Abstract
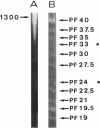
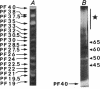
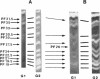
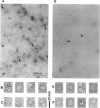
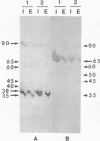
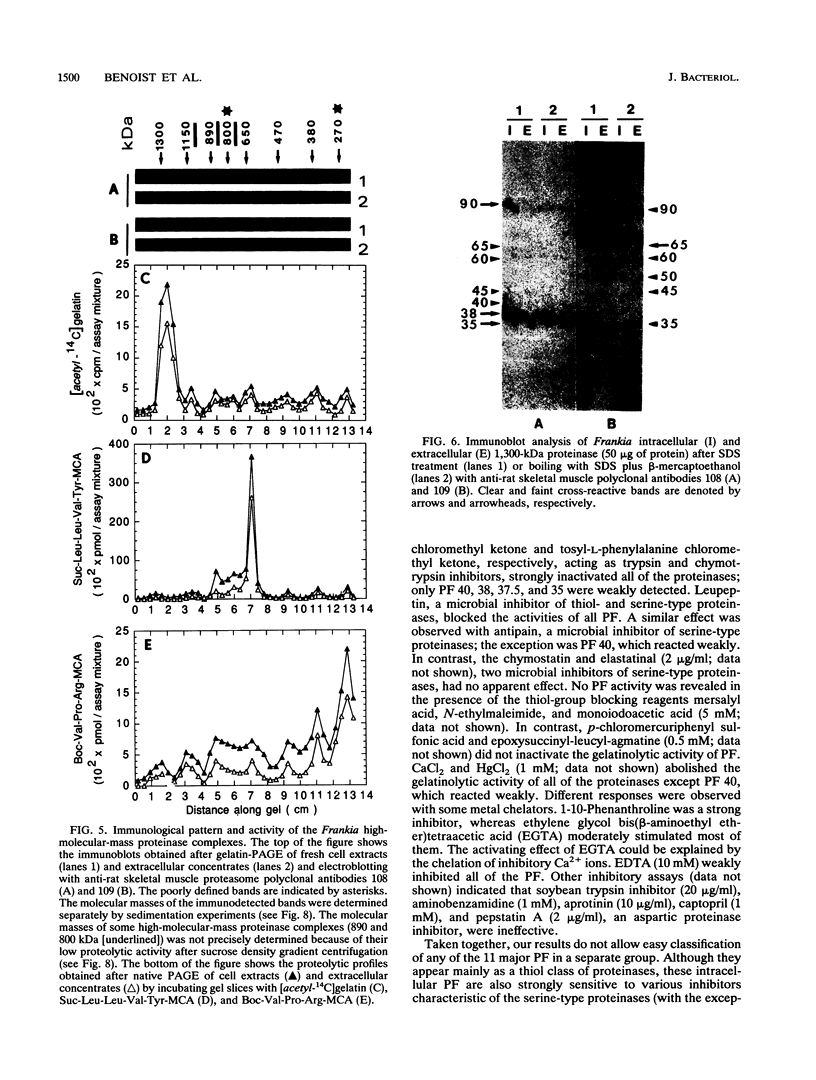
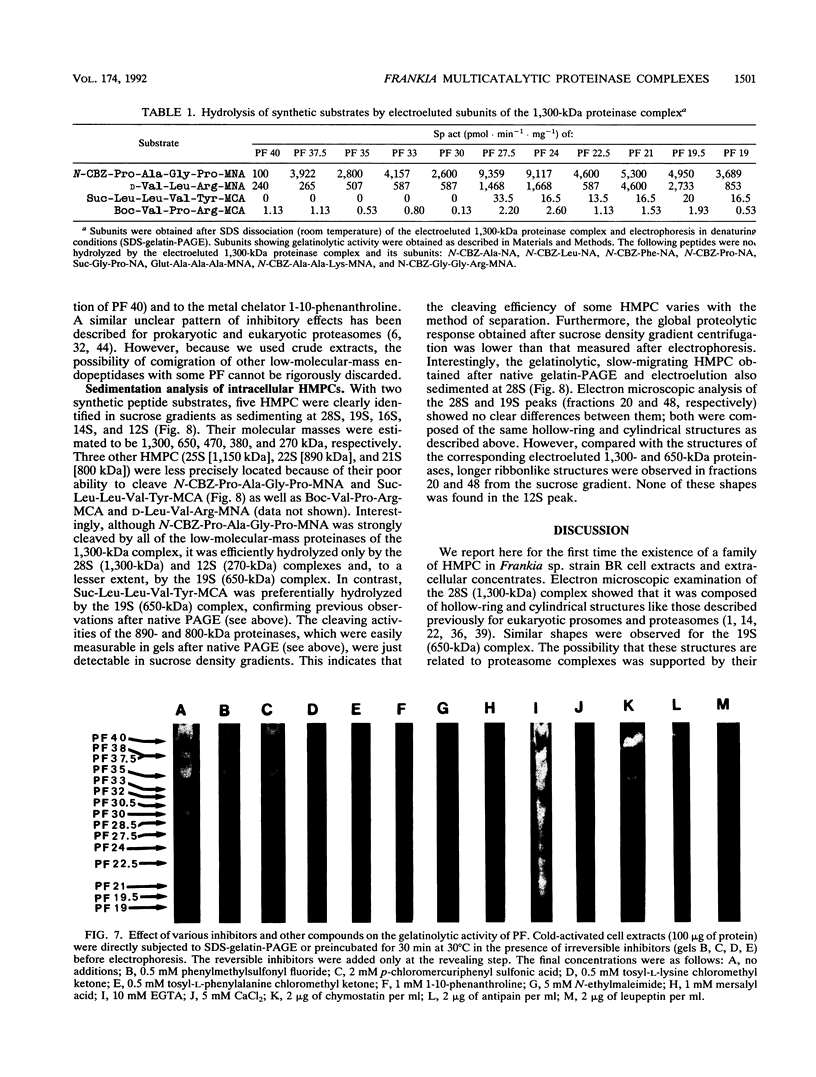
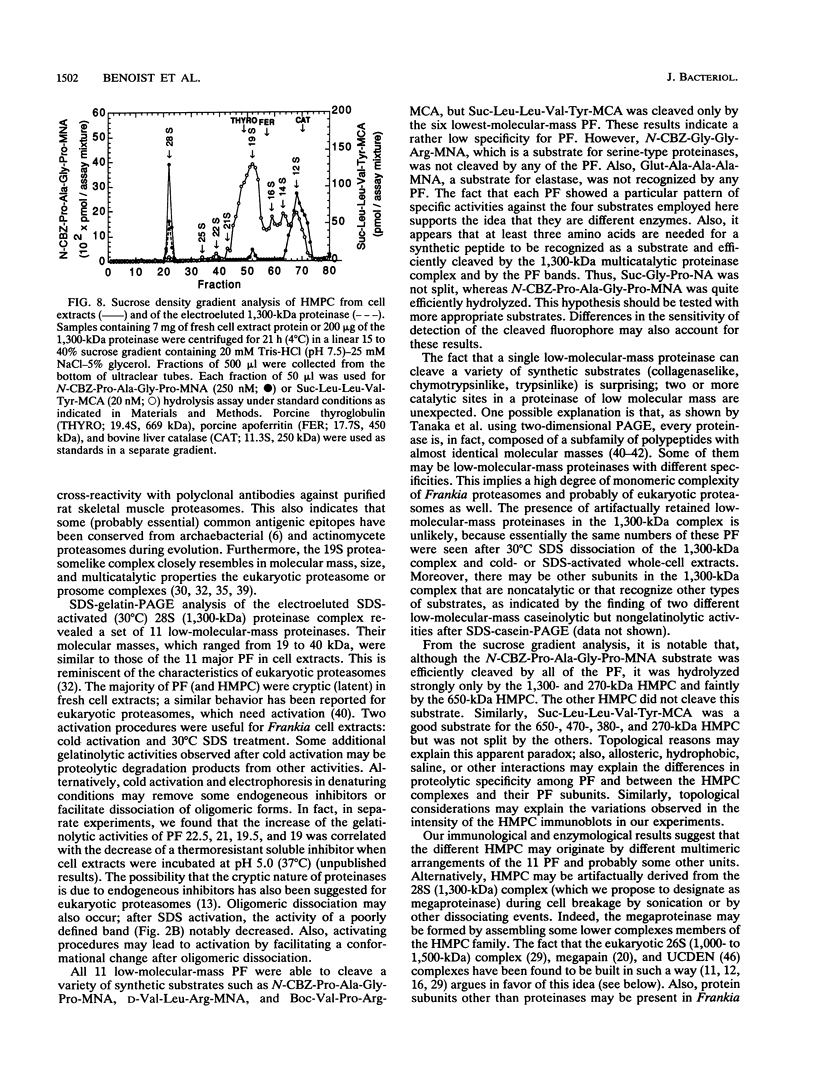
A major-high-molecular mass proteinase and seven latent minor proteinases were found in cell extracts and in concentrates of culture medium from Frankia sp. strain BR after nondenaturing electrophoresis in mixed gelatin-polyacrylamide gels. All of these complexes showed multicatalytic properties. Their molecular masses and their sedimentation coefficients varied from 1,300 kDa (28S) to 270 kDa (12S). The electroeluted 1,300-kDa proteinase complex dissociated into 11 low-molecular-mass proteinases (40 to 19 kDa) after sodium dodecyl sulfate activation at 30 degrees C and electrophoresis under denaturing conditions. All of these electroeluted proteinases hydrolyzed N-carbobenzoxy-Pro-Ala-Gly-Pro-4-methoxy-beta- naphthylamide, D-Val-Leu-Arg-4-methoxy-beta-naphthylamide, and Boc-Val-Pro-Arg-4-methyl-7-coumarylamide, whereas Suc-Leu-Leu-Val-Tyr-4-methyl-7-coumarylamide was cleaved only by the six lower-molecular-mass proteinases (27.5 to 19 kDa). Examination by electron microscopy of uranyl acetate-stained, electroeluted 1,300- and 650-kDa intracellular and extracellular proteinase complexes showed ring-shaped and cylindrical particles (10 to 11 nm in diameter, 15 to 16 nm long) similar to those of eukaryotic prosomes and proteasomes. Polyclonal antibodies raised against rat skeletal muscle proteasomes cross-reacted with all of the high-molecular-mass proteinase complexes and, after denaturation of the electroeluted 1,300-kDa band, with polypeptides of 35 to 38, 65, and 90 kDa. Electrophoresis of the activated cell extracts under denaturing conditions revealed 11 to 17 gelatinases from 40 to 19 kDa, including the 11 proteinases of the 1,300-kDa proteinase complex. The inhibition pattern of these proteinases is complex. Thiol-reactive compounds and 1-10-phenanthroline strongly inhibited all of the proteinases, but inhibitors against serine-type proteinases were also effective for most of them.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrigo A. P., Tanaka K., Goldberg A. L., Welch W. J. Identity of the 19S 'prosome' particle with the large multifunctional protease complex of mammalian cells (the proteasome). Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):192–194. doi: 10.1038/331192a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist P., Schwencke J. Native agarose-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis allowing the detection of aminopeptidase, dehydrogenase, and esterase activities at the nanogram level: enzymatic patterns in some Frankia strains. Anal Biochem. 1990 Jun;187(2):337–344. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90466-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond J. S., Butler P. E. Intracellular proteases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:333–364. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlmann B., Kopp F., Kuehn L., Niedel B., Pfeifer G., Hegerl R., Baumeister W. The multicatalytic proteinase (prosome) is ubiquitous from eukaryotes to archaebacteria. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 17;251(1-2):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81441-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlmann B., Kuehn L., Rutschmann M., Reinauer H. Purification and characterization of a multicatalytic high-molecular-mass proteinase from rat skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):161–170. doi: 10.1042/bj2280161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels M. J., Barber C. E., Turner P. C., Sawczyc M. K., Byrde R. J., Fielding A. H. Cloning of genes involved in pathogenicity of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris using the broad host range cosmid pLAFR1. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3323–3328. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02298.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll J., Goldberg A. L. Skeletal muscle proteasome can degrade proteins in an ATP-dependent process that does not require ubiquitin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):787–791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll J., Goldberg A. L. The proteasome (multicatalytic protease) is a component of the 1500-kDa proteolytic complex which degrades ubiquitin-conjugated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):4789–4792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eytan E., Ganoth D., Armon T., Hershko A. ATP-dependent incorporation of 20S protease into the 26S complex that degrades proteins conjugated to ubiquitin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7751–7755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagan J. M., Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. Skeletal muscle and liver contain a soluble ATP + ubiquitin-dependent proteolytic system. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 15;243(2):335–343. doi: 10.1042/bj2430335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkenburg P. E., Haass C., Kloetzel P. M., Niedel B., Kopp F., Kuehn L., Dahlmann B. Drosophila small cytoplasmic 19S ribonucleoprotein is homologous to the rat multicatalytic proteinase. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):190–192. doi: 10.1038/331190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganoth D., Leshinsky E., Eytan E., Hershko A. A multicomponent system that degrades proteins conjugated to ubiquitin. Resolution of factors and evidence for ATP-dependent complex formation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12412–12419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardes M., Bousquet J., Lalonde M. Isozyme Variation among 40 Frankia Strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jul;53(7):1596–1603. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.7.1596-1603.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough R., Pratt G., Rechsteiner M. Purification of two high molecular weight proteases from rabbit reticulocyte lysate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8303–8313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita M., Hamakubo T., Fukui I., Murachi T., Toyohara H. Significant amount of multicatalytic proteinase identified on membrane from human erythrocyte. J Biochem. 1990 Mar;107(3):440–444. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt J. A., Escher C., Wolf D. H. Proteinase yscE of yeast shows homology with the 20 S cylinder particles of Xenopus laevis. FEBS Lett. 1988 Oct 24;239(1):35–40. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80540-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews W., Driscoll J., Tanaka K., Ichihara A., Goldberg A. L. Involvement of the proteasome in various degradative processes in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2597–2601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire M. J., DeMartino G. N. Purification and characterization of a high molecular weight proteinase (macropain) from human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Sep 26;873(2):279–289. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90055-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller A., Benoist P., Diem H. G., Schwencke J. Age-dependent changes in extracellular proteins, aminopeptidase and proteinase activities in Frankia isolate BR. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Dec;137(12):2787–2796. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-12-2787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orino E., Tanaka K., Tamura T., Sone S., Ogura T., Ichihara A. ATP-dependent reversible association of proteasomes with multiple protein components to form 26S complexes that degrade ubiquitinated proteins in human HL-60 cells. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jun 24;284(2):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80686-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M. The multicatalytic proteinase complex, a major extralysosomal proteolytic system. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 13;29(45):10289–10297. doi: 10.1021/bi00497a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivett A. J. Intracellular protein degradation. Essays Biochem. 1990;25:39–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivett A. J. The multicatalytic proteinase of mammalian cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Jan;268(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90558-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I., Berger A. On the size of the active site in proteases. I. Papain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Apr 20;27(2):157–162. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(67)80055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherrer K. Prosomes, subcomplexes of untranslated mRNP. Mol Biol Rep. 1990 Feb;14(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00422709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid H. P., Akhayat O., Martins De Sa C., Puvion F., Koehler K., Scherrer K. The prosome: an ubiquitous morphologically distinct RNP particle associated with repressed mRNPs and containing specific ScRNA and a characteristic set of proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):29–34. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01757.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skilton H. E., Eperon I. C., Rivett A. J. Co-purification of a small RNA species with multicatalytic proteinase (proteasome) from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1991 Feb 25;279(2):351–355. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80185-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Ichihara A. Proteasomes (multicatalytic proteinase complexes) in eukaryotic cells. Cell Struct Funct. 1990 Jun;15(3):127–132. doi: 10.1247/csf.15.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Ii K., Ichihara A., Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. A high molecular weight protease in the cytosol of rat liver. I. Purification, enzymological properties, and tissue distribution. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15197–15203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Tamura T., Kumatori A., Kwak T. H., Chung C. H., Ichihara A. Separation of yeast proteasome subunits. Immunoreactivity with antibodies against ATP-dependent protease Ti from Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 15;164(3):1253–1261. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91804-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Yoshimura T., Ichihara A., Ikai A., Nishigai M., Morimoto Y., Sato M., Tanaka N., Katsube Y., Kameyama K. Molecular organization of a high molecular weight multi-protease complex from rat liver. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 20;203(4):985–996. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90123-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaithilingam I., Cook R. A. High-molecular-mass proteases (possible proteasomes) in Escherichia coli K12. Biochem Int. 1989 Dec;19(6):1297–1307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varner J. E., Lin L. S. Plant cell wall architecture. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):231–239. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90896-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman L., Fagan J. M., Goldberg A. L. Demonstration of two distinct high molecular weight proteases in rabbit reticulocytes, one of which degrades ubiquitin conjugates. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2451–2457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]