Abstract
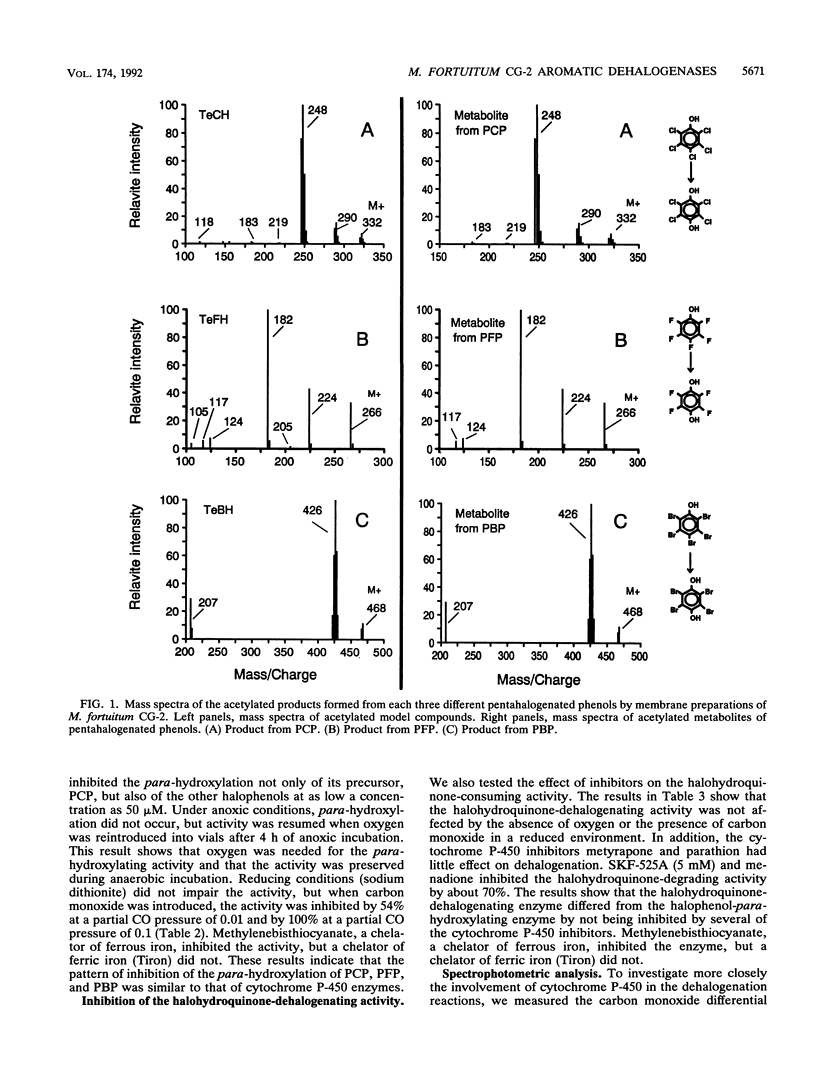
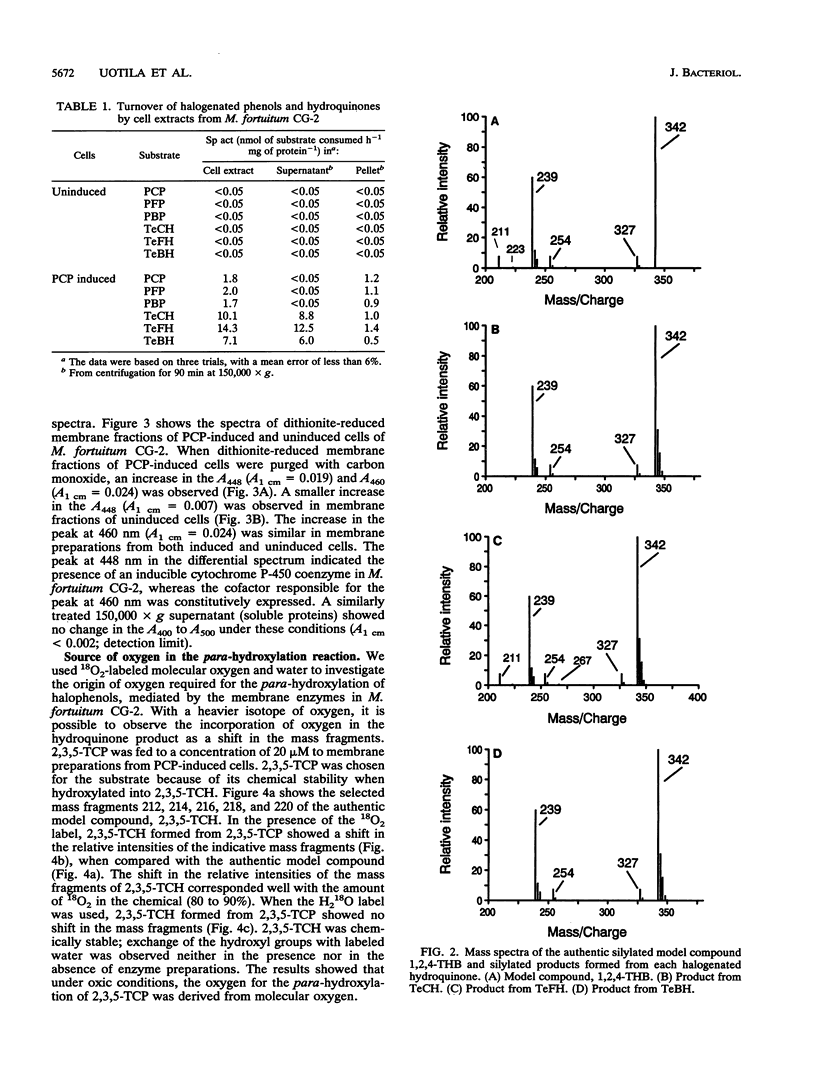
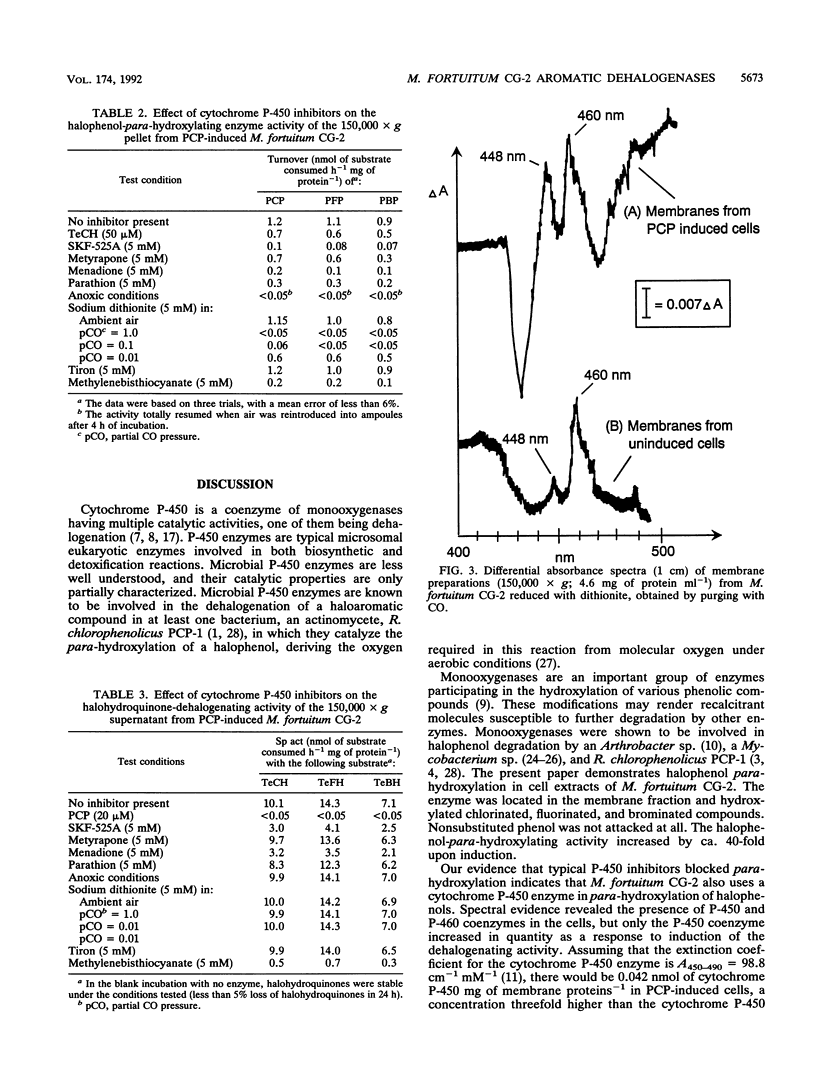
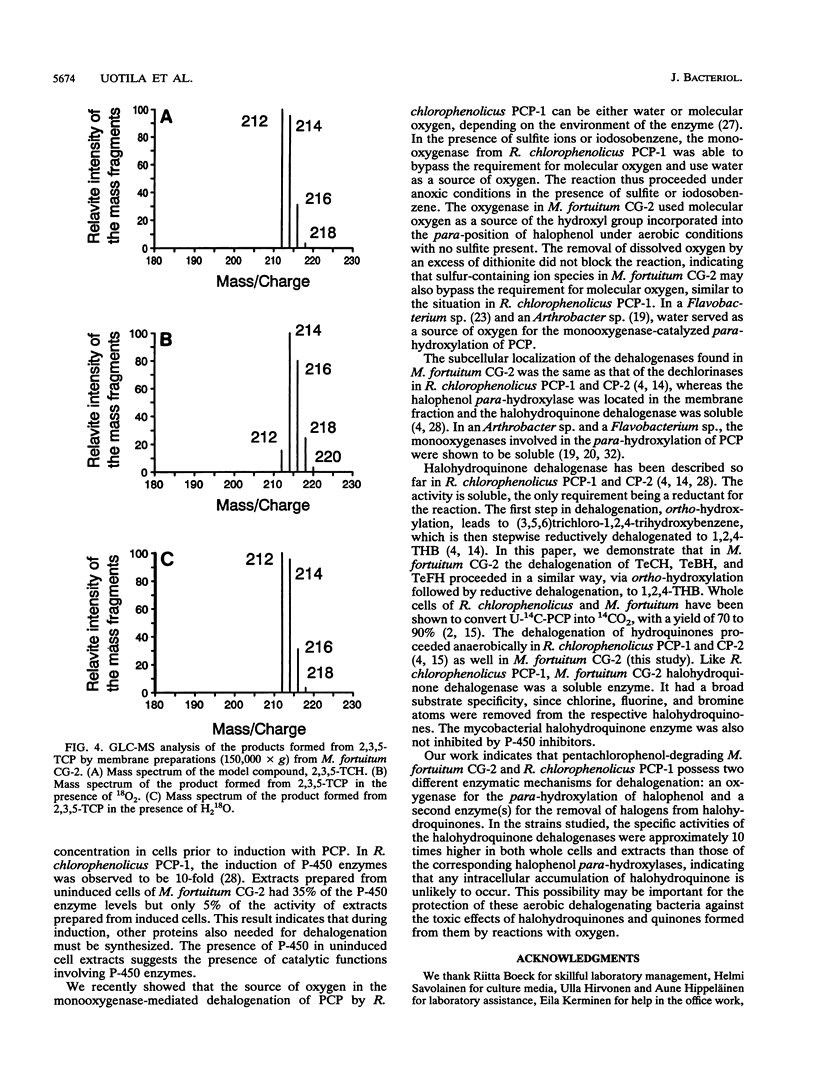
Two different dehalogenation enzymes were found in cell extracts of Mycobacterium fortuitum CG-2. The first enzyme was a halophenol para-hydroxylase, a membrane-associated monooxygenase that required molecular oxygen and catalyzed the para-hydroxylation and dehalogenation of chlorinated, fluorinated, and brominated phenols to the corresponding halogenated hydroquinones. The membrane preparation with this activity was inhibited by cytochrome P-450 inhibitors and also showed an increase in the A448 caused by CO. The second enzyme hydroxylated and reductively dehalogenated tetrahalohydroquinones to 1,2,4-trihydroxybenzene. This halohydroquinone-dehalogenating enzyme was soluble, did not require oxygen, and was not inhibited by cytochrome P-450 inhibitors.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apajalahti J. H., Salkinoja-Salonen M. S. Complete dechlorination of tetrachlorohydroquinone by cell extracts of pentachlorophenol-induced Rhodococcus chlorophenolicus. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5125–5130. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5125-5130.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apajalahti J. H., Salkinoja-Salonen M. S. Dechlorination and para-hydroxylation of polychlorinated phenols by Rhodococcus chlorophenolicus. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):675–681. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.675-681.