Abstract
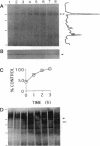
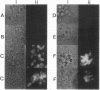
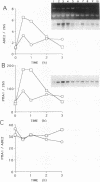
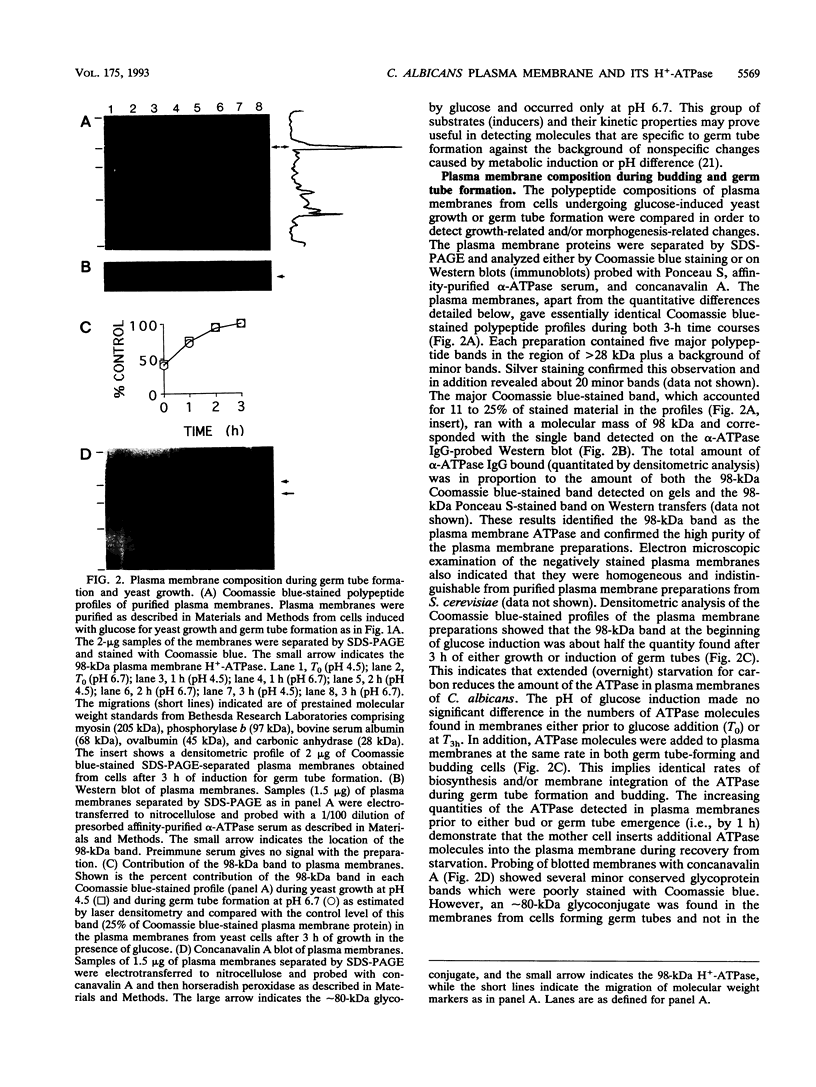
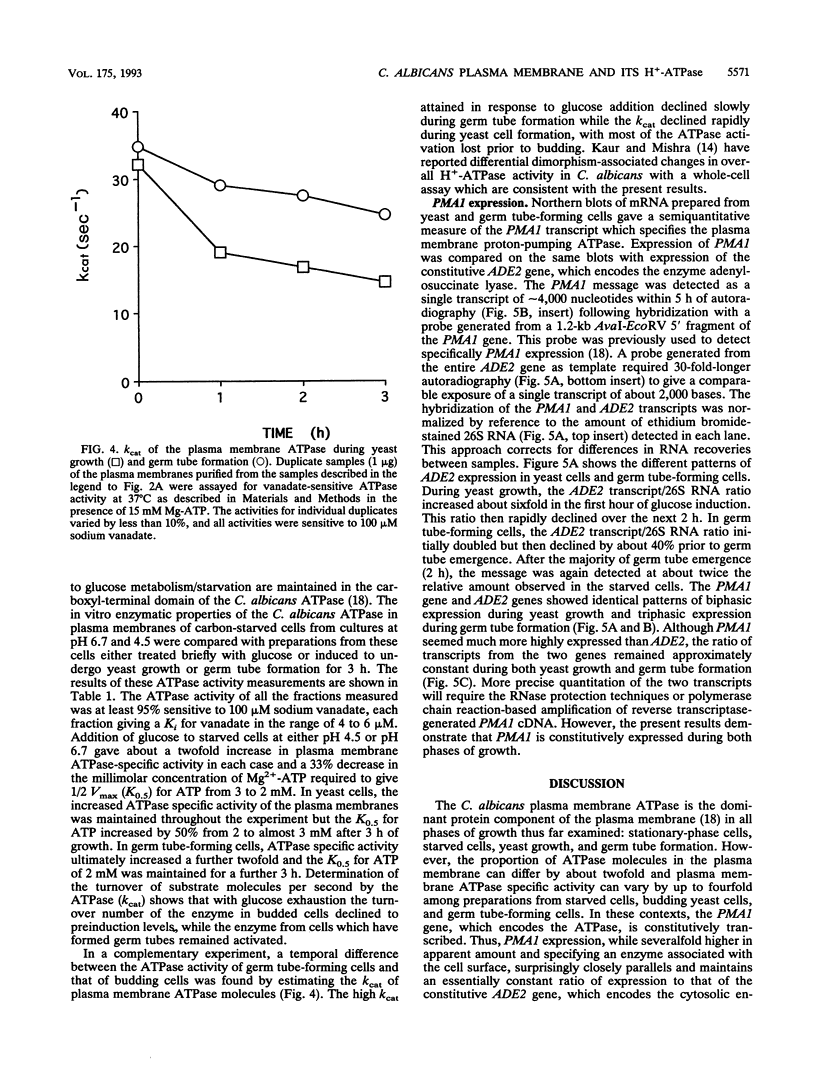
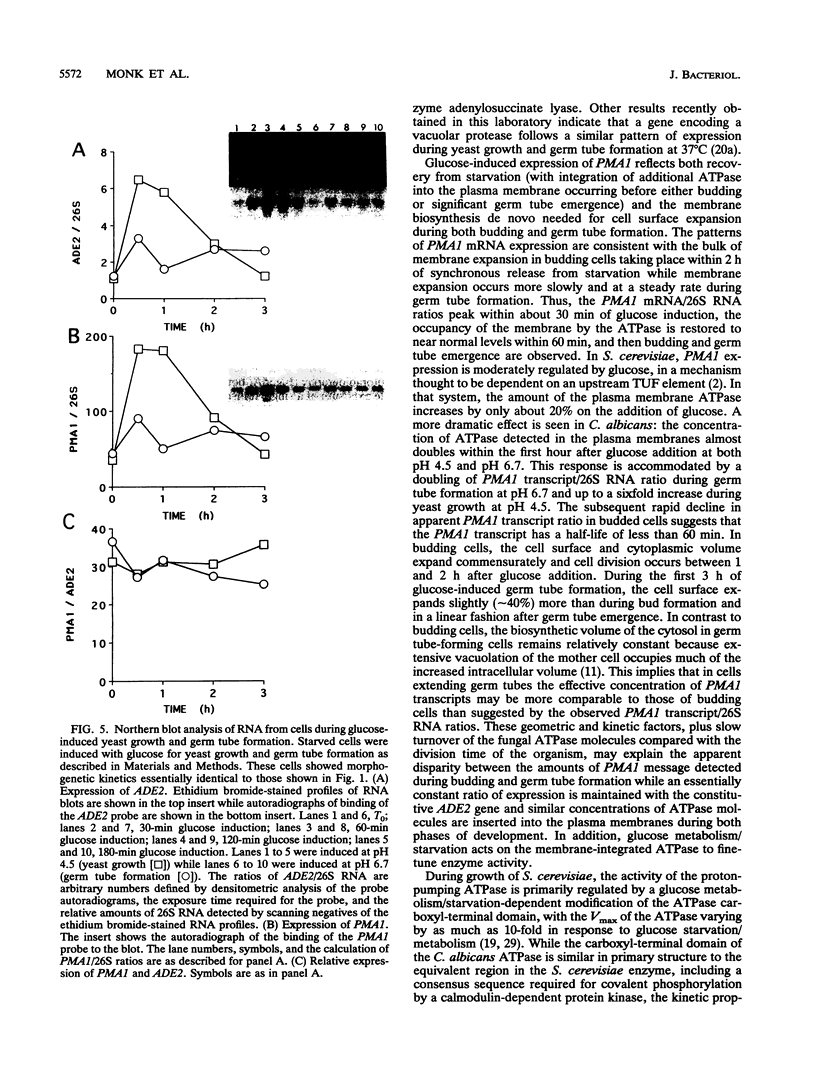
PMA1 expression, plasma membrane H(+)-ATPase enzyme kinetics, and the distribution of the ATPase have been studied in carbon-starved Candida albicans induced with glucose for yeast growth at pH 4.5 and for germ tube formation at pH 6.7. PMA1 expression parallels expression of the constitutive ADE2 gene, increasing up to sixfold during yeast growth and twofold during germ tube formation. Starved cells contain about half the concentration of plasma membrane ATPase of growing cells. The amount of plasma membrane ATPase is normalized prior to either budding or germ tube emergence by the insertion of additional ATPase molecules, while ATPase antigen appears uniformly distributed over the entire plasma membrane surface during both growth phases. Glucose addition rapidly activates the ATPase twofold regardless of the pH of induction. The turnover of substrate molecules per second by the enzyme in membranes from budding cells quickly declines, but the enzyme from germ tube-forming cells maintains its turnover of substrate molecules per second and a higher affinity for Mg-ATP. The plasma membrane ATPase of C. albicans is therefore regulated at several levels; by glucose metabolism/starvation-related factors acting on gene expression, by signals generated through glucose metabolism/starvation which are thought to covalently modify the carboxyl-terminal domain of the enzyme, and possibly by additional signals which may be specific to germ tube formation. The extended period of intracellular alkalinization associated with germ tube formation may result from regulation of proton-pumping ATPase activity coupled with higher ratios of cell surface to effective cytosolic volume.
Full text
PDF

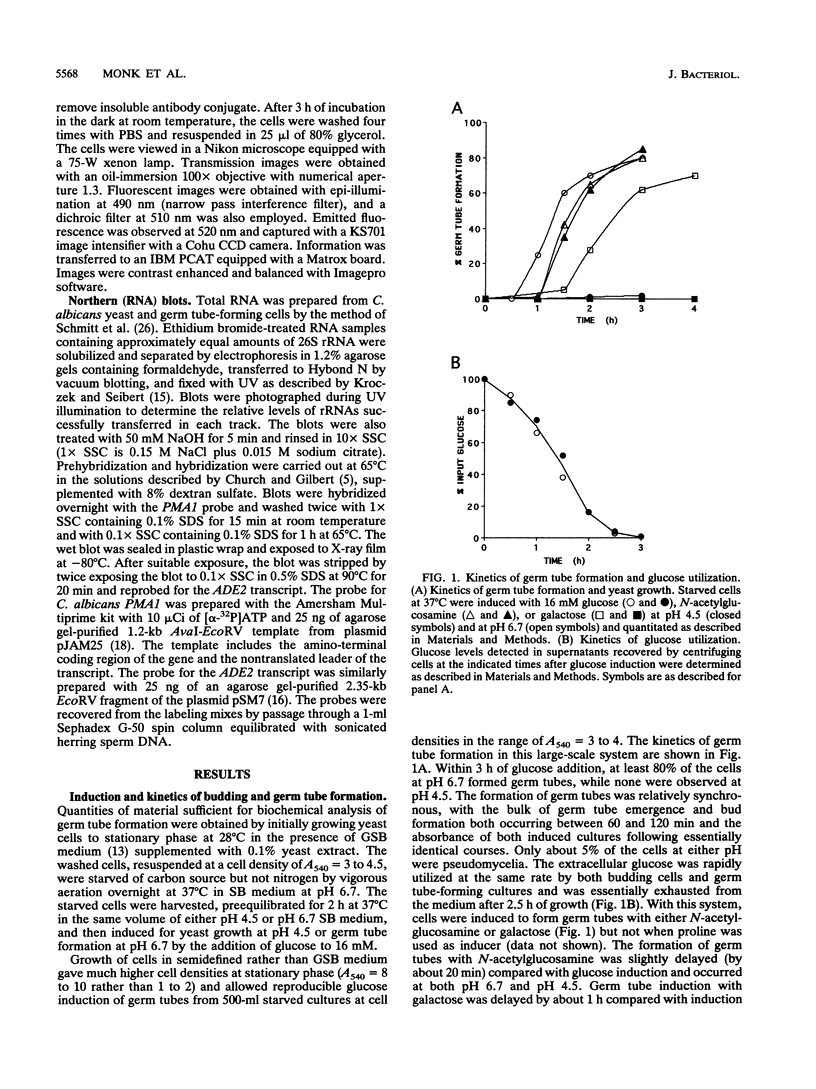



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capieaux E., Vignais M. L., Sentenac A., Goffeau A. The yeast H+-ATPase gene is controlled by the promoter binding factor TUF. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7437–7446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova M., Gil M. L., Cardeñoso L., Martinez J. P., Sentandreu R. Identification of wall-specific antigens synthesized during germ tube formation by Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):262–271. