Abstract
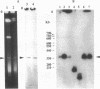
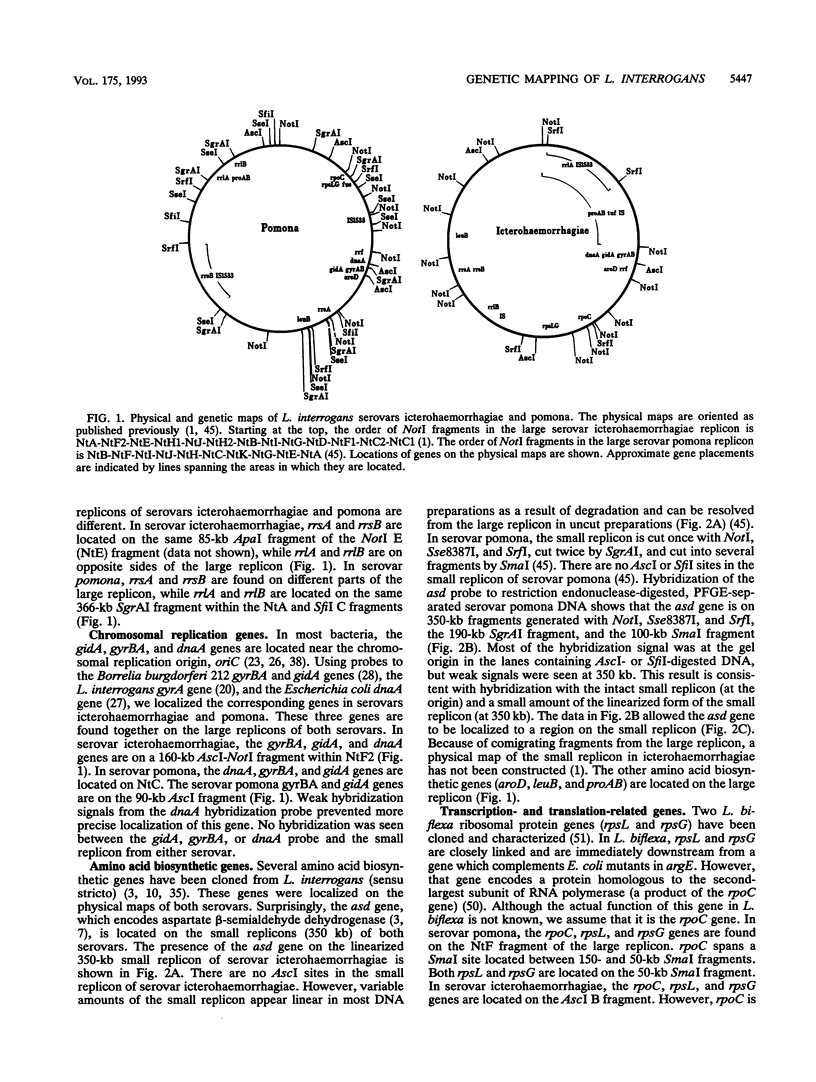
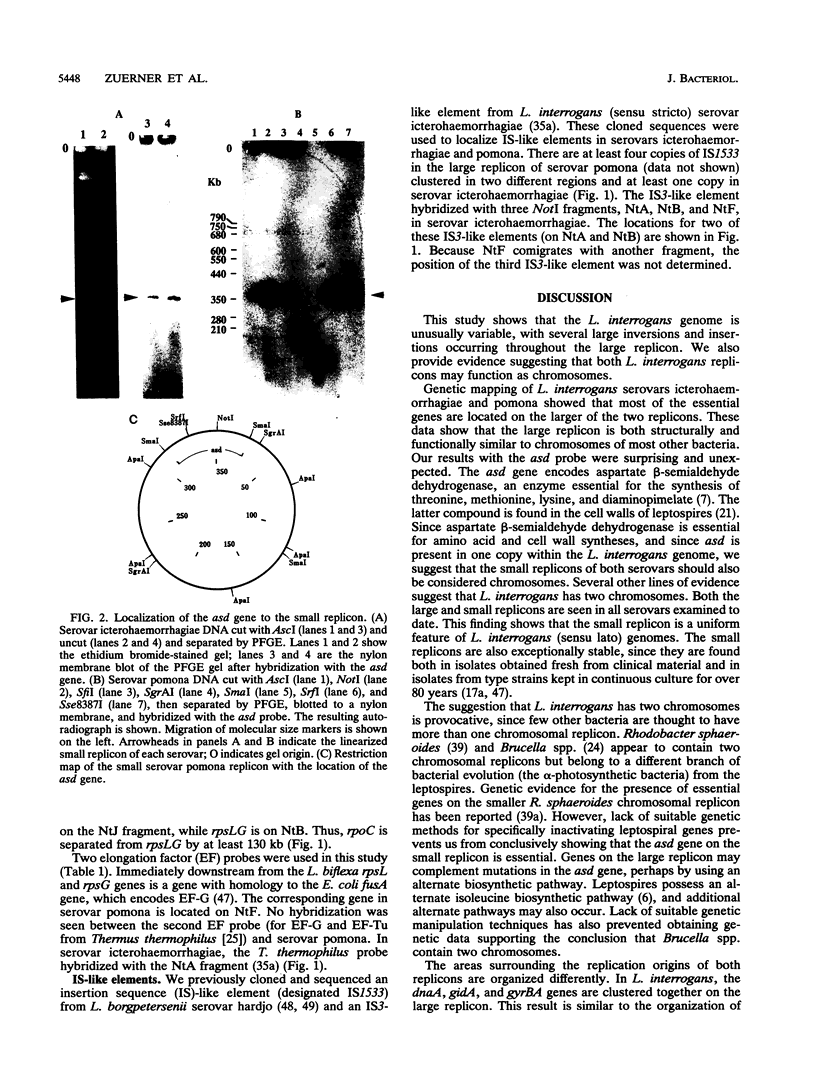
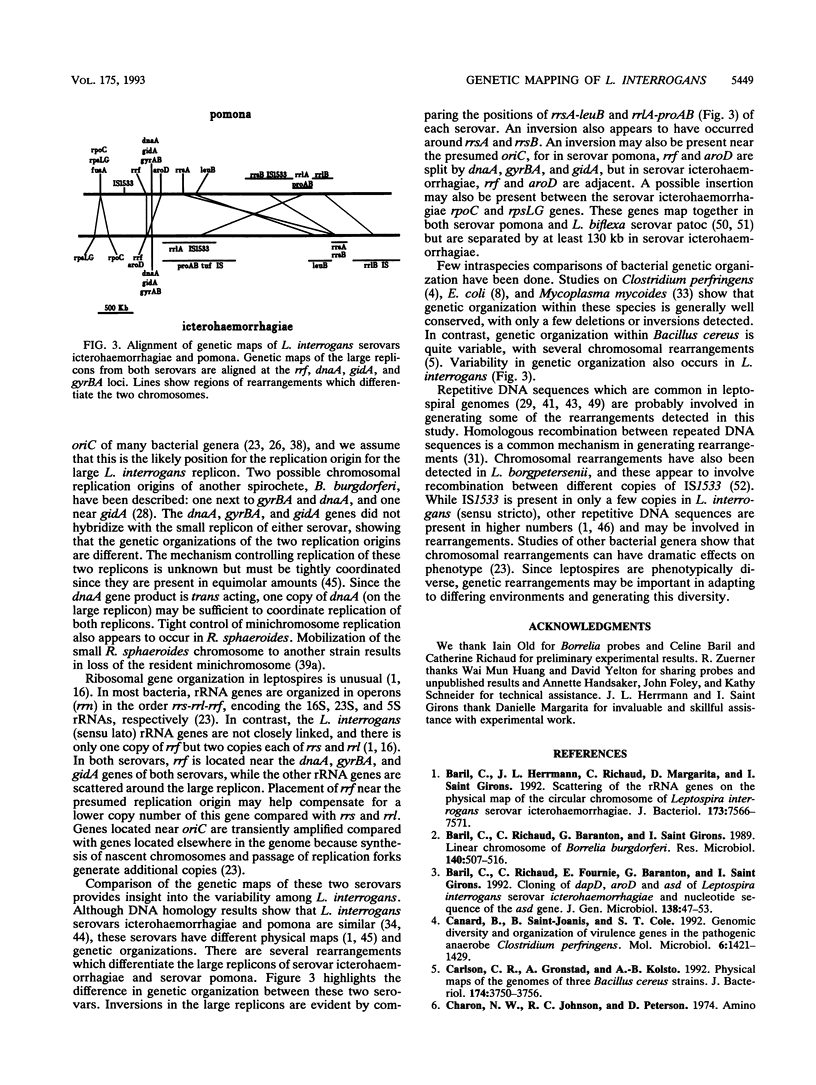
Genetic maps were constructed for Leptospira interrogans serovars icterohaemorrhagiae and pomona. Previously we independently constructed physical maps of the genomes for these two serovars. The genomes of both serovars consist of a large replicon (4.4 to 4.6 Mb) and a small replicon (350 kb). Genes were localized on the physical maps by using Southern blot analysis with specific probes. Among the probes used were genes encoding a variety of essential enzymes and genes usually found near bacterial chromosomal replication origins. Most of the essential genes are on the larger replicon of each serovar. However, the smaller replicons of both serovars contain the asd gene. The asd gene encodes aspartate beta-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, an enzyme essential in amino acid and cell wall biosyntheses. The finding that both L. interrogans replicons contain essential genes suggests that both replicons are chromosomes. Comparison of the genetic maps of the larger replicons of the two serovars showed evidence of large rearrangements. These data show that there is considerable intraspecies heterogeneity in L. interrogans.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baril C., Herrmann J. L., Richaud C., Margarita D., Girons I. S. Scattering of the rRNA genes on the physical map of the circular chromosome of Leptospira interrogans serovar icterohaemorrhagiae. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(23):7566–7571. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.23.7566-7571.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baril C., Richaud C., Baranton G., Saint Girons I. S. Linear chromosome of Borrelia burgdorferi. Res Microbiol. 1989 Oct;140(8):507–516. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(89)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baril C., Richaud C., Fournié E., Baranton G., Saint Girons I. Cloning of dapD, aroD and asd of Leptospira interrogans serovar icterohaemorrhagiae, and nucleotide sequence of the asd gene. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Jan;138(1):47–53. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-1-47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canard B., Saint-Joanis B., Cole S. T. Genomic diversity and organization of virulence genes in the pathogenic anaerobe Clostridium perfringens. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jun;6(11):1421–1429. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson C. R., Grønstad A., Kolstø A. B. Physical maps of the genomes of three Bacillus cereus strains. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3750–3756. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3750-3756.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels D. L. The complete AvrII restriction map of the Escherichia coli genome and comparisons of several laboratory strains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 11;18(9):2649–2651. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.9.2649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson B. E., MacDougall J., Saint Girons I. Physical map of the linear chromosome of the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi 212, a causative agent of Lyme disease, and localization of rRNA genes. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3766–3774. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3766-3774.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding M., Yelton D. B. Cloning and analysis of the leuB gene of Leptospira interrogans serovar pomona. J Gen Microbiol. 