Abstract
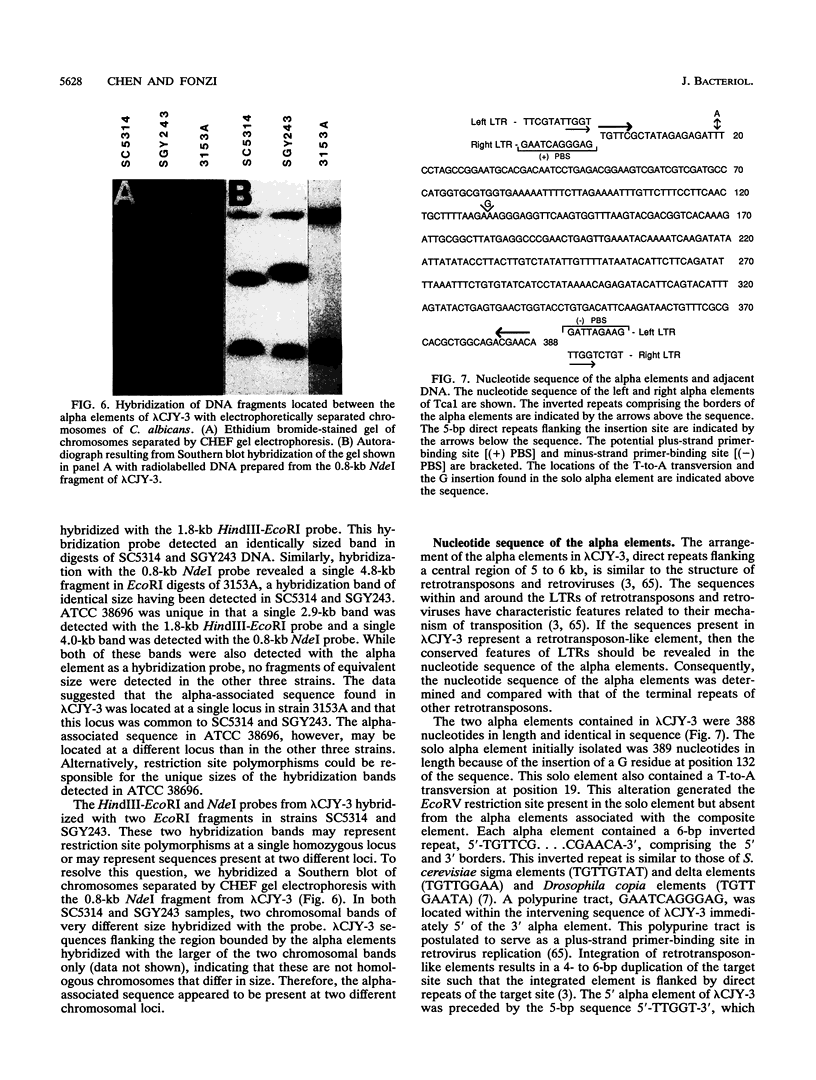
A repetitive element was isolated from the genome of Candida albicans. This repetitive element, which we designated alpha, was localized to a 500-bp fragment of genomic DNA. The alpha element was dispersed in the genome and varied in copy number and genomic location in the strains examined. Analyses of various loci containing the alpha element identified a locus containing a composite element. This composite element consisted of two direct repeats of the alpha element separated by approximately 5.5 kb of DNA, a structural arrangement similar to that of retrovirus-like transposable elements. The flanking alpha elements of the composite structure were 388 bp in length and were identical in sequence. They were bounded by the nucleotides 5'-TG. ... CA-3', which were part of a delimiting inverted repeat, a feature conserved in the long terminal repeats of retroviruses and retrovirus-like elements. As in retrovirus-like elements, the entire composite element, including the alpha elements, was transcribed into an approximately unit-length mRNA. The expression of this transcript was greatly increased when cells were grown at 25 versus 37 degrees C. As has been found in many retrotransposons, the composite element was flanked by a 5-bp duplication and varied in both copy number and genomic location in various strains. We conclude that the composite element is a retrotransposon-like element, and we have designated this element Tca1. We suggest that Tca1 may be relevant to the genomic evolution of C. albicans and the pathogenic potential of the organism.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antley P. P., Hazen K. C. Role of yeast cell growth temperature on Candida albicans virulence in mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2884–2890. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2884-2890.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedell G. W., Soll D. R. Effects of low concentrations of zinc on the growth and dimorphism of Candida albicans: evidence for zinc-resistant and -sensitive pathways for mycelium formation. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):348–354. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.348-354.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Garfinkel D. J., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Ty elements transpose through an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaleff D. T., Fink G. R. Genetic events associated with an insertion mutation in yeast. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90130-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. J., Bilanchone V. W., Haywood L. J., Dildine S. L., Sandmeyer S. B. A yeast sigma composite element, TY3, has properties of a retrotransposon. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1413–1423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curcio M. J., Hedge A. M., Boeke J. D., Garfinkel D. J. Ty RNA levels determine the spectrum of retrotransposition events that activate gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Jan;220(2):213–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00260484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. E., Glee P. M., Horn H. L. Candida albicans- and Candida stellatoidea-specific DNA fragment. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1720–1724. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1720-1724.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downs K. M., Brennan G., Liebman S. W. Deletions extending from a single Ty1 element in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3451–3457. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eibel H., Gafner J., Stotz A., Philippsen P. Characterization of the yeast mobile element Ty1. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):609–617. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder R. T., Loh E. Y., Davis R. W. RNA from the yeast transposable element Ty1 has both ends in the direct repeats, a structure similar to retrovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2432–2436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder R. T., St John T. P., Stinchcomb D. T., Davis R. W., Scherer S., Davis R. W. Studies on the transposable element Ty1 of yeast. I. RNA homologous to Ty1. II. Recombination and expression of Ty1 and adjacent sequences. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):581–591. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farabaugh P. J., Fink G. R. Insertion of the eukaryotic transposable element Ty1 creates a 5-base pair duplication. Nature. 1980 Jul 24;286(5771):352–356. doi: 10.1038/286352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghannoum M., Abu Elteen K. Correlative relationship between proteinase production, adherence and pathogenicity of various strains of Candida albicans. J Med Vet Mycol. 1986 Oct;24(5):407–413. doi: 10.1080/02681218680000621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillum A. M., Tsay E. Y., Kirsch D. R. Isolation of the Candida albicans gene for orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase by complementation of S. cerevisiae ura3 and E. coli pyrF mutations. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;198(2):179–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00328721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman J. A., Chan W., Gorman J. W. Repeated use of GAL1 for gene disruption in Candida albicans. Genetics. 1991 Sep;129(1):19–24. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen L. J., Chalker D. L., Sandmeyer S. B. Ty3, a yeast retrotransposon associated with tRNA genes, has homology to animal retroviruses. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5245–5256. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helling R. B., Goodman H. M., Boyer H. W. Analysis of endonuclease R-EcoRI fragments of DNA from lambdoid bacteriophages and other viruses by agarose-gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1235–1244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1235-1244.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Swain A., Falkow S. Analysis of expression and thermoregulation of the Yersinia pseudotuberculosis inv gene with hybrid proteins. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2133–2138. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2133-2138.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney B., Staskawicz B. J. Characterization of IS476 and its role in bacterial spot disease of tomato and pepper. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):143–148. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.143-148.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith G., Dirheimer G. Reinvestigation of the primary structure of brewer's yeast tRNA 3 Arg. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 15;92(1):116–119. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91527-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R., Miller S. M., Kurtz M. B. One-step gene disruption by cotransformation to isolate double auxotrophs in Candida albicans. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Sep;214(1):24–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00340174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Ando Y., Shiba T. Unusual priming mechanism of RNA-directed DNA synthesis in copia retrovirus-like particles of Drosophila. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):824–826. doi: 10.1038/323824a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford C. J., Gallwitz D. Evidence for an intron-contained sequence required for the splicing of yeast RNA polymerase II transcripts. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):519–527. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90433-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasker B. A., Page L. S., Lott T. J., Kobayashi G. S., Medoff G. Characterization of CARE-1: Candida albicans repetitive element-1. Gene. 1991 Jun 15;102(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90536-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. L., Buckley H. R., Campbell C. C. An amino acid liquid synthetic medium for the development of mycelial and yeast forms of Candida Albicans. Sabouraudia. 1975 Jul;13(2):148–153. doi: 10.1080/00362177585190271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman S., Shalit P., Picologlou S. Ty elements are involved in the formation of deletions in DEL1 strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1981 Nov;26(3 Pt 1):401–409. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90209-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lochmüller H., Stucka R., Feldmann H. A hot-spot for transposition of various Ty elements on chromosome V in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet. 1989 Oct;16(4):247–252. doi: 10.1007/BF00422110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOURAD S., FRIEDMAN L. Pathogenicity of Candida. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:550–556. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.550-556.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee B. B., Koltin Y., Gorman J. A., Magee P. T. Assignment of cloned genes to the seven electrophoretically separated Candida albicans chromosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4721–4726. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason M. M., Lasker B. A., Riggsby W. S. Molecular probe for identification of medically important Candida species and Torulopsis glabrata. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Mar;25(3):563–566. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.3.563-566.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattia E., Carruba G., Angiolella L., Cassone A. Induction of germ tube formation by N-acetyl-D-glucosamine in Candida albicans: uptake of inducer and germinative response. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):555–562. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.555-562.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T. Temperature regulation of virulence genes in pathogenic bacteria: a general strategy for human pathogens? Microb Pathog. 