Abstract
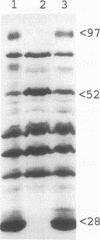
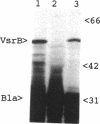
