Abstract
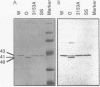
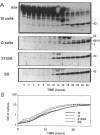
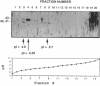
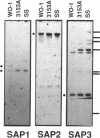
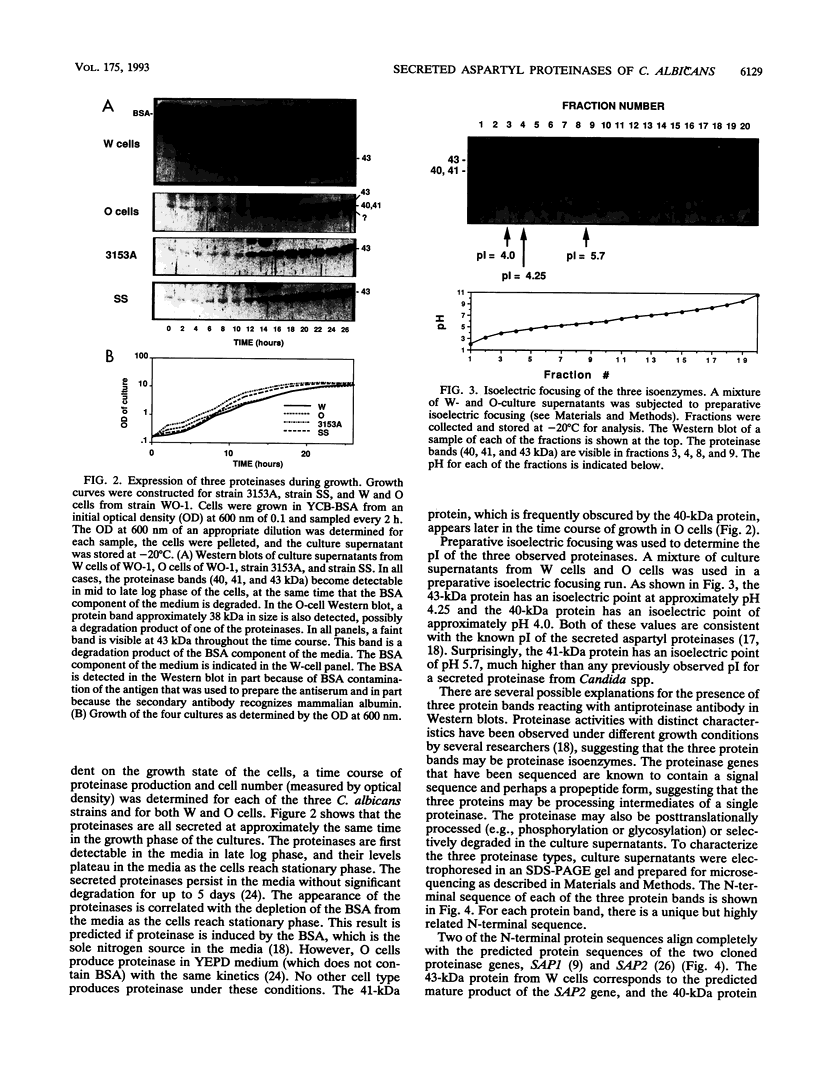
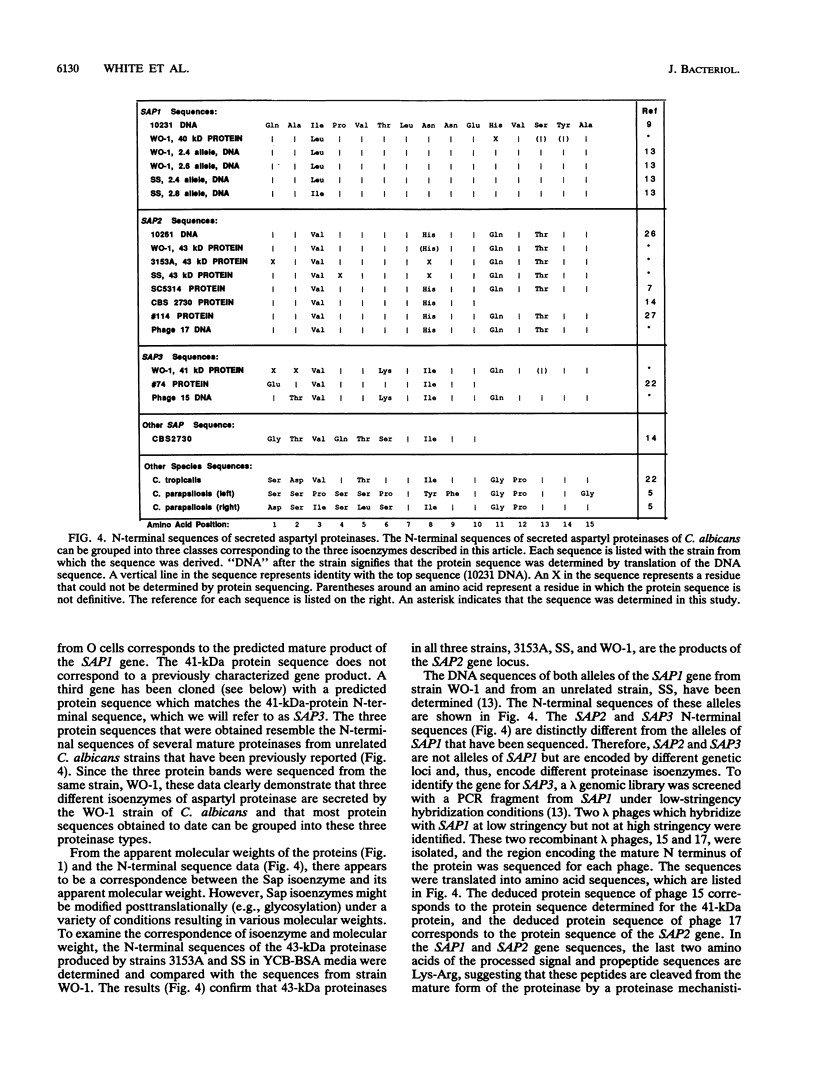
The secreted aspartyl proteinases of Candida albicans (products of the SAP genes) are thought to contribute to virulence through their effects on Candida adherence, invasion, and pathogenicity. From a single strain of C. albicans (WO-1) which expresses a phenotypic switching system, three secreted aspartyl proteinases have been identified as determined by molecular weight and N-terminal sequence. Each of the three identified proteins represents the mature form of one of three distinct proteinase isoenzymes, two of which correspond to the recently cloned SAP1 and SAP2 genes (previously referred to as CAP, PEP, or PRA). A genomic library was screened under low-stringency hybridization conditions with a polymerase chain reaction fragment from SAP1. In addition to clones of SAP1 and SAP2, a clone containing SAP3, a novel third secreted proteinase gene, was identified and sequenced. The three aspartyl proteinase isoenzymes differ in primary sequence and pI, suggesting that they may play different roles in virulence and pathogenesis. All three of these proteinases are expressed in the same strain. However, the pattern of proteinase expression is correlated with the switch phenotype of the cell. Opaque cells of strain WO-1 express Sap1 and Sap3, while white cells of the same strain express Sap2. The differential expression of three Sap proteinases may contribute to virulence in C. albicans.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. M., Soll D. R. Unique phenotype of opaque cells in the white-opaque transition of Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5579–5588. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5579-5588.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. E. Putative virulence factors of Candida albicans. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:187–218. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.001155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas L. J. Candida proteinases and candidosis. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 1988;8(2):121–129. doi: 10.3109/07388558809150541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganesan K., Banerjee A., Datta A. Molecular cloning of the secretory acid proteinase gene from Candida albicans and its use as a species-specific probe. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):2972–2977. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.2972-2977.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hube B., Turver C. J., Odds F. C., Eiffert H., Boulnois G. J., Köchel H., Rüchel R. Sequence of the Candida albicans gene encoding the secretory aspartate proteinase. J Med Vet Mycol. 1991;29(2):129–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Brake A., Blair L., Kunisawa R., Thorner J. Isolation of the putative structural gene for the lysine-arginine-cleaving endopeptidase required for processing of yeast prepro-alpha-factor. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1075–1089. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90442-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lott T. J., Page L. S., Boiron P., Benson J., Reiss E. Nucleotide sequence of the Candida albicans aspartyl proteinase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1779–1779. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison C. J., Hurst S. F., Bragg S. L., Kuykendall R. J., Diaz H., Pohl J., Reiss E. Heterogeneity of the purified extracellular aspartyl proteinase from Candida albicans: characterization with monoclonal antibodies and N-terminal amino acid sequence analysis. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):2030–2036. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.2030-2036.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow B., Srikantha T., Soll D. R. Transcription of the gene for a pepsinogen, PEP1, is regulated by white-opaque switching in Candida albicans. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):2997–3005. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.2997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüchel R., de Bernardis F., Ray T. L., Sullivan P. A., Cole G. T. Candida acid proteinases. J Med Vet Mycol. 1992;30 (Suppl 1):123–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slutsky B., Staebell M., Anderson J., Risen L., Pfaller M., Soll D. R. "White-opaque transition": a second high-frequency switching system in Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):189–197. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.189-197.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll D. R. High-frequency switching in Candida albicans. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1992 Apr;5(2):183–203. doi: 10.1128/cmr.5.2.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staib F. Serum-proteins as nitrogen source for yeastlike fungi. Sabouraudia. 1965 Oct;4(3):187–193. doi: 10.1080/00362176685190421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Togni G., Sanglard D., Falchetto R., Monod M. Isolation and nucleotide sequence of the extracellular acid protease gene (ACP) from the yeast Candida tropicalis. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jul 29;286(1-2):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80969-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward M. P., Young W. W., Jr, Bloodgood R. A. Detection of monoclonal antibodies specific for carbohydrate epitopes using periodate oxidation. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Apr 8;78(1):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90337-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright R. J., Carne A., Hieber A. D., Lamont I. L., Emerson G. W., Sullivan P. A. A second gene for a secreted aspartate proteinase in Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(23):7848–7853. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.23.7848-7853.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Nohara K., Uchida K., Yamaguchi H. Purification and characterization of secretory proteinase of Candida albicans. Microbiol Immunol. 1992;36(6):637–641. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1992.tb02064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Viragh P. A., Sanglard D., Togni G., Falchetto R., Monod M. Cloning and sequencing of two Candida parapsilosis genes encoding acid proteases. J Gen Microbiol. 1993 Feb;139(2):335–342. doi: 10.1099/00221287-139-2-335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]