Abstract
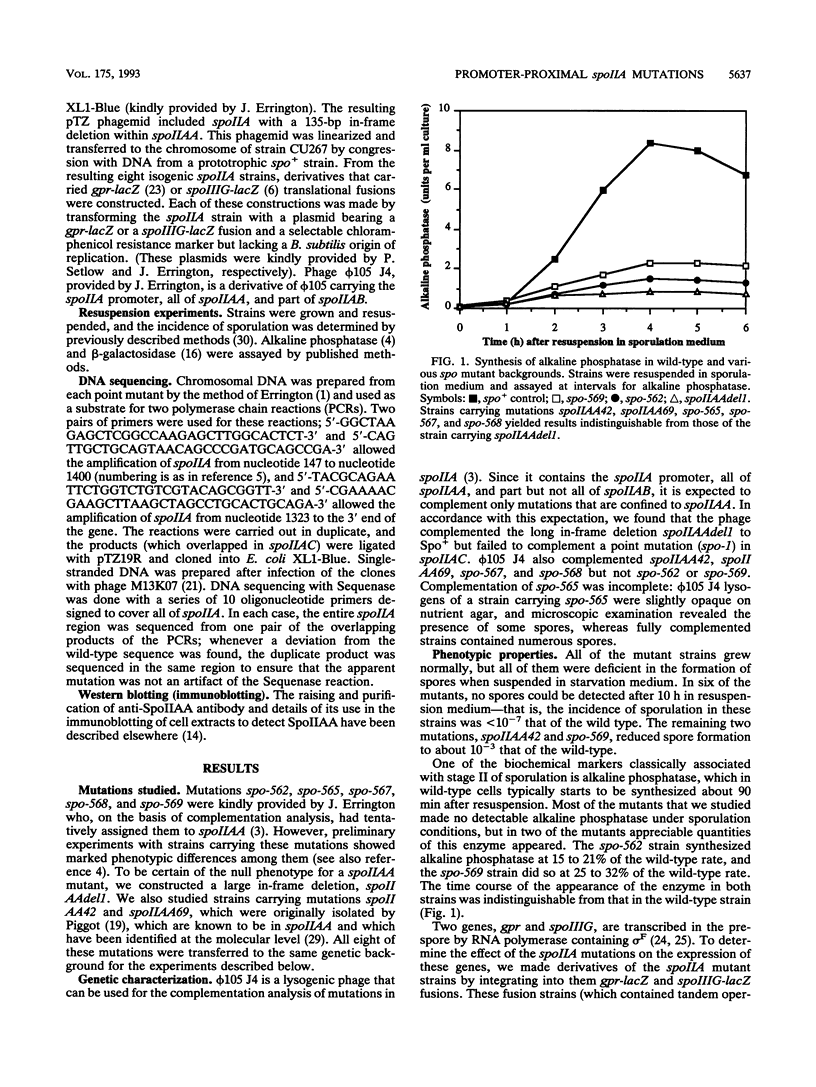
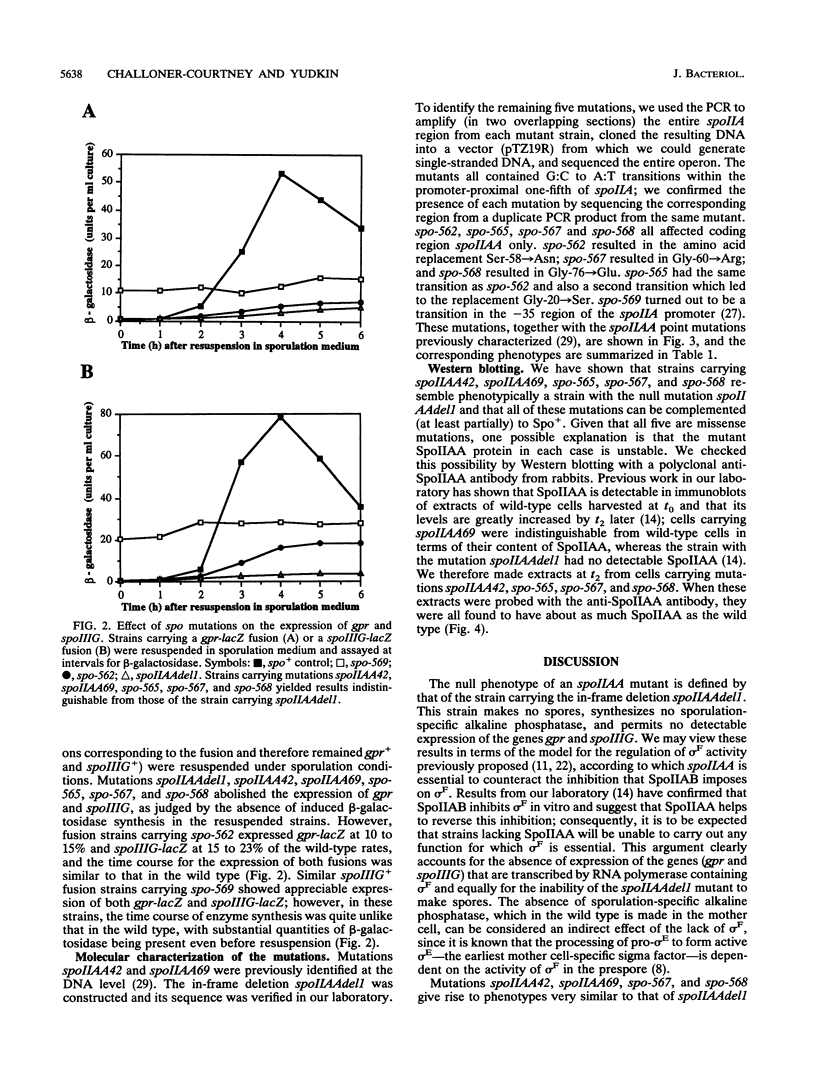
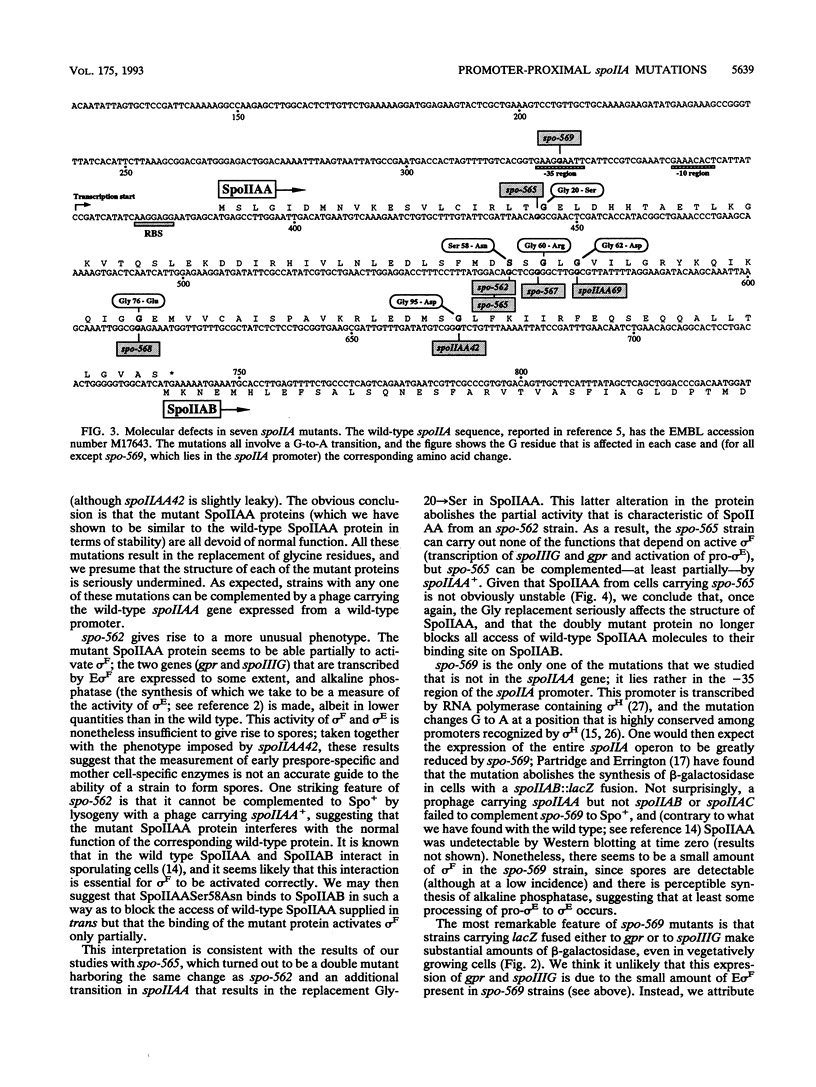
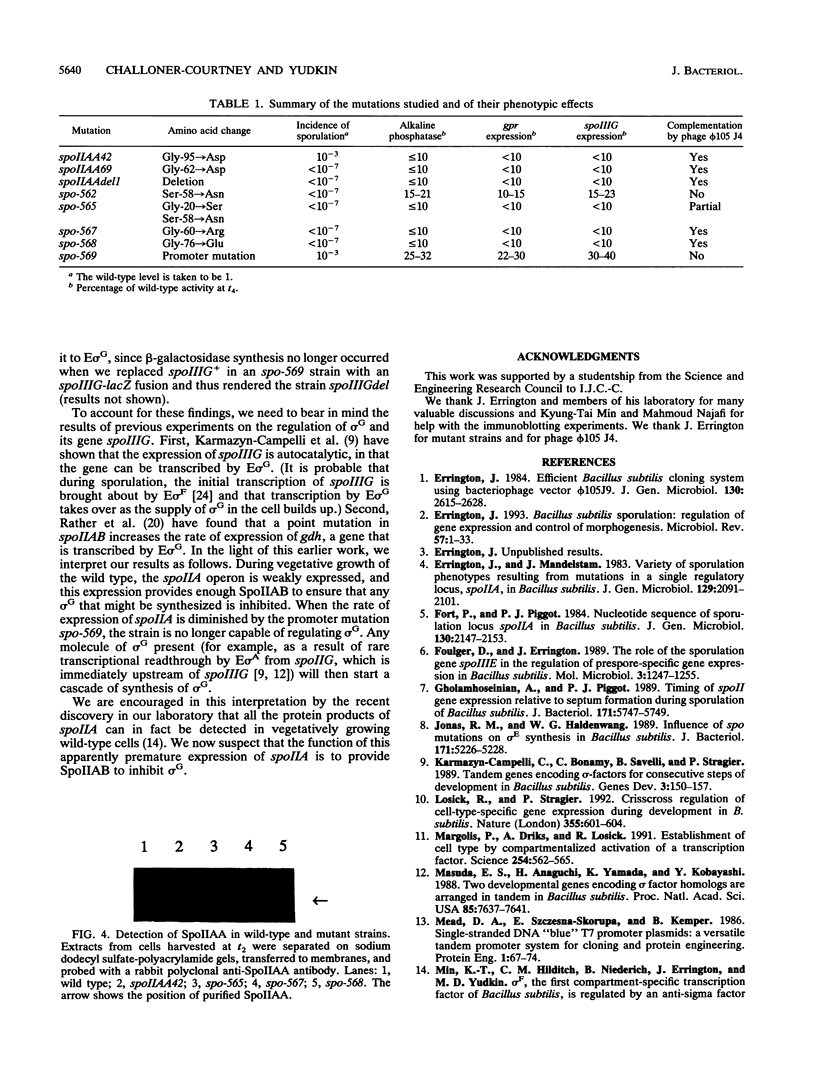
Eight mutations lying within the promoter-proximal one-fifth of the spoIIA locus of Bacillus subtilis were studied. Two of these mutations (spoIIAA42 and spoIIAA69) were previously characterized at the DNA level, five more (spo-562, spo-565, spo-567, spo-568, and spo-569) were isolated in our laboratory several years ago but not fully characterized, and the eight (an in-frame deletion confined to spoIIAA, the first gene in the spoIIA operon) was constructed for this study. DNA sequencing showed that spo-569 was a transitions in the -35 region of the spoIIA promoter; the remaining point mutations were all G:C to A:T transitions in spoIIAA, with spo-565 having two transitions, one of which was identical to that in spo-562. All the spoIIAA mutations except spo-562 led to the replacement of Gly residues. The incidence of sporulation, the rate of synthesis of sporulation-associated alkaline phosphatase, and the rate of expression of the forespore-specific genes gpr and spoIIIG were determined for isogenic strains carrying the eight mutations. All the mutations except spoIIAA42 and spo-569 (which were slightly leaky) made the strains asporogenous, and all except spo-562 and spo-569 abolished the synthesis of alkaline phosphatase and the expression of gpr and spoIIIG. spo-562 allowed alkaline phosphatase synthesis and gpr and spoIIIG expression to occur at about 15% of the wild-type rates but with normal kinetics. spo-59 allowed appreciable gpr and spoIIIG expression during exponential growth; we attribute this expression to transcription by RNA polymerase containing sigma G and suggest that a spo-569 strain makes insufficient SpoIIAB to inhibit sigma G in growing cells.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Errington J. Bacillus subtilis sporulation: regulation of gene expression and control of morphogenesis. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Mar;57(1):1–33. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.1.1-33.