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.262-271.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen-Wu J. L., Zwicker J., Bowen A. R., Robbins P. W. Expression of chitin synthase genes during yeast and hyphal growth phases of Candida albicans. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(4):497–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01494.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cid A., Serrano R. Mutations of the yeast plasma membrane H+-ATPase which cause thermosensitivity and altered regulation of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14134–14139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson M. J., Tuite M. F., Roberts N. A., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M., Perkins R. E., Conroy S. C., Fothergill L. A. Conservation of high efficiency promoter sequences in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2625–2637. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D. G. Development of cell polarity in budding yeast. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1093–1096. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90001-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D. G., Miller K. G., Botstein D. Yeast actin-binding proteins: evidence for a role in morphogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2551–2561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gow N. A., Gooday G. W. Vacuolation, branch production and linear growth of germ tubes in Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Sep;128(9):2195–2198. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-9-2195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R. Identification of concanavalin A-binding proteins after sodium dodecyl sulfate--gel electrophoresis and protein blotting. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jun;123(1):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90634-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes A. R., Shepherd M. G. Nutritional factors determine germ tube formation in Candida albicans. J Med Vet Mycol. 1988 Apr;26(2):127–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur S., Mishra P. Dimorphism-associated changes in plasma membrane H(+)-ATPase activity of Candida albicans. Arch Microbiol. 