1993 May;139(5):1093–1103. doi: 10.1099/00221287-139-5-1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLINGHAUSEN H. C., Jr, MCCULLOUGH W. G. NUTRITION OF LEPTOSPIRA POMONA AND GROWTH OF 13 OTHER SEROTYPES: FRACTIONATION OF OLEIC ALBUMIN COMPLEX AND A MEDIUM OF BOVINE ALBUMIN AND POLYSORBATE 80. Am J Vet Res. 1965 Jan;26:45–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferdows M. S., Barbour A. G. Megabase-sized linear DNA in the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5969–5973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga M., Horie I., Mifuchi I. Isolation and characterization of the 5S rRNA gene of Leptospira interrogans. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3264–3268. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3264-3268.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga M., Horie I., Mifuchi I. Nucleotide sequence of a 23S ribosomal RNA gene from Leptospira interrogans serovar canicola strain Moulton. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):2123–2123. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.2123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga M., Horie I., Okuzako N., Mifuchi I. Nucleotide sequence of a 16S rRNA gene for Leptospira interrogans serovar canicola strain Moulton. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 25;18(2):366–366. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.2.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga M., Mifuchi I. Unique organization of Leptospira interrogans rRNA genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5763–5767. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5763-5767.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway S. C. Leptospirosis in New Zealand: an ecological view. N Z Vet J. 1981 Jul;29(7):109–112. doi: 10.1080/00480169.1981.34815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann J. L., Baril C., Bellenger E., Perolat P., Baranton G., Saint Girons I. Genome conservation in isolates of Leptospira interrogans. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7582–7588. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7582-7588.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann J. L., Bellenger E., Perolat P., Baranton G., Saint Girons I. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of NotI digests of leptospiral DNA: a new rapid method of serovar identification. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jul;30(7):1696–1702. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.7.1696-1702.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Harris V. G. Differentiation of pathogenic and saprophytic letospires. I. Growth at low temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):27–31. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.27-31.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C. The spirochetes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:89–106. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawiec S., Riley M. Organization of the bacterial chromosome. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):502–539. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.4.502-539.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaux S., Paillisson J., Carles-Nurit M. J., Bourg G., Allardet-Servent A., Ramuz M. Presence of two independent chromosomes in the Brucella melitensis 16M genome. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(3):701–705. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.3.701-705.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickel F. S., Spremulli L. L. Organization of the genes for protein synthesis elongation factors Tu and G in the cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):78–82. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.78-82.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara N., Yoshikawa H. Genes and their organization in the replication origin region of the bacterial chromosome. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Mar;6(5):629–634. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01510.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmori H., Kimura M., Nagata T., Sakakibara Y. Structural analysis of the dnaA and dnaN genes of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1984 May;28(2):159–170. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90253-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old I. G., MacDougall J., Saint Girons I., Davidson B. E. Mapping of genes on the linear chromosome of the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi: possible locations for its origin of replication. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Dec 1;78(2-3):245–250. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90034-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacciarini M. L., Savio M. L., Tagliabue S., Rossi C. Repetitive sequences cloned from Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo genotype hardjoprajitno and their application to serovar identification. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 May;30(5):1243–1249. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.5.1243-1249.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paster B. J., Dewhirst F. E., Weisburg W. G., Tordoff L. A., Fraser G. J., Hespell R. B., Stanton T. B., Zablen L., Mandelco L., Woese C. R. Phylogenetic analysis of the spirochetes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):6101–6109. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.6101-6109.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petes T. D., Hill C. W. Recombination between repeated genes in microorganisms. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:147–168. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.001051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H., Simon M. I., Barbour A. G. Transposition of structural genes to an expression sequence on a linear plasmid causes antigenic variation in the bacterium Borrelia hermsii. Nature. 1985 Nov 21;318(6043):257–263. doi: 10.1038/318257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyle L. E., Taylor T., Finch L. R. Genomic maps of some strains within the Mycoplasma mycoides cluster. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7265–7268. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7265-7268.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramadass P., Jarvis B. D., Corner R. J., Penny D., Marshall R. B. Genetic characterization of pathogenic Leptospira species by DNA hybridization. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;42(2):215–219. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-2-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richaud C., Margarita D., Baranton G., Saint Girons I. Cloning of genes required for amino acid biosynthesis from Leptospira interrogans serovar icterohaemorrhagiae. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Apr;136(4):651–656. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-4-651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saint Girons I., Norris S. J., Göbel U., Meyer J., Walker E. M., Zuerner R. Genome structure of spirochetes. Res Microbiol. 1992 Jul-Aug;143(6):615–621. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90119-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., Garon C. F., Schwan T. G. Borrelia burgdorferi contains repeated DNA sequences that are species specific and plasmid associated. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):847–853. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.847-853.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. W., Yee T. W., Baird C., Krishnapillai V. Pseudomonad replication origins: a paradigm for bacterial origins? Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2581–2587. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01966.