Abstract
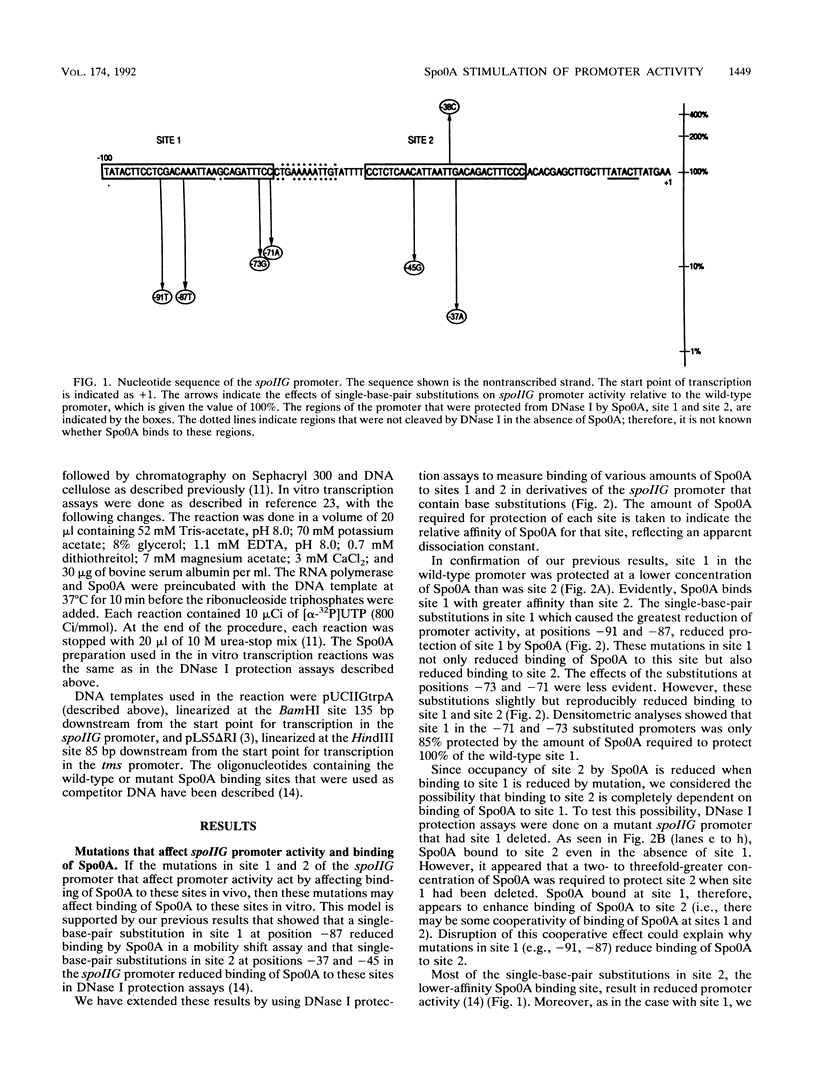
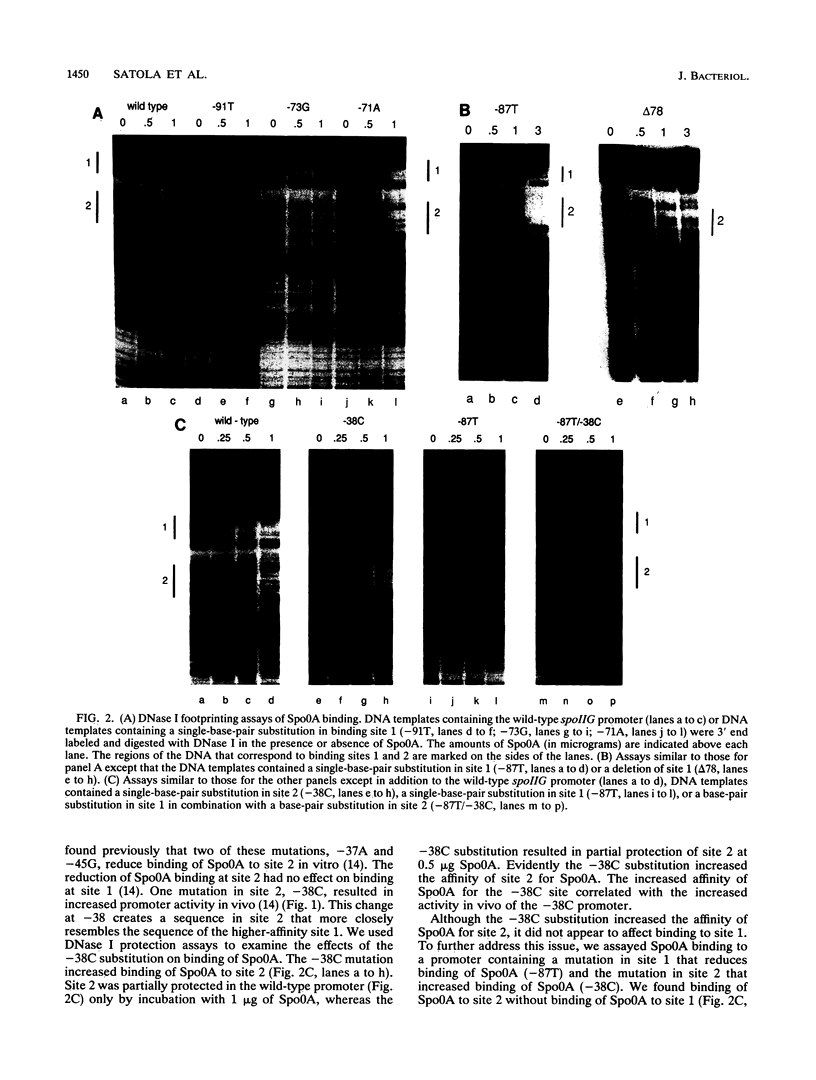
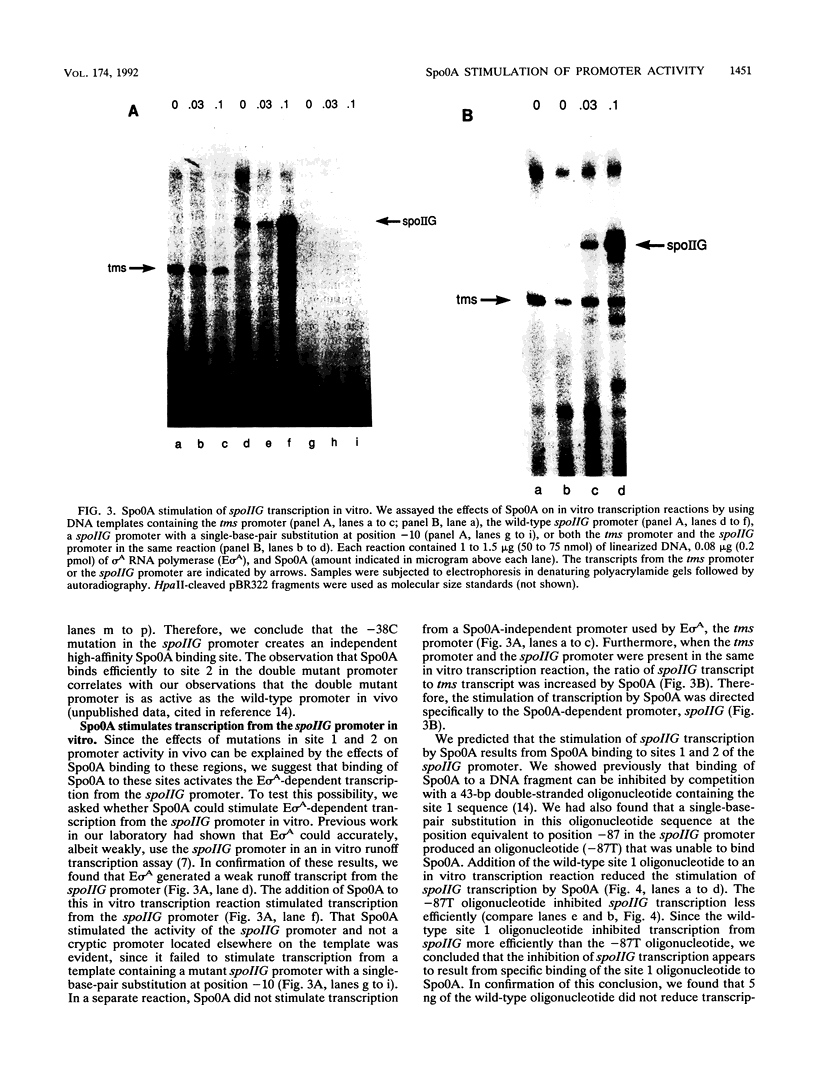
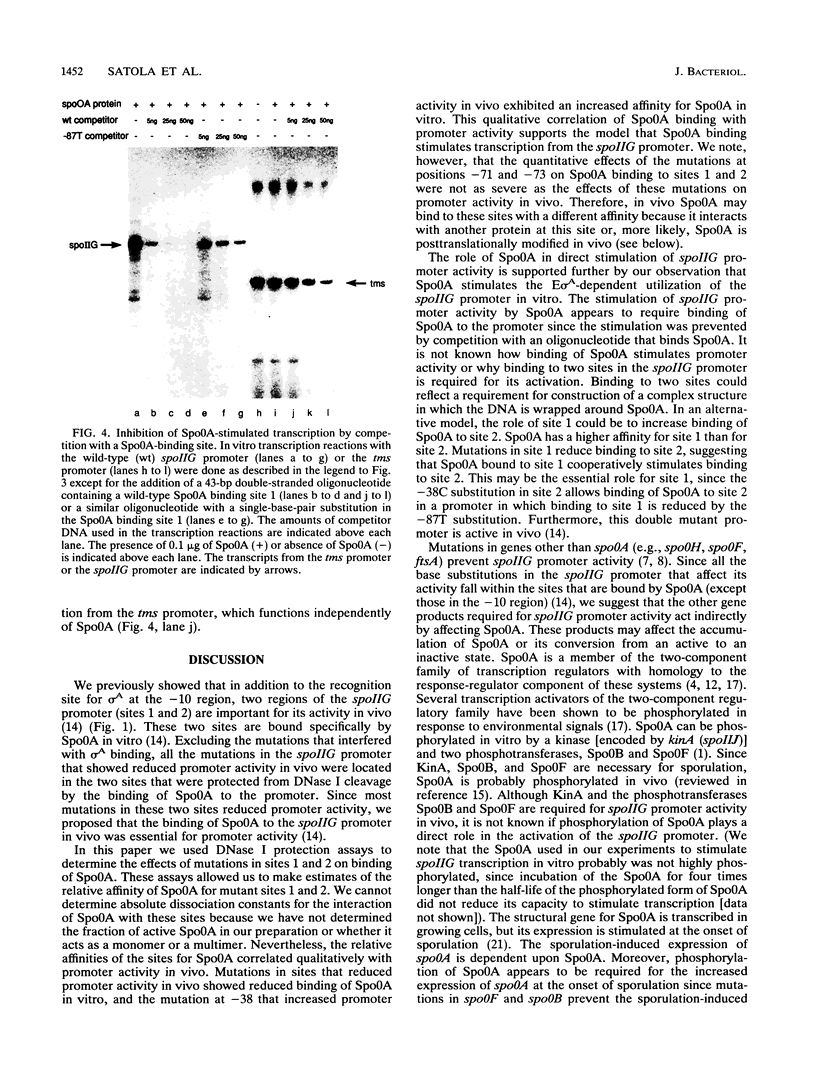
The spoIIG promoter is used by RNA polymerase containing sigma A (E sigma A), the primary form of RNA polymerase found in vegetative cells in Bacillus subtilis. However, the spoIIG promoter is active only after the onset of sporulation. Activation of the spoIIG promoter requires the product of the spo0A gene (Spo0A). Spo0A is a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein which binds to two sites in the spoIIG promoter that are essential for promoter activity. We found that single-base-pair substitutions in these two regions that reduced promoter activity in vivo caused reduced binding of Spo0A in vitro, and one substitution that increased promoter activity in vivo increased the affinity of Spo0A for this DNA in vitro. Furthermore, Spo0A stimulated transcription from the spoIIG promoter by E sigma A in vitro. These results support the model that binding of Spo0A activates E sigma A-dependent transcription from the spoIIG promoter after the onset of sporulation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burbulys D., Trach K. A., Hoch J. A. Initiation of sporulation in B. subtilis is controlled by a multicomponent phosphorelay. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):545–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90238-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie G. E., Farnham P. J., Platt T. Synthetic sites for transcription termination and a functional comparison with tryptophan operon termination sites in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4180–4184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari F. A., Trach K., LeCoq D., Spence J., Ferrari E., Hoch J. A. Characterization of the spo0A locus and its deduced product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2647–2651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán P., Westpheling J., Youngman P. Characterization of the promoter region of the Bacillus subtilis spoIIE operon. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1598–1609. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1598-1609.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo M., Lampe M., Ray C., Schafer W., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Genetic studies of a secondary RNA polymerase sigma factor in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3464–3469. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3464-3469.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney T. J., Kirchman P. A., Moran C. P., Jr Gene encoding sigma E is transcribed from a sigma A-like promoter in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3058–3064. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3058-3064.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney T. J., Moran C. P., Jr Organization and regulation of an operon that encodes a sporulation-essential sigma factor in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3329–3339. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3329-3339.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney T. J., York K., Youngman P., Moran C. P., Jr Genetic evidence that RNA polymerase associated with sigma A factor uses a sporulation-specific promoter in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9109–9113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmedo G., Ninfa E. G., Stock J., Youngman P. Novel mutations that alter the regulation of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Evidence that phosphorylation of regulatory protein SpoOA controls the initiation of sporulation. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):359–372. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80357-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. B., Gocht M., Marahiel M. A., Zuber P. AbrB, a regulator of gene expression in Bacillus, interacts with the transcription initiation regions of a sporulation gene and an antibiotic biosynthesis gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8457–8461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satola S., Kirchman P. A., Moran C. P., Jr Spo0A binds to a promoter used by sigma A RNA polymerase during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4533–4537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Stock A. M., Mottonen J. M. Signal transduction in bacteria. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):395–400. doi: 10.1038/344395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch M., Webb V., Spiegelman G., Hoch J. A. The SpoOA protein of Bacillus subtilis is a repressor of the abrB gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1801–1805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. J., Howard M. G., Piggot P. J. Regulation of transcription of the Bacillus subtilis spoIIA locus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):692–698. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.692-698.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. J., Piggot P. J., Tatti K. M., Moran C. P., Jr Transcription of the Bacillus subtilis spoIIA locus. Gene. 1991 May 15;101(1):113–116. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90231-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita S., Yoshikawa H., Kawamura F., Takahashi H., Yamamoto T., Kobayashi Y., Saito H. The effect of spo0 mutations on the expression of spo0A- and spo0F-lacZ fusions. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Oct;205(1):28–33. doi: 10.1007/BF02428029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber P., Losick R. Use of a lacZ fusion to study the role of the spoO genes of Bacillus subtilis in developmental regulation. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90230-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]