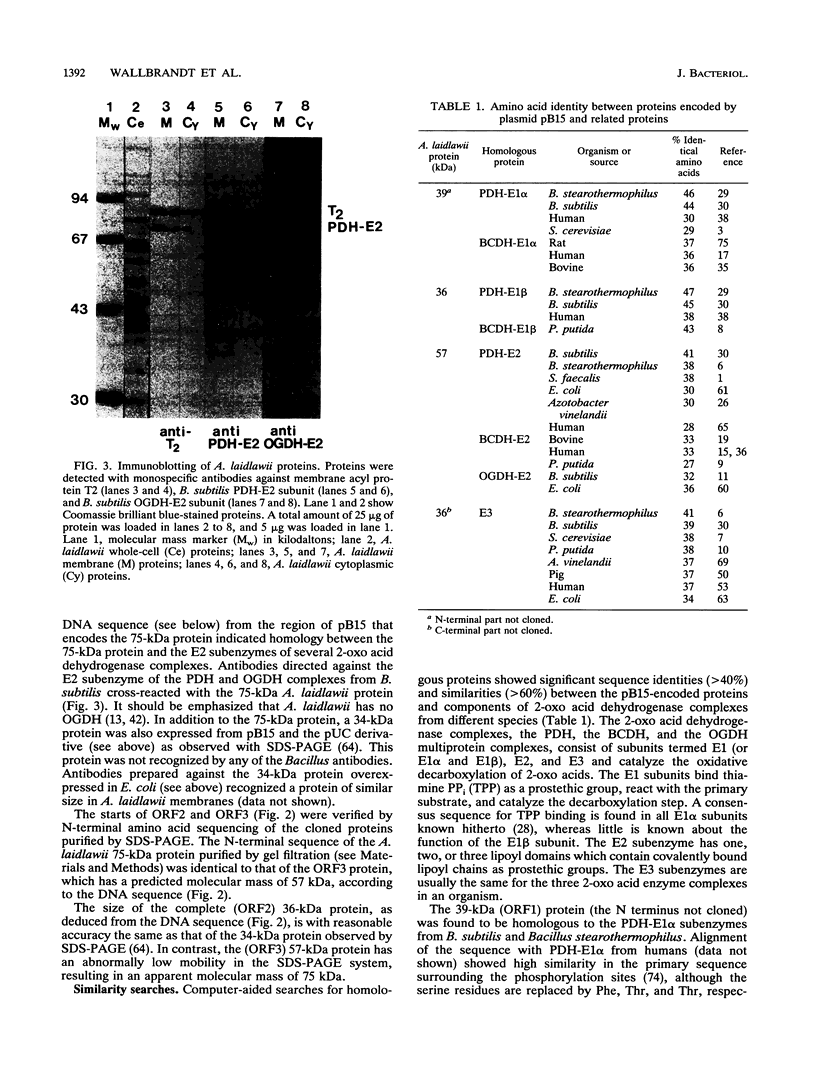




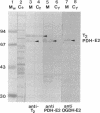
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen A. G., Perham R. N. Two lipoyl domains in the dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase chain of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Streptococcus faecalis. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 5;287(1-2):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behal R. H., Browning K. S., Reed L. J. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequence of the alpha subunit of yeast pyruvate dehydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Oct 31;164(2):941–946. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91549-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisswanger H., Henning U. A new dihydrolipoamide transacetylase in Escherichia coli K12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 15;321(1):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borges A., Hawkins C. F., Packman L. C., Perham R. N. Cloning and sequence analysis of the genes encoding the dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase and dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase components of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Bacillus stearothermophilus. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 26;194(1):95–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19432.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning K. S., Uhlinger D. J., Reed L. J. Nucleotide sequence for yeast dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1831–1834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns G., Brown T., Hatter K., Idriss J. M., Sokatch J. R. Similarity of the E1 subunits of branched-chain-oxoacid dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas putida to the corresponding subunits of mammalian branched-chain-oxoacid and pyruvate dehydrogenases. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Sep 15;176(2):311–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14283.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns G., Brown T., Hatter K., Sokatch J. R. Comparison of the amino acid sequences of the transacylase components of branched chain oxoacid dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas putida, and the pyruvate and 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenases of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Sep 1;176(1):165–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14264.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns G., Brown T., Hatter K., Sokatch J. R. Sequence analysis of the lpdV gene for lipoamide dehydrogenase of branched-chain-oxoacid dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas putida. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 15;179(1):61–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson P., Hederstedt L. Genetic characterization of Bacillus subtilis odhA and odhB, encoding 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase and dihydrolipoamide transsuccinylase, respectively. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3667–3672. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3667-3672.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantopoulos G., McGarrity G. J. Activities of oxidative enzymes in mycoplasmas. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2012–2016. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2012-2016.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danner D. J., Litwer S., Herring W. J., Pruckler J. Construction and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the full-length preprotein for human branched chain acyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7742–7746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. W., Chuang J. L., Griffin T. A., Lau K. S., Cox R. P., Chuang D. T. Molecular phenotypes in cultured maple syrup urine disease cells. Complete E1 alpha cDNA sequence and mRNA and subunit contents of the human branched chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3448–3453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fussey S. P., Bassendine M. F., James O. F., Yeaman S. J. Characterisation of the reactivity of autoantibodies in primary biliary cirrhosis. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 27;246(1-2):49–53. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80251-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin T. A., Lau K. S., Chuang D. T. Characterization and conservation of the inner E2 core domain structure of branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex from bovine liver. Construction of a cDNA encoding the entire transacylase (E2b) precursor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14008–14014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest J. R., Angier S. J., Russell G. C. Structure, expression, and protein engineering of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;573:76–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb14988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest J. R., Creaghan I. T. Further studies with lipoamide dehydrogenase mutants of Escherichia coli K12. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Mar;81(1):237–245. doi: 10.1099/00221287-81-1-237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest J. R., Creaghan I. T. Gene-protein relationships of the alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes of Escherichia coli K12: isolation and characterization of lipoamide dehydrogenase mutants. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Mar;75(1):197–210. doi: 10.1099/00221287-75-1-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest J. R. Gene-protein relationships of the alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes of Escherichia coli K12: Chromosomal location of the lipoamide dehydrogenase gene. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Feb;80(2):523–532. doi: 10.1099/00221287-80-2-523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest J. R., Lewis H. M., Graham L. D., Packman L. C., Perham R. N. Genetic reconstruction and functional analysis of the repeating lipoyl domains in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1985 Oct 20;185(4):743–754. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENNING U., HERZ C. EIN STRUKTURGEN-KOMPLEX FUER DEN PYRUVAT-DEHYDROGENASE-KOMPLEX VON ESCHERICHIA COLI K 12. Z Vererbungsl. 1964 Nov 11;95:260–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanemaaijer R., Janssen A., de Kok A., Veeger C. The dihydrolipoyltransacetylase component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from Azotobacter vinelandii. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jul 1;174(4):593–599. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harr R., Fällman P., Häggström M., Wahlström L., Gustafsson P. GENEUS, a computer system for DNA and protein sequence analysis containing an information retrieval system for the EMBL data library. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):273–284. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins C. F., Borges A., Perham R. N. A common structural motif in thiamin pyrophosphate-binding enzymes. FEBS Lett. 1989 Sep 11;255(1):77–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins C. F., Borges A., Perham R. N. Cloning and sequence analysis of the genes encoding the alpha and beta subunits of the E1 component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Bacillus stearothermophilus. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jul 31;191(2):337–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemilä H., Palva A., Paulin L., Arvidson S., Palva I. Secretory S complex of Bacillus subtilis: sequence analysis and identity to pyruvate dehydrogenase. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5052–5063. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5052-5063.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi S., Marty-Mazars D., Tai P. C., Davis B. D. Localization and quantitation of proteins characteristic of the complexed membrane of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1215–1221. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1215-1221.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu C. W., Lau K. S., Griffin T. A., Chuang J. L., Fisher C. W., Cox R. P., Chuang D. T. Isolation and sequencing of a cDNA encoding the decarboxylase (E1)alpha precursor of bovine branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex. Expression of E1 alpha mRNA and subunit in maple-syrup-urine-disease and 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):9007–9014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummel K. B., Litwer S., Bradford A. P., Aitken A., Danner D. J., Yeaman S. J. Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA for branched chain acyltransferase with analysis of the deduced protein structure. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6165–6168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike K., Ohta S., Urata Y., Kagawa Y., Koike M. Cloning and sequencing of cDNAs encoding alpha and beta subunits of human pyruvate dehydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):41–45. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindblom G., Brentel I., Sjölund M., Wikander G., Wieslander A. Phase equilibria of membrane lipids from Acholeplasma laidlawii: importance of a single lipid forming nonlamellar phases. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7502–7510. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe P. N., Hodgson J. A., Perham R. N. Dual role of a single multienzyme complex in the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate and branched-chain 2-oxo acids in Bacillus subtilis. Biochem J. 1983 Oct 1;215(1):133–140. doi: 10.1042/bj2150133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manolukas J. T., Barile M. F., Chandler D. K., Pollack J. D. Presence of anaplerotic reactions and transamination, and the absence of the tricarboxylic acid cycle in mollicutes. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Mar;134(3):791–800. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-3-791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElhaney R. N. The influence of membrane lipid composition and physical properties of membrane structure and function in Acholeplasma laidlawii. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1989;17(1):1–32. doi: 10.3109/10408418909105720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGarrity G. J., Constantopoulos G., Barranger J. A. Effect of mycoplasma infection on pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activity of normal and pyruvate dehydrogenase complex-deficient fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Apr;151(2):557–562. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90403-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyström S., Johansson K. E., Wieslander A. Selective acylation of membrane proteins in Acholeplasma laidlawii. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Apr 1;156(1):85–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oba T., Andachi Y., Muto A., Osawa S. CGG: an unassigned or nonsense codon in Mycoplasma capricolum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):921–925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oku H., Kaneda T. Biosynthesis of branched-chain fatty acids in Bacillus subtilis. A decarboxylase is essential for branched-chain fatty acid synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18386–18396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otulakowski G., Robinson B. H. Isolation and sequence determination of cDNA clones for porcine and human lipoamide dehydrogenase. Homology to other disulfide oxidoreductases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17313–17318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman L. C., Hale G., Perham R. N. Repeating functional domains in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1315–1319. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01969.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack J. D., Tryon V. V., Beaman K. D. The metabolic pathways of Acholeplasma and Mycoplasma: an overview. Yale J Biol Med. 1983 Sep-Dec;56(5-6):709–716. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pons G., Raefsky-Estrin C., Carothers D. J., Pepin R. A., Javed A. A., Jesse B. W., Ganapathi M. K., Samols D., Patel M. S. Cloning and cDNA sequence of the dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase component human alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1422–1426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell G. C., Guest J. R. Sequence similarities within the family of dihydrolipoamide acyltransferases and discovery of a previously unidentified fungal enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 29;1076(2):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(91)90271-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell G. C., Williamson R. A., Guest J. R. Partial complementation of pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency by independently expressed lipoyl and catalytic domains of the dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase component. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Aug;51(3):267–271. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90408-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito Y., Silvius J. R., McElhaney N. Membrane lipid biosynthesis in Acholeplasma laidlawii B: de novo biosynthesis of saturated fatty acids by growing cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):497–504. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.497-504.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer M. E., Darlison M. G., Stephens P. E., Duckenfield I. K., Guest J. R. Nucleotide sequence of the sucB gene encoding the dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase of Escherichia coli K12 and homology with the corresponding acetyltransferase. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 1;141(2):361–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens P. E., Darlison M. G., Lewis H. M., Guest J. R. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli K12. Nucleotide sequence encoding the dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase component. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;133(3):481–489. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens P. E., Darlison M. G., Lewis H. M., Guest J. R. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli K12. Nucleotide sequence encoding the pyruvate dehydrogenase component. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):155–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens P. E., Lewis H. M., Darlison M. G., Guest J. R. Nucleotide sequence of the lipoamide dehydrogenase gene of Escherichia coli K12. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Oct 3;135(3):519–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegman V., Wallbrandt P., Nyström S., Johansson K. E., Jonsson B. H., Wieslander A. Cloning and expression of Acholeplasma laidlawii membrane acyl proteins in Escherichia coli. Isr J Med Sci. 1987 May;23(5):408–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thekkumkara T. J., Ho L., Wexler I. D., Pons G., Liu T. C., Patel M. S. Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA for the dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase component of human pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. FEBS Lett. 1988 Nov 21;240(1-2):45–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80337-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Tully J. G., Rose D. L., Petzel J. P., Oyaizu H., Yang D., Mandelco L., Sechrest J., Lawrence T. G., Van Etten J. A phylogenetic analysis of the mycoplasmas: basis for their classification. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6455–6467. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6455-6467.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westphal A. H., de Kok A. Lipoamide dehydrogenase from Azotobacter vinelandii. Molecular cloning, organization and sequence analysis of the gene. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Mar 1;172(2):299–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13887.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieslander A., Rilfors L., Lindblom G. Metabolic changes of membrane lipid composition in Acholeplasma laidlawii by hydrocarbons, alcohols, and detergents: arguments for effects on lipid packing. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7511–7517. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Maniloff J., Zablen L. B. Phylogenetic analysis of the mycoplasmas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):494–498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamao F., Muto A., Kawauchi Y., Iwami M., Iwagami S., Azumi Y., Osawa S. UGA is read as tryptophan in Mycoplasma capricolum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2306–2309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeaman S. J., Hutcheson E. T., Roche T. E., Pettit F. H., Brown J. R., Reed L. J., Watson D. C., Dixon G. H. Sites of phosphorylation on pyruvate dehydrogenase from bovine kidney and heart. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2364–2370. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang B., Kuntz M. J., Goodwin G. W., Harris R. A., Crabb D. W. Molecular cloning of a cDNA for the E1 alpha subunit of rat liver branched chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15220–15224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]