1989 Jul;7(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90106-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCourtie J., Douglas L. J. Relationship between cell surface composition, adherence, and virulence of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):6–12. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.6-12.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz W. G. Candida albicans strain delineation. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Oct;3(4):321–334. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.4.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers K. K., Fonzi W. A., Sypherd P. S. Isolation and sequence analysis of the gene for translation elongation factor 3 from Candida albicans. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1705–1710. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder G. S., Fink G. R. DNA rearrangements associated with a transposable element in yeast. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):239–249. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. Deletions of a tyrosine tRNA gene in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90306-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rustchenko-Bulgac E. P. Variations of Candida albicans electrophoretic karyotypes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(20):6586–6596. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.20.6586-6596.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadhu C., McEachern M. J., Rustchenko-Bulgac E. P., Schmid J., Soll D. R., Hicks J. B. Telomeric and dispersed repeat sequences in Candida yeasts and their use in strain identification. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):842–850. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.842-850.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Stevens D. A. A Candida albicans dispersed, repeated gene family and its epidemiologic applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1452–1456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd M. G., Poulter R. T., Sullivan P. A. Candida albicans: biology, genetics, and pathogenicity. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:579–614. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slutsky B., Buffo J., Soll D. R. High-frequency switching of colony morphology in Candida albicans. Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):666–669. doi: 10.1126/science.3901258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slutsky B., Staebell M., Anderson J., Risen L., Pfaller M., Soll D. R. "White-opaque transition": a second high-frequency switching system in Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):189–197. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.189-197.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge J. A., Blinderman L. A. ExoMeth sequencing of DNA: eliminating the need for subcloning and oligonucleotide primers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9208–9212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staib F. Proteolysis and pathogenicity of Candida albicans strains. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1969 May 28;37(4):345–348. doi: 10.1007/BF02129881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles J. I. Use of integrative transformation of yeast in the cloning of mutant genes and large segments of contiguous chromosomal sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:290–300. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stucka R., Lochmüller H., Feldmann H. Ty4, a novel low-copy number element in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: one copy is located in a cluster of Ty elements and tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):4993–5001. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.4993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundstrom P., Smith D., Sypherd P. S. Sequence analysis and expression of the two genes for elongation factor 1 alpha from the dimorphic yeast Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):2036–2045. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.2036-2045.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Arsdell S. W., Stetler G. L., Thorner J. The yeast repeated element sigma contains a hormone-inducible promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):749–759. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warmington J. R., Waring R. B., Newlon C. S., Indge K. J., Oliver S. G. Nucleotide sequence characterization of Ty 1-17, a class II transposon from yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 25;13(18):6679–6693. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.18.6679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan W. L., Magee P. T. Natural heterozygosity in Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):896–903. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.896-903.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan W. L., Soll D. R. Mitotic recombination in Candida albicans: recessive lethal alleles linked to a gene required for methionine biosynthesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;187(3):477–485. doi: 10.1007/BF00332632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]