Abstract
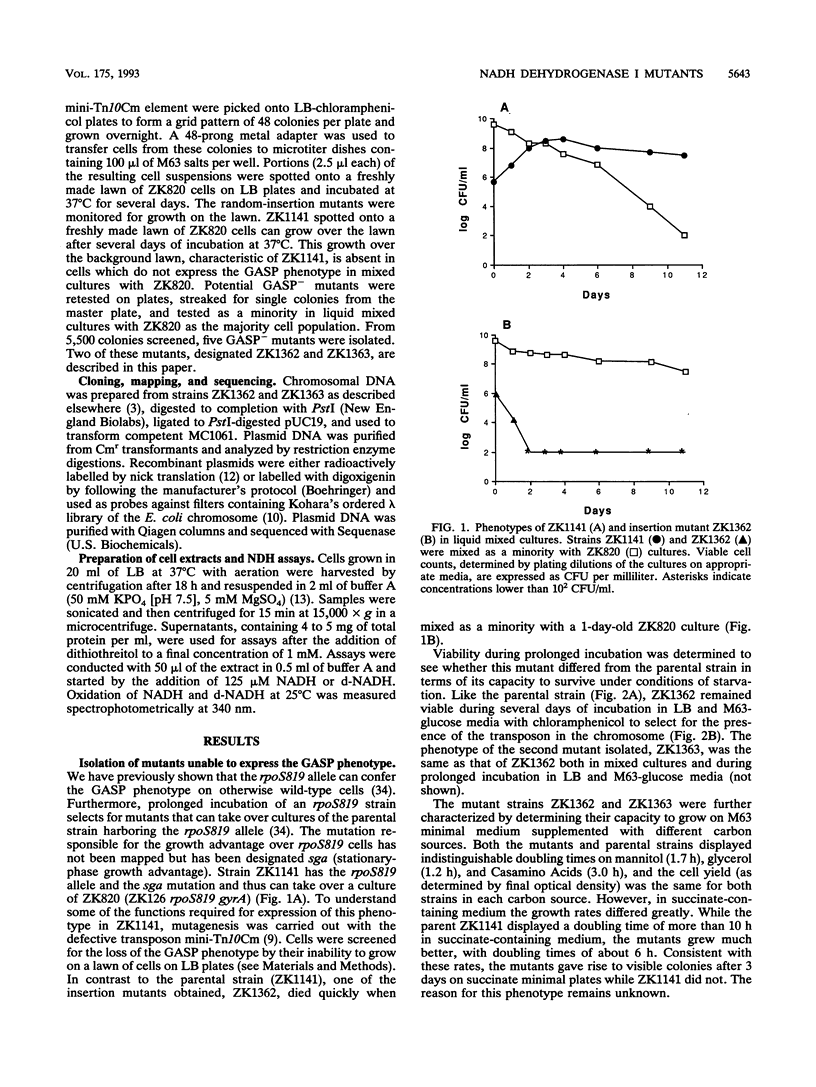
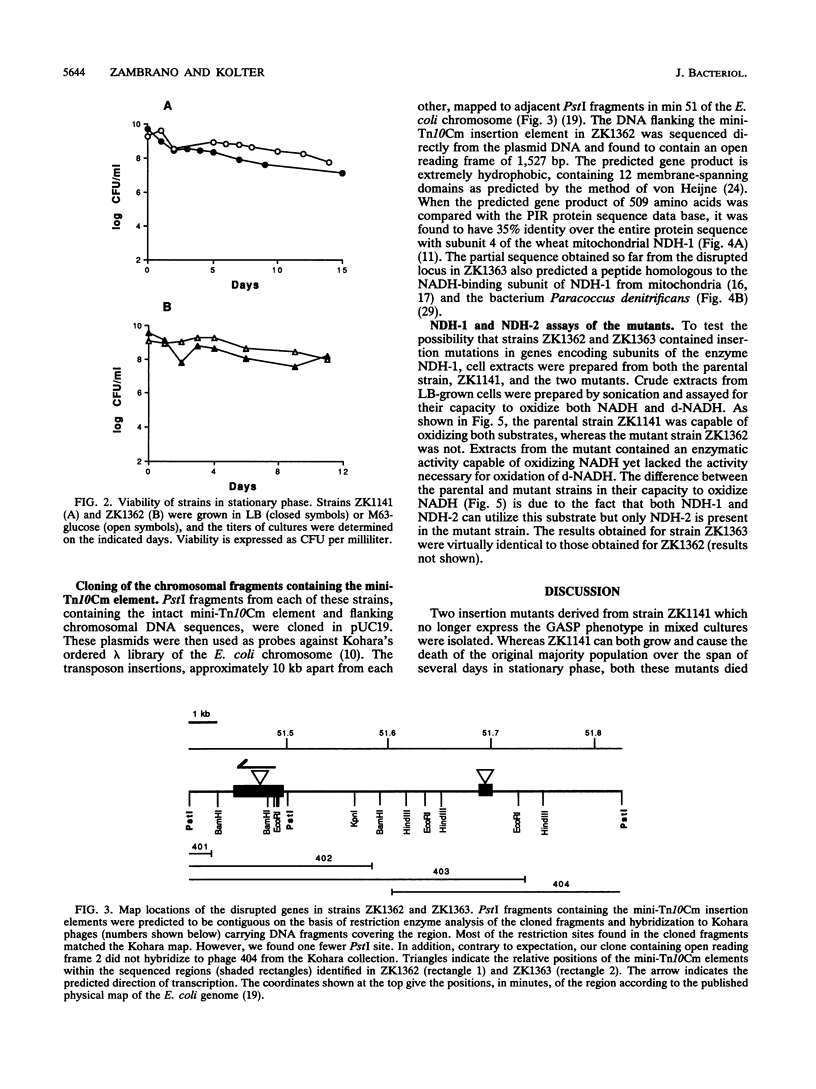
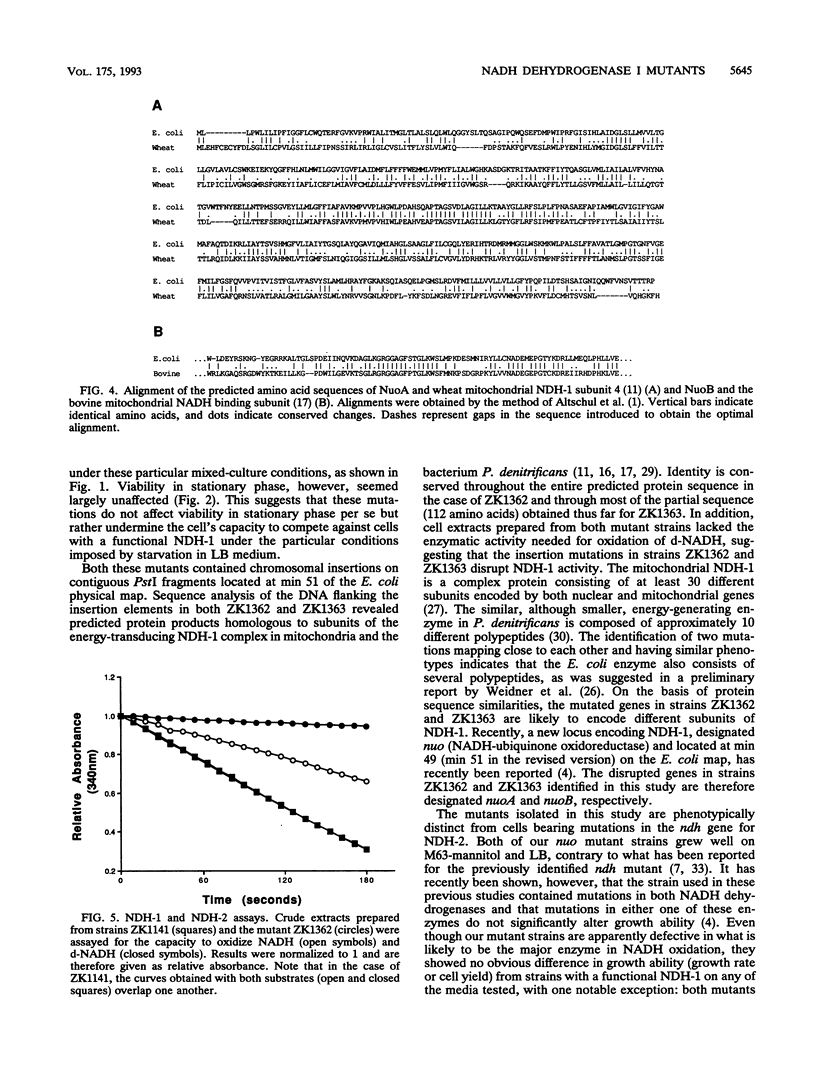
We have previously characterized mutant strains of Escherichia coli that are able to take over stationary-phase cultures. Here we describe two insertion mutations that prevent such strains from expressing this phenotype. Both insertions were mapped to min 51, and sequence analysis revealed that both mutated genes encode proteins homologous to subunits of mitochondrial NADH dehydrogenase I. Crude extracts prepared from both mutant strains were able to oxidize NADH but lacked the enzymatic activity needed to oxidize deamino-NADH, a substrate specific for NADH dehydrogenase I. This is the first identification of genes encoding subunits of NADH dehydrogenase I in E. coli. The significance of the inability of these mutant strains to compete in stationary-phase cultures is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anraku Y. Bacterial electron transport chains. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:101–132. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calhoun M. W., Gennis R. B. Demonstration of separate genetic loci encoding distinct membrane-bound respiratory NADH dehydrogenases in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(10):3013–3019. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.10.3013-3019.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M., Miyoshi T., Takashina S., Unemoto T. Purification of NADH-ferricyanide dehydrogenase and NADH-quinone reductase from Escherichia coli membranes and their roles in the respiratory chain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Oct 26;977(1):62–69. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(89)80009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengge-Aronis R. Survival of hunger and stress: the role of rpoS in early stationary phase gene regulation in E. coli. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):165–168. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90655-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imlay J., Fridovich I. Exogenous quinones directly inhibit the respiratory NADH dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Jul;296(1):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90581-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaworowski A., Mayo G., Shaw D. C., Campbell H. D., Young I. G. Characterization of the respiratory NADH dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli and reconstitution of NADH oxidase in ndh mutant membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 9;20(12):3621–3628. doi: 10.1021/bi00515a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Bender J., Gottesman S. Uses of transposons with emphasis on Tn10. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:139–180. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04009-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamattina L., Grienenberger J. M. RNA editing of the transcript coding for subunit 4 of NADH dehydrogenase in wheat mitochondria: uneven distribution of the editing sites among the four exons. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3275–3282. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita K., Ohnishi T., Kaback H. R. NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductases of the Escherichia coli aerobic respiratory chain. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7732–7737. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Kaback H. R. Immunochemical analysis of membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 17;18(8):1413–1422. doi: 10.1021/bi00575a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel S. D., Aebersold R., Attardi G. cDNA-derived amino acid sequence of the NADH-binding 51-kDa subunit of the bovine respiratory NADH dehydrogenase reveals striking similarities to a bacterial NAD(+)-reducing hydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4225–4229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilkington S. J., Skehel J. M., Gennis R. B., Walker J. E. Relationship between mitochondrial NADH-ubiquinone reductase and a bacterial NAD-reducing hydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 26;30(8):2166–2175. doi: 10.1021/bi00222a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puustinen A., Finel M., Haltia T., Gennis R. B., Wikström M. Properties of the two terminal oxidases of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 23;30(16):3936–3942. doi: 10.1021/bi00230a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegele D. A., Kolter R. Life after log. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(2):345–348. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.2.345-348.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro S., Roberts R. E., Guest J. R. FNR-dependent repression of the ndh gene of Escherichia coli and metal ion requirement for FNR-regulated gene expression. Mol Microbiol. 1989 May;3(5):601–608. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Takayanagi Y., Fujita N., Ishihama A., Takahashi H. Heterogeneity of the principal sigma factor in Escherichia coli: the rpoS gene product, sigma 38, is a second principal sigma factor of RNA polymerase in stationary-phase Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3511–3515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tormo A., Almirón M., Kolter R. surA, an Escherichia coli gene essential for survival in stationary phase. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4339–4347. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4339-4347.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way J. C., Davis M. A., Morisato D., Roberts D. E., Kleckner N. New Tn10 derivatives for transposon mutagenesis and for construction of lacZ operon fusions by transposition. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):369–379. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner U., Nehls U., Schneider R., Fecke W., Leif H., Schmiede A., Friedrich T., Zensen R., Schulte U., Ohnishi T. Molecular genetic studies of complex I in Neurospora crassa, Aspergillus niger and Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jul 17;1101(2):177–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H., Friedrich T., Hofhaus G., Preis D. The respiratory-chain NADH dehydrogenase (complex I) of mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1991 May 8;197(3):563–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15945.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertman K. F., Wyman A. R., Botstein D. Host/vector interactions which affect the viability of recombinant phage lambda clones. Gene. 1986;49(2):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X. M., Matsuno-Yagi A., Yagi T. The NADH-binding subunit of the energy-transducing NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase of Paracoccus denitrificans: gene cloning and deduced primary structure. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 2;30(26):6422–6428. doi: 10.1021/bi00240a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X., Matsuno-Yagi A., Yagi T. Structural features of the 66-kDa subunit of the energy-transducing NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase (NDH-1) of Paracoccus denitrificans. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Jul;296(1):40–48. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90542-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young I. G., Jaworowski A., Poulis M. I. Amplification of the respiratory NADH dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli by gene cloning. Gene. 1978 Sep;4(1):25–36. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young I. G., Rogers B. L., Campbell H. D., Jaworowski A., Shaw D. C. Nucleotide sequence coding for the respiratory NADH dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli. UUG initiation codon. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May;116(1):165–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young I. G., Wallace B. J. Mutations affecting the reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 6;449(3):376–385. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90149-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambrano M. M., Siegele D. A., Almirón M., Tormo A., Kolter R. Microbial competition: Escherichia coli mutants that take over stationary phase cultures. Science. 1993 Mar 19;259(5102):1757–1760. doi: 10.1126/science.7681219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Membrane protein structure prediction. Hydrophobicity analysis and the positive-inside rule. J Mol Biol. 1992 May 20;225(2):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90934-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