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errington J. Efficient Bacillus subtilis cloning system using bacteriophage vector phi 105J9. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Oct;130(10):2615–2628. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-10-2615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errington J., Mandelstam J. Variety of sporulation phenotypes resulting from mutations in a single regulatory locus, spoIIA, in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jul;129(7):2091–2101. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-7-2091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Piggot P. J. Nucleotide sequence of sporulation locus spoIIA in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Aug;130(8):2147–2153. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-8-2147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulger D., Errington J. The role of the sporulation gene spoIIIE in the regulation of prespore-specific gene expression in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1247–1255. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gholamhoseinian A., Piggot P. J. Timing of spoII gene expression relative to septum formation during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5747–5749. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5747-5749.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas R. M., Haldenwang W. G. Influence of spo mutations on sigma E synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5226–5228. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5226-5228.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmazyn-Campelli C., Bonamy C., Savelli B., Stragier P. Tandem genes encoding sigma-factors for consecutive steps of development in Bacillus subtilis. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):150–157. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Stragier P. Crisscross regulation of cell-type-specific gene expression during development in B. subtilis. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):601–604. doi: 10.1038/355601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis P., Driks A., Losick R. Establishment of cell type by compartmentalized activation of a transcription factor. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):562–565. doi: 10.1126/science.1948031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda E. S., Anaguchi H., Yamada K., Kobayashi Y. Two developmental genes encoding sigma factor homologs are arranged in tandem in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7637–7641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead D. A., Szczesna-Skorupa E., Kemper B. Single-stranded DNA 'blue' T7 promoter plasmids: a versatile tandem promoter system for cloning and protein engineering. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):67–74. doi: 10.1093/protein/1.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge S. R., Foulger D., Errington J. The role of sigma F in prespore-specific transcription in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Mar;5(3):757–767. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00746.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J. Mapping of asporogenous mutations of Bacillus subtilis: a minimum estimate of the number of sporeulation operons. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1241–1253. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1241-1253.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rather P. N., Coppolecchia R., DeGrazia H., Moran C. P., Jr Negative regulator of sigma G-controlled gene expression in stationary-phase Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):709–715. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.709-715.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R., Margolis P., Duncan L., Coppolecchia R., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Control of developmental transcription factor sigma F by sporulation regulatory proteins SpoIIAA and SpoIIAB in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9221–9225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D. X., Cabrera-Martinez R. M., Setlow P. Control of transcription of the Bacillus subtilis spoIIIG gene, which codes for the forespore-specific transcription factor sigma G. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):2977–2984. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.2977-2984.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman M. D., Setlow P. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and regulation of the Bacillus subtilis gpr gene, which codes for the protease that initiates degradation of small, acid-soluble proteins during spore germination. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):291–300. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.291-300.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatti K. M., Jones C. H., Moran C. P., Jr Genetic evidence for interaction of sigma E with the spoIIID promoter in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(24):7828–7833. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.24.7828-7833.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. J., Howard M. G., Piggot P. J. Regulation of transcription of the Bacillus subtilis spoIIA locus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):692–698. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.692-698.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yudkin M. D., Jarvis K. A., Raven S. E., Fort P. Effects of transition mutations in the regulatory locus spoIIA on the incidence of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Apr;131(4):959–962. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-4-959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yudkin M. D. Structure and function in a Bacillus subtilis sporulation-specific sigma factor: molecular nature of mutations in spoIIAC. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):475–481. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yudkin M. D., Turley L. Suppression of asporogeny in Bacillus subtilis. Allele-specific suppression of a mutation in the spoIIA locus. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Nov;121(1):69–78. doi: 10.1099/00221287-121-1-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



