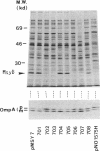
Abstract
Escherichia coli genes were cloned onto a multicopy plasmid and selected by the ability to restore growth and protein export defects caused by a temperature-sensitive secY or secA mutation. When secA51 was used as the primary mutation, only clones carrying groE, which specifies the chaperonin class of heat shock protein, were obtained. Selection using secY24 yielded three major classes of genes. The first class encodes another heat shock protein, HtpG; the most frequently obtained second class encodes a neutral histonelike protein, H-NS; and the third class, msyB, encodes a 124-residue protein of which 38 residues are acidic amino acids. Possible mechanisms of suppression as well as the significance and limitations of the multicopy suppression approach are discussed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akimaru J., Matsuyama S., Tokuda H., Mizushima S. Reconstitution of a protein translocation system containing purified SecY, SecE, and SecA from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6545–6549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A. Eukaryotic Mr 83,000 heat shock protein has a homologue in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5177–5181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassford P. J., Jr, Silhavy T. J., Beckwith J. R. Use of gene fusion to study secretion of maltose-binding protein into Escherichia coli periplasm. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):19–31. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.19-31.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brundage L., Hendrick J. P., Schiebel E., Driessen A. J., Wickner W. The purified E. coli integral membrane protein SecY/E is sufficient for reconstitution of SecA-dependent precursor protein translocation. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90111-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J. Transposition and fusion of the lac genes to selected promoters in Escherichia coli using bacteriophage lambda and Mu. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):541–555. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalman F. C., Scherrer L. C., Taylor L. P., Akil H., Pratt W. B. Localization of the 90-kDa heat shock protein-binding site within the hormone-binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor by peptide competition. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3482–3490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Hanley-Way S., Silhavy T. J. Suppressor mutations that restore export of a protein with a defective signal sequence. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90272-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falconi M., Gualtieri M. T., La Teana A., Losso M. A., Pon C. L. Proteins from the prokaryotic nucleoid: primary and quaternary structure of the 15-kD Escherichia coli DNA binding protein H-NS. Mol Microbiol. 1988 May;2(3):323–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00035.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardel C., Johnson K., Jacq A., Beckwith J. The secD locus of E.coli codes for two membrane proteins required for protein export. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3209–3216. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07519.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. R., Salmond G. P. The identification of the Escherichia coli ftsY gene product: an unusual protein. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Apr;4(4):575–583. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göransson M., Sondén B., Nilsson P., Dagberg B., Forsman K., Emanuelsson K., Uhlin B. E. Transcriptional silencing and thermoregulation of gene expression in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):682–685. doi: 10.1038/344682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl F. U., Lecker S., Schiebel E., Hendrick J. P., Wickner W. The binding cascade of SecB to SecA to SecY/E mediates preprotein targeting to the E. coli plasma membrane. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):269–279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90160-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Hinton J. C., Hulton C. S., Owen-Hughes T., Pavitt G. D., Seirafi A. Protein H1: a role for chromatin structure in the regulation of bacterial gene expression and virulence? Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2007–2012. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulton C. S., Seirafi A., Hinton J. C., Sidebotham J. M., Waddell L., Pavitt G. D., Owen-Hughes T., Spassky A., Buc H., Higgins C. F. Histone-like protein H1 (H-NS), DNA supercoiling, and gene expression in bacteria. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):631–642. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90458-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Akiyama Y. In vivo analysis of integration of membrane proteins in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Sep;5(9):2243–2253. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02154.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Cerretti D. P., Nashimoto H., Nomura M. Characterization of an amber mutation in the structural gene for ribosomal protein L15, which impairs the expression of the protein export gene, secY, in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2319–2324. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02133.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Hirota Y., Akiyama Y. Temperature-sensitive sec mutants of Escherichia coli: inhibition of protein export at the permissive temperature. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1742–1743. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1742-1743.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Wittekind M., Nomura M., Shiba K., Yura T., Miura A., Nashimoto H. A temperature-sensitive mutant of E. coli exhibiting slow processing of exported proteins. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):789–797. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P., Kanehisa M., DeLisi C. The detection and classification of membrane-spanning proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 28;815(3):468–476. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90375-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumamoto C. A., Beckwith J. Evidence for specificity at an early step in protein export in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):267–274. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.267-274.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumamoto C. A. Molecular chaperones and protein translocation across the Escherichia coli inner membrane. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jan;5(1):19–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01821.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. A., Beckwith J. Suppression of growth and protein secretion defects in Escherichia coli secA mutants by decreasing protein synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):878–883. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.878-883.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill R., Cunningham K., Brundage L. A., Ito K., Oliver D., Wickner W. SecA protein hydrolyzes ATP and is an essential component of the protein translocation ATPase of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):961–966. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03458.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May G., Dersch P., Haardt M., Middendorf A., Bremer E. The osmZ (bglY) gene encodes the DNA-binding protein H-NS (H1a), a component of the Escherichia coli K12 nucleoid. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Oct;224(1):81–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00259454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakańo A., Muramatsu M. A novel GTP-binding protein, Sar1p, is involved in transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2677–2691. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Beckwith J. E. coli mutant pleiotropically defective in the export of secreted proteins. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):765–772. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Beckwith J. Regulation of a membrane component required for protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):311–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B. Identification of five new essential genes involved in the synthesis of a secreted protein in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):285–291. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.285-291.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pon C. L., Calogero R. A., Gualerzi C. O. Identification, cloning, nucleotide sequence and chromosomal map location of hns, the structural gene for Escherichia coli DNA-binding protein H-NS. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 May;212(2):199–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00334684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Beckwith J. Genetic analysis of protein export in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:215–248. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.001243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiebel E., Driessen A. J., Hartl F. U., Wickner W. Delta mu H+ and ATP function at different steps of the catalytic cycle of preprotein translocase. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):927–939. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90317-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiba K., Ito K., Nakamura Y., Dondon J., Grunberg-Manago M. Altered translation initiation factor 2 in the cold-sensitive ssyG mutant affects protein export in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):3001–3006. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04598.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiba K., Ito K., Yura T., Cerretti D. P. A defined mutation in the protein export gene within the spc ribosomal protein operon of Escherichia coli: isolation and characterization of a new temperature-sensitive secY mutant. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):631–635. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01859.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiba K., Ito K., Yura T. Mutation that suppresses the protein export defect of the secY mutation and causes cold-sensitive growth of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):696–701. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.696-701.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiba K., Ito K., Yura T. Suppressors of the secY24 mutation: identification and characterization of additional ssy genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):849–856. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.849-856.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stader J., Gansheroff L. J., Silhavy T. J. New suppressors of signal-sequence mutations, prlG, are linked tightly to the secE gene of Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1045–1052. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swidersky U. E., Hoffschulte H. K., Müller M. Determinants of membrane-targeting and transmembrane translocation during bacterial protein export. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1777–1785. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08302.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueguchi C., Ito K. Escherichia coli sec mutants accumulate a processed immature form of maltose-binding protein (MBP), a late-phase intermediate in MBP export. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5643–5649. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5643-5649.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyk T. K., Gatenby A. A., LaRossa R. A. Demonstration by genetic suppression of interaction of GroE products with many proteins. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):451–453. doi: 10.1038/342451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada H., Muramatsu S., Mizuno T. An Escherichia coli protein that preferentially binds to sharply curved DNA. J Biochem. 1990 Sep;108(3):420–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G., Gavel Y. Topogenic signals in integral membrane proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jul 1;174(4):671–678. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]