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro C. E., Wade R. S., Belser N. O. Biodehalogenation: reactions of cytochrome P-450 with polyhalomethanes. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 1;24(1):204–210. doi: 10.1021/bi00322a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunsalus I. C., Wagner G. C. Bacterial P-450cam methylene monooxygenase components: cytochrome m, putidaredoxin, and putidaredoxin reductase. Methods Enzymol. 1978;52:166–188. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)52019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häggblom M. M., Apajalahti J. H., Salkinoja-Salonen M. S. Hydroxylation and dechlorination of chlorinated guaiacols and syringols by Rhodococcus chlorophenolicus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Mar;54(3):683–687. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.3.683-687.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häggblom M. M., Janke D., Salkinoja-Salonen M. S. Hydroxylation and Dechlorination of Tetrachlorohydroquinone by Rhodococcus sp. Strain CP-2 Cell Extracts. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Feb;55(2):516–519. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.2.516-519.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häggblom M. M., Nohynek L. J., Salkinoja-Salonen M. S. Degradation and O-methylation of chlorinated phenolic compounds by Rhodococcus and Mycobacterium strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Dec;54(12):3043–3052. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.12.3043-3052.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenk T., Müller R., Lingens F. Mechanism of enzymatic dehalogenation of pentachlorophenol by Arthrobacter sp. strain ATCC 33790. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7272–7274. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7272-7274.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenk T., Müller R., Mörsberger F., Otto M. K., Lingens F. Enzymatic dehalogenation of pentachlorophenol by extracts from Arthrobacter sp. strain ATCC 33790. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5487–5491. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5487-5491.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. E., Finnerty W. R. Construction of an Escherichia coli-Rhodococcus shuttle vector and plasmid transformation in Rhodococcus spp. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):638–645. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.638-645.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiert J. G., Crawford R. L. Catabolism of pentachlorophenol by a Flavobacterium sp. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):825–830. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uotila J. S., Salkinoja-Salonen M. S., Apajalahti J. H. Dechlorination of pentachlorophenol by membrane bound enzymes of Rhodococcus chlorophenolicus PCP-I. Biodegradation. 1991;2(1):25–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00122422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xun L., Orser C. S. Purification and properties of pentachlorophenol hydroxylase, a flavoprotein from Flavobacterium sp. strain ATCC 39723. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4447–4453. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4447-4453.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


