Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austin S., Dixon R. The prokaryotic enhancer binding protein NTRC has an ATPase activity which is phosphorylation and DNA dependent. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2219–2228. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05281.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M., Norman D. G., Campbell I. D. Protein modules. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jan;16(1):13–17. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90009-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkmann A., Böck A. Characterization of a cis regulatory DNA element necessary for formate induction of the formate dehydrogenase gene (fdhF) of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Feb;3(2):187–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb01807.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan R. G., Matthews B. W. The helix-turn-helix DNA binding motif. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):1903–1906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck M., Cannon W. Specific binding of the transcription factor sigma-54 to promoter DNA. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):422–424. doi: 10.1038/358422a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck M., Cannon W., Woodcock J. Transcriptional activation of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase promoter may involve DNA loop formation. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Sep;1(2):243–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buikema W. J., Szeto W. W., Lemley P. V., Orme-Johnson W. H., Ausubel F. M. Nitrogen fixation specific regulatory genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Rhizobium meliloti share homology with the general nitrogen regulatory gene ntrC of K. pneumoniae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4539–4555. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon W. V., Kreutzer R., Kent H. M., Morett E., Buck M. Activation of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifU promoter: identification of multiple and overlapping upstream NifA binding sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1693–1701. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon W., Charlton W., Buck M. Organization and function of binding sites for the transcriptional activator NifA in the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifE and nifU promoters. J Mol Biol. 1991 Aug 20;220(4):915–931. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90363-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras A., Drummond M. The effect on the function of the transcriptional activator NtrC from Klebsiella pneumoniae of mutations in the DNA-recognition helix. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):4025–4039. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.4025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornish E. C., Argyropoulos V. P., Pittard J., Davidson B. E. Structure of the Escherichia coli K12 regulatory gene tyrR. Nucleotide sequence and sites of initiation of transcription and translation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):403–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
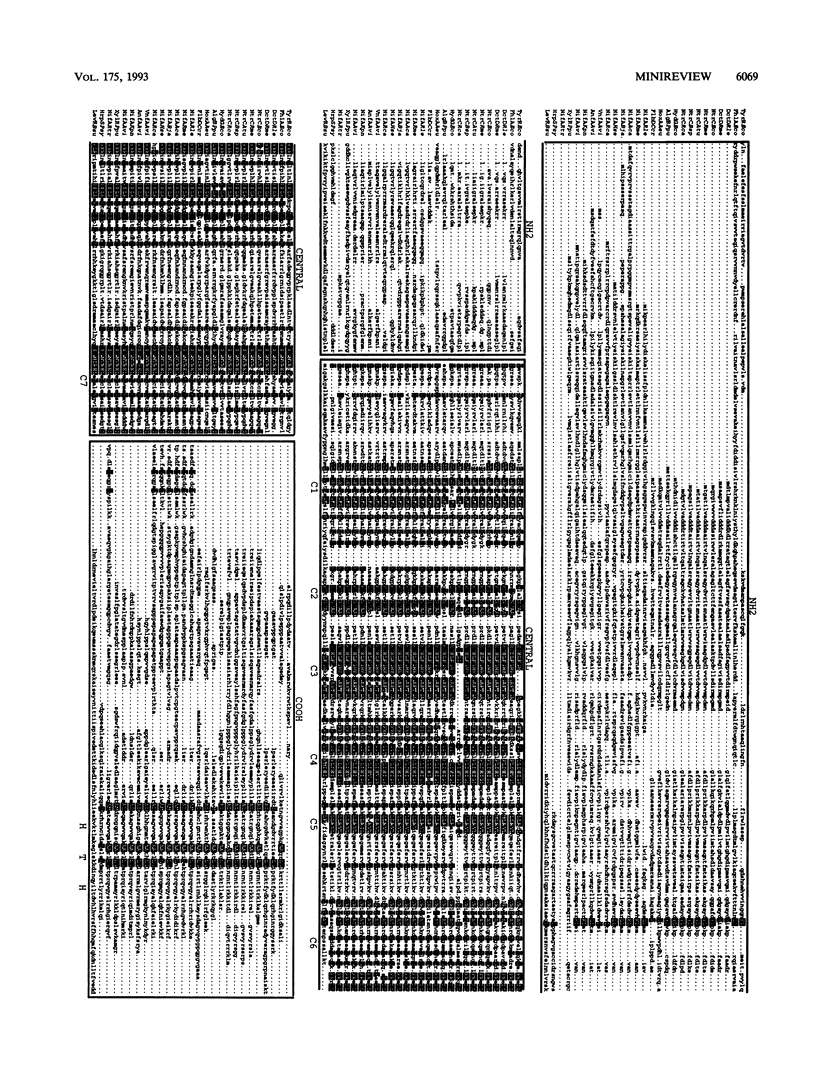
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Virts E., Palomares A., Kim C. H. The nifA gene of Rhizobium meliloti is oxygen regulated. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3217–3223. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3217-3223.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd I. B., Egan J. B. Improved detection of helix-turn-helix DNA-binding motifs in protein sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5019–5026. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Stein and Moore Award address. Reconstructing history with amino acid sequences. Protein Sci. 1992 Feb;1(2):191–200. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond M. H., Contreras A., Mitchenall L. A. The function of isolated domains and chimaeric proteins constructed from the transcriptional activators NifA and NtrC of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jan;4(1):29–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02012.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond M., Whitty P., Wootton J. Sequence and domain relationships of ntrC and nifA from Klebsiella pneumoniae: homologies to other regulatory proteins. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):441–447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04230.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Débarbouillé M., Martin-Verstraete I., Klier A., Rapoport G. The transcriptional regulator LevR of Bacillus subtilis has domains homologous to both sigma 54- and phosphotransferase system-dependent regulators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2212–2216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Débarbouillé M., Martin-Verstraete I., Kunst F., Rapoport G. The Bacillus subtilis sigL gene encodes an equivalent of sigma 54 from gram-negative bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9092–9096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive sequence alignment as a prerequisite to correct phylogenetic trees. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):351–360. doi: 10.1007/BF02603120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H M, Hennecke H. Direct response of Bradyrhizobium japonicum nifA-mediated nif gene regulation to cellular oxygen status. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Oct;209(3):621–626. doi: 10.1007/BF00331174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H. M., Bruderer T., Hennecke H. Essential and non-essential domains in the Bradyrhizobium japonicum NifA protein: identification of indispensable cysteine residues potentially involved in redox reactivity and/or metal binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2207–2224. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster-Hartnett D., Kranz R. G. Analysis of the promoters and upstream sequences of nifA1 and nifA2 in Rhodobacter capsulatus; activation requires ntrC but not rpoN. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Apr;6(8):1049–1060. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb02170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Kim P. S. Modular structure of transcription factors: implications for gene regulation. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):717–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90378-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry D. C., Kuby S. A., Mildvan A. S. ATP-binding site of adenylate kinase: mechanistic implications of its homology with ras-encoded p21, F1-ATPase, and other nucleotide-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):907–911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover T. R., Santero E., Porter S., Kustu S. The integration host factor stimulates interaction of RNA polymerase with NIFA, the transcriptional activator for nitrogen fixation operons. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90284-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huala E., Ausubel F. M. The central domain of Rhizobium meliloti NifA is sufficient to activate transcription from the R. meliloti nifH promoter. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3354–3365. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3354-3365.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huala E., Stigter J., Ausubel F. M. The central domain of Rhizobium leguminosarum DctD functions independently to activate transcription. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(4):1428–1431. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.4.1428-1431.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R., Haselkorn R. The DNA sequence of the Rhodobacter capsulatus ntrA, ntrB and ntrC gene analogues required for nitrogen fixation. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Feb;215(3):507–516. doi: 10.1007/BF00427050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kranz R. G., Pace V. M., Caldicott I. M. Inactivation, sequence, and lacZ fusion analysis of a regulatory locus required for repression of nitrogen fixation genes in Rhodobacter capsulatus. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):53–62. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.53-62.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S., North A. K., Weiss D. S. Prokaryotic transcriptional enhancers and enhancer-binding proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90163-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S., Santero E., Keener J., Popham D., Weiss D. Expression of sigma 54 (ntrA)-dependent genes is probably united by a common mechanism. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):367–376. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.367-376.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonetto M., Gribskov M., Gross C. A. The sigma 70 family: sequence conservation and evolutionary relationships. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):3843–3849. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.3843-3849.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minchin S. D., Austin S., Dixon R. A. Transcriptional activation of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifLA promoter by NTRC is face-of-the-helix dependent and the activator stabilizes the interaction of sigma 54-RNA polymerase with the promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3491–3499. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08514.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morett E., Buck M. In vivo studies on the interaction of RNA polymerase-sigma 54 with the Klebsiella pneumoniae and Rhizobium meliloti nifH promoters. The role of NifA in the formation of an open promoter complex. J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 5;210(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morett E., Cannon W., Buck M. The DNA-binding domain of the transcriptional activator protein NifA resides in its carboxy terminus, recognises the upstream activator sequences of nif promoters and can be separated from the positive control function of NifA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11469–11488. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morett E., Fischer H. M., Hennecke H. Influence of oxygen on DNA binding, positive control, and stability of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum NifA regulatory protein. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3478–3487. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3478-3487.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. M., Gerster T., Schaffner W. Enhancer sequences and the regulation of gene transcription. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 1;176(3):485–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14306.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North A. K., Klose K. E., Stedman K. M., Kustu S. Prokaryotic enhancer-binding proteins reflect eukaryote-like modularity: the puzzle of nitrogen regulatory protein C. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(14):4267–4273. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.14.4267-4273.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittard A. J., Davidson B. E. TyrR protein of Escherichia coli and its role as repressor and activator. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jul;5(7):1585–1592. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popham D. L., Szeto D., Keener J., Kustu S. Function of a bacterial activator protein that binds to transcriptional enhancers. Science. 1989 Feb 3;243(4891):629–635. doi: 10.1126/science.2563595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitzer L. J., Magasanik B. Transcription of glnA in E. coli is stimulated by activator bound to sites far from the promoter. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):785–792. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90553-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitzer L. J., Movsas B., Magasanik B. Activation of glnA transcription by nitrogen regulator I (NRI)-phosphate in Escherichia coli: evidence for a long-range physical interaction between NRI-phosphate and RNA polymerase. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5512–5522. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5512-5522.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronson C. W., Astwood P. M., Nixon B. T., Ausubel F. M. Deduced products of C4-dicarboxylate transport regulatory genes of Rhizobium leguminosarum are homologous to nitrogen regulatory gene products. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7921–7934. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
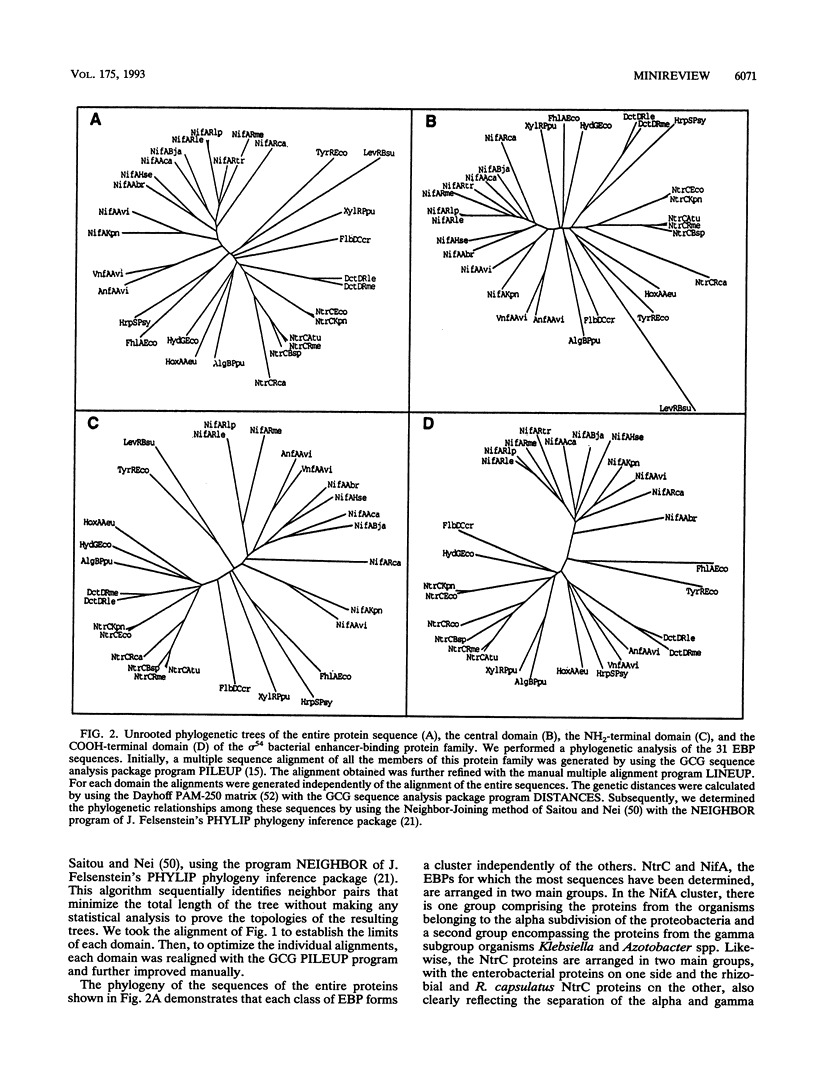
- Saitou N., Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasse-Dwight S., Gralla J. D. Role of eukaryotic-type functional domains found in the prokaryotic enhancer receptor factor sigma 54. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):945–954. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90269-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiau S. P., Chen P., Reitzer L. J. Effects of insertions and deletions in glnG (ntrC) of Escherichia coli on nitrogen regulator I-dependent DNA binding and transcriptional activation. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;175(1):190–199. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.1.190-199.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Stock A. M., Mottonen J. M. Signal transduction in bacteria. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):395–400. doi: 10.1038/344395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su W., Porter S., Kustu S., Echols H. DNA-looping and enhancer activity: association between DNA-bound NtrC activator and RNA polymerase at the bacterial glnA promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5504–5508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thöny B., Hennecke H. The -24/-12 promoter comes of age. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;5(4):341–357. doi: 10.1016/0168-6445(89)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., Carey M., Gralla J. D. Polymerase II promoter activation: closed complex formation and ATP-driven start site opening. Science. 1992 Jan 24;255(5043):450–453. doi: 10.1126/science.1310361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedel A., Weiss D. S., Popham D., Dröge P., Kustu S. A bacterial enhancer functions to tether a transcriptional activator near a promoter. Science. 1990 Apr 27;248(4954):486–490. doi: 10.1126/science.1970441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss D. S., Batut J., Klose K. E., Keener J., Kustu S. The phosphorylated form of the enhancer-binding protein NTRC has an ATPase activity that is essential for activation of transcription. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):155–167. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90579-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss V., Magasanik B. Phosphorylation of nitrogen regulator I (NRI) of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8919–8923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