1991;156(5):412–415. doi: 10.1007/BF00248719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroczek R. A., Siebert E. Optimization of northern analysis by vacuum-blotting, RNA-transfer visualization, and ultraviolet fixation. Anal Biochem. 1990 Jan;184(1):90–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil J. B. Functional characterization of a pyrimidine-rich element in the 5'-noncoding region of the yeast iso-1-cytochrome c gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1045–1054. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk B. C., Kurtz M. B., Marrinan J. A., Perlin D. S. Cloning and characterization of the plasma membrane H(+)-ATPase from Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(21):6826–6836. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.21.6826-6836.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk B. C., Montesinos C., Ferguson C., Leonard K., Serrano R. Immunological approaches to the transmembrane topology and conformational changes of the carboxyl-terminal regulatory domain of yeast plasma membrane H(+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18097–18103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J. Regulation of cell surface polarity from bacteria to mammals. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):948–955. doi: 10.1126/science.1439806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C. Candida infections: an overview. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1987;15(1):1–5. doi: 10.3109/10408418709104444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paranjape V., Roy B. G., Datta A. Involvement of calcium, calmodulin and protein phosphorylation in morphogenesis of Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Nov;136(11):2149–2154. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-11-2149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portillo F., Serrano R. Growth control strength and active site of yeast plasma membrane ATPase studied by site-directed mutagenesis. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 22;186(3):501–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15235.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad R. Nutrient transport in Candida albicans, a pathogenic yeast. Yeast. 