Abstract
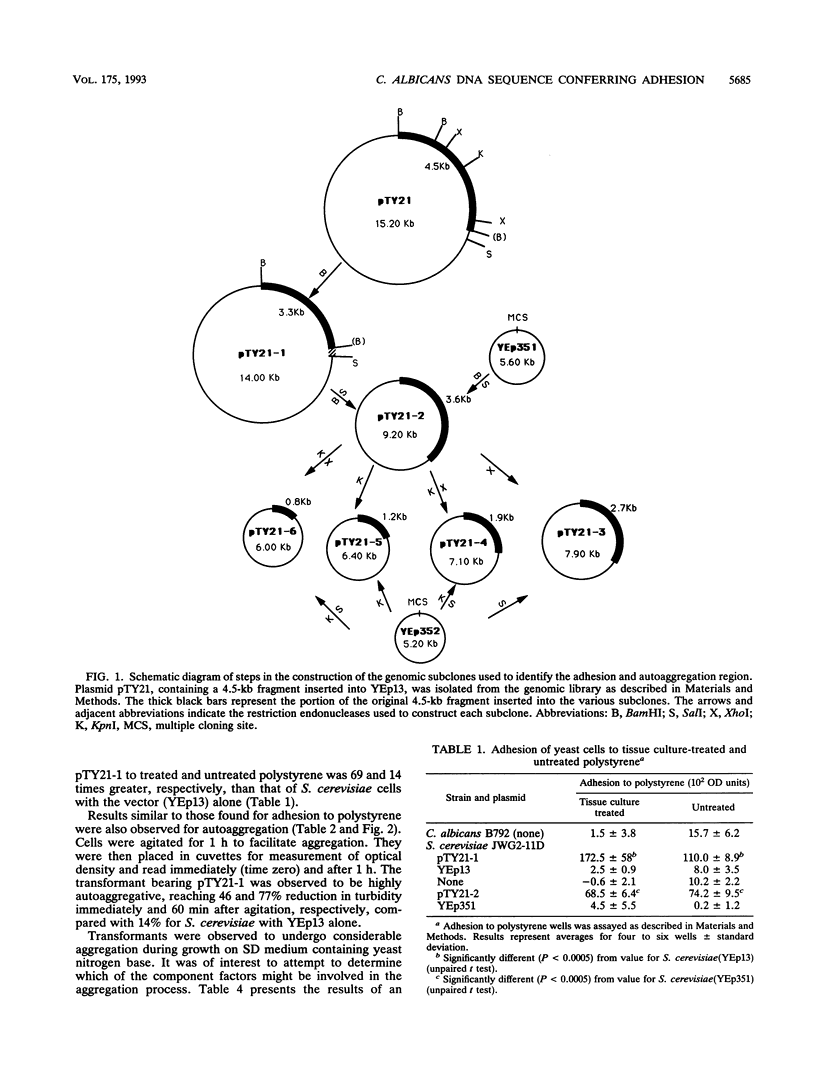
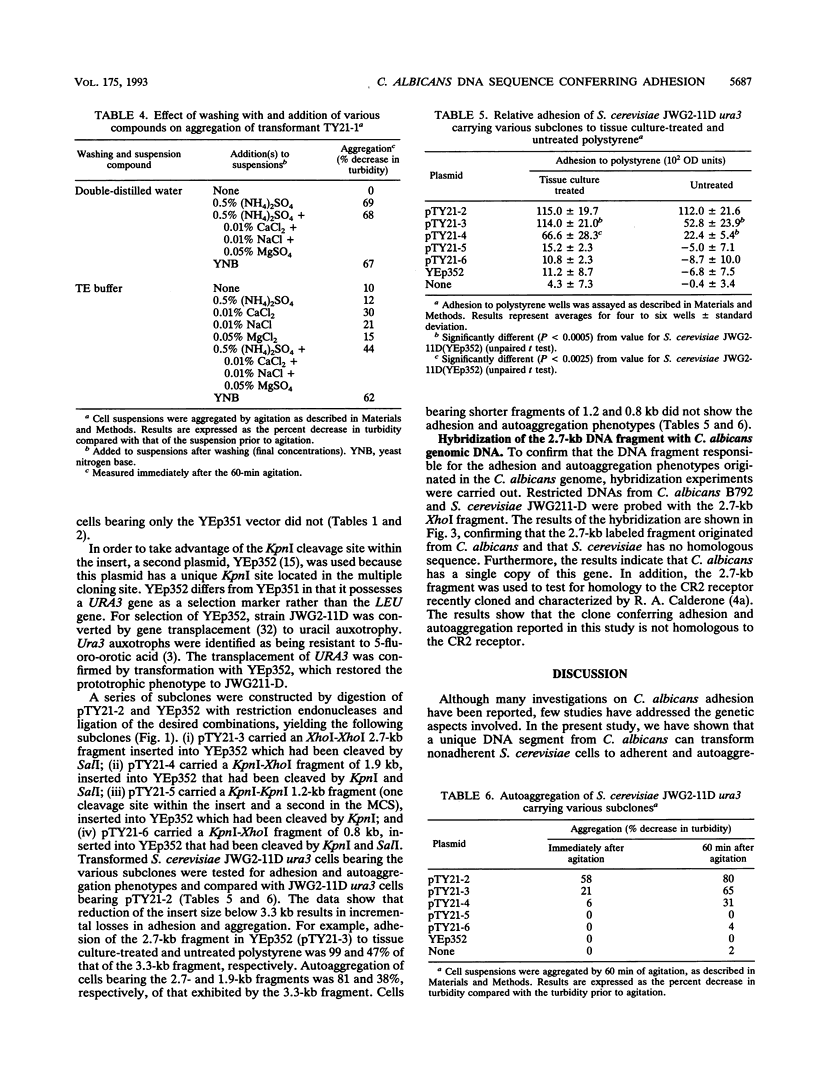
Candida albicans is an opportunistic pathogen which may give rise to superficial and systemic infections. In the present study, C. albicans adhesion was studied by expression of C. albicans DNA sequences encoding adhesion functions in a nonadherent strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Adherent transformant cells of S. cerevisiae harbouring a C. albicans genomic library cloned in a yeast-Escherichia coli shuttle vector were selected by using tissue culture-treated polystyrene as the attachment substratum. One transformant exhibited enhanced adhesion to treated and untreated polystyrene as well as autoaggregation, unlike control cells bearing the vector alone. Analysis of this clone revealed an insert of ca. 4.5 kb from C. albicans. Curing of the plasmid resulted in loss of adhesion and autoaggregation properties. A subclone bearing a reduced insert of 3.3 kb retained the ability to autoaggregate, to bind to treated and untreated polystyrene, and to adhere to buccal epithelial cells, unlike appropriate controls. Further subcloning of the insert to 2.7- and 1.9-kb fragments resulted in incremental decreases in adhesion and autoaggregation, whereas smaller fragments did not confer these properties. Hybridization of the 2.7-kb segment with C. albicans and S. cerevisiae DNA confirmed its origin as a single-copy sequence in the C. albicans genome as well as the absence of a homologous sequence in the genome of S. cerevisiae. The data suggest that the adhesion and aggregation phenomena of the transformant cells are related to expression of a C. albicans surface antigen encoded by the cloned DNA fragment.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R., Strathern J. N., Hicks J. B. Transformation in yeast: development of a hybrid cloning vector and isolation of the CAN1 gene. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):121–133. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderone R. A., Braun P. C. Adherence and receptor relationships of Candida albicans. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Mar;55(1):1–20. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.1.1-20.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung K. J., Hill W. B. Studies on the pink, adenine-deficient strains of Candida albicans. I. Cultural and morphological characteristics. Sabouraudia. 1970 May;8(1):48–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critchley I. A., Douglas L. J. Isolation and partial characterization of an adhesin from Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):629–636. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fling M. E., Kopf J., Tamarkin A., Gorman J. A., Smith H. A., Koltin Y. Analysis of a Candida albicans gene that encodes a novel mechanism for resistance to benomyl and methotrexate. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Jun;227(2):318–329. doi: 10.1007/BF00259685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghannoum M. A., Burns G. R., Elteen K. A., Radwan S. S. Experimental evidence for the role of lipids in adherence of Candida spp. to human buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):189–193. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.189-193.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen K. C., Brawner D. L., Riesselman M. H., Jutila M. A., Cutler J. E. Differential adherence of hydrophobic and hydrophilic Candida albicans yeast cells to mouse tissues. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):907–912. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.907-912.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen K. C., Hazen B. W. Hydrophobic surface protein masking by the opportunistic fungal pathogen Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1499–1508. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1499-1508.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen K. C., Lay J. G., Hazen B. W., Fu R. C., Murthy S. Partial biochemical characterization of cell surface hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3469–3476. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3469-3476.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen K. C. Participation of yeast cell surface hydrophobicity in adherence of Candida albicans to human epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1894–1900. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1894-1900.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Koerner T. J., Tzagoloff A. Yeast/E. coli shuttle vectors with multiple unique restriction sites. Yeast. 1986 Sep;2(3):163–167. doi: 10.1002/yea.320020304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Winston F. A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. J. Adhesion and association mechanisms of Candida albicans. Curr Top Med Mycol. 1988;2:73–169. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-3730-3_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. J., Calderone R. A., Cutler J. E., Kanabe T., Riesselman M. H., Robert R., Senet J. M., Annaix V., Bouali A., Mahaza C. Molecular basis of Candida albicans adhesion. J Med Vet Mycol. 1992;30 (Suppl 1):95–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. J., Rogers A. L., Yancey R. J., Jr Environmental alteration and phenotypic regulation of Candida albicans adhesion to plastic. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3876–3881. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3876-3881.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihn J. C., Masy C. L., Mestdagh M. M. Yeast flocculation: competition between nonspecific repulsion and specific bonding in cell adhesion. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Jun;34(6):773–778. doi: 10.1139/m88-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz M. B., Kirsch D. R., Kelly R. The molecular genetics of Candida albicans. Microbiol Sci. 1988 Feb;5(2):58–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie A. M., Rivera-Calderon R. L. Agar overlay method to measure adherence of Staphylococcus epidermidis to four plastic surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Nov;50(5):1322–1324. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.5.1322-1324.