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suwanto A., Kaplan S. Chromosome transfer in Rhodobacter sphaeroides: Hfr formation and genetic evidence for two unique circular chromosomes. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(4):1135–1145. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.4.1135-1145.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suwanto A., Kaplan S. Physical and genetic mapping of the Rhodobacter sphaeroides 2.4.1 genome: presence of two unique circular chromosomes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5850–5859. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5850-5859.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiermann A. B., Handsaker A. L., Moseley S. L., Kingscote B. New method for classification of leptospiral isolates belonging to serogroup pomona by restriction endonuclease analysis: serovar kennewicki. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;21(4):585–587. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.4.585-587.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eys G. J., Zaal J., Schoone G. J., Terpstra W. J. DNA hybridization with hardjobovis-specific recombinant probes as a method for type discrimination of Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Mar;134(3):567–574. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-3-567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker E. M., Arnett J. K., Heath J. D., Norris S. J. Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum has a single, circular chromosome with a size of approximately 900 kilobase pairs. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2476–2479. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2476-2479.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward M. J., Sullivan G. J. Nucleotide sequence of a repetitive element isolated from Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo type hardjo-bovis. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 May;137(5):1101–1109. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-5-1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuerner R. L., Bolin C. A. Repetitive sequence element cloned from Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo type hardjo-bovis provides a sensitive diagnostic probe for bovine leptospirosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2495–2500. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2495-2500.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuerner R. L., Charon N. W. Nucleotide sequence analysis of a gene cloned from Leptospira biflexa serovar patoc which complements an argE defect in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4548–4554. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4548-4554.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuerner R. L., Charon N. W. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the Leptospira biflexa serovar patoc rpsL and rpsG genes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):6165–6168. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.6165-6168.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuerner R. L., Ellis W. A., Bolin C. A., Montgomery J. M. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms distinguish Leptospira borgpetersenii serovar hardjo type hardjo-bovis isolates from different geographical locations. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Mar;31(3):578–583. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.3.578-583.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuerner R. L. Physical map of chromosomal and plasmid DNA comprising the genome of Leptospira interrogans. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):4857–4860. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.4857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]