1987 Dec;3(4):209–221. doi: 10.1002/yea.320030402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. E., Brown T. A., Trumpower B. L. A rapid and simple method for preparation of RNA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):3091–3092. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.3091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R., Kielland-Brandt M. C., Fink G. R. Yeast plasma membrane ATPase is essential for growth and has homology with (Na+ + K+), K+- and Ca2+-ATPases. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):689–693. doi: 10.1038/319689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R., Portillo F., Monk B. C., Palmgren M. G. The regulatory domain of fungal and plant plasma membrane H(+)-ATPase. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1992;607:131–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R. Structure and function of proton translocating ATPase in plasma membranes of plants and fungi. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 24;947(1):1–28. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd M. G., Yin C. Y., Ram S. P., Sullivan P. A. Germ tube induction in Candida albicans. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Jan;26(1):21–26. doi: 10.1139/m80-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll D. R., Bedell G., Thiel J., Brummel M. The dependency of nuclear division on volume in the dimorphic yeast Candida albicans. Exp Cell Res. 1981 May;133(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90356-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll D. R., Mitchell L. H. Filament ring formation in the dimorphic yeast Candida albicans. J Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;96(2):486–493. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.2.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart E., Gow N. A., Bowen D. V. Cytoplasmic alkalinization during germ tube formation in Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 May;134(5):1079–1087. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-5-1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallejo C. G., Serrano R. Physiology of mutants with reduced expression of plasma membrane H+-ATPase. Yeast. 1989 Jul-Aug;5(4):307–319. doi: 10.1002/yea.320050411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]