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollert M. W., Wadsworth E., Calderone R. A. Reduced expression of the functionally active complement receptor for iC3b but not for C3d on an avirulent mutant of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):909–913. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.909-913.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbluh A., Mevarech M., Koltin Y., Gorman J. A. Isolation of genes from Candida albicans by complementation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(3):500–502. doi: 10.1007/BF00425739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. Targeting, disruption, replacement, and allele rescue: integrative DNA transformation in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:281–301. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotrosen D., Calderone R. A., Edwards J. E., Jr Adherence of Candida species to host tissues and plastic surfaces. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Jan-Feb;8(1):73–85. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandin R. L., Rogers A. L. Inhibition of adherence of Candida albicans to human epithelial cells. Mycopathologia. 1982 Jan 15;77(1):23–26. doi: 10.1007/BF00588652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Magee P. T. Genetics of Candida albicans. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Sep;54(3):226–241. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.3.226-241.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. A., Gorman J. W., Koltin Y., Gorman J. A. Functional expression of the Candida albicans beta-tubulin gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1990 May 31;90(1):115–123. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90446-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel J. D., Myers P. G., Kaye D., Levison M. E. Adherence of Candida albicans to human vaginal and buccal epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jan;143(1):76–82. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.1.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronchin G., Bouchara J. P., Robert R., Senet J. M. Adherence of Candida albicans germ tubes to plastic: ultrastructural and molecular studies of fibrillar adhesins. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1987–1993. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1987-1993.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels J. G., de Vries O. M., Asgeirsdóttir S. A., Springer J. The thn mutation of Schizophyllum commune, which suppresses formation of aerial hyphae, affects expression of the Sc3 hydrophobin gene. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Oct;137(10):2439–2445. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-10-2439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels JGH., De Vries OMH., Asgeirsdottir S. A., Schuren FHJ. Hydrophobin Genes Involved in Formation of Aerial Hyphae and Fruit Bodies in Schizophyllum. Plant Cell. 1991 Aug;3(8):793–799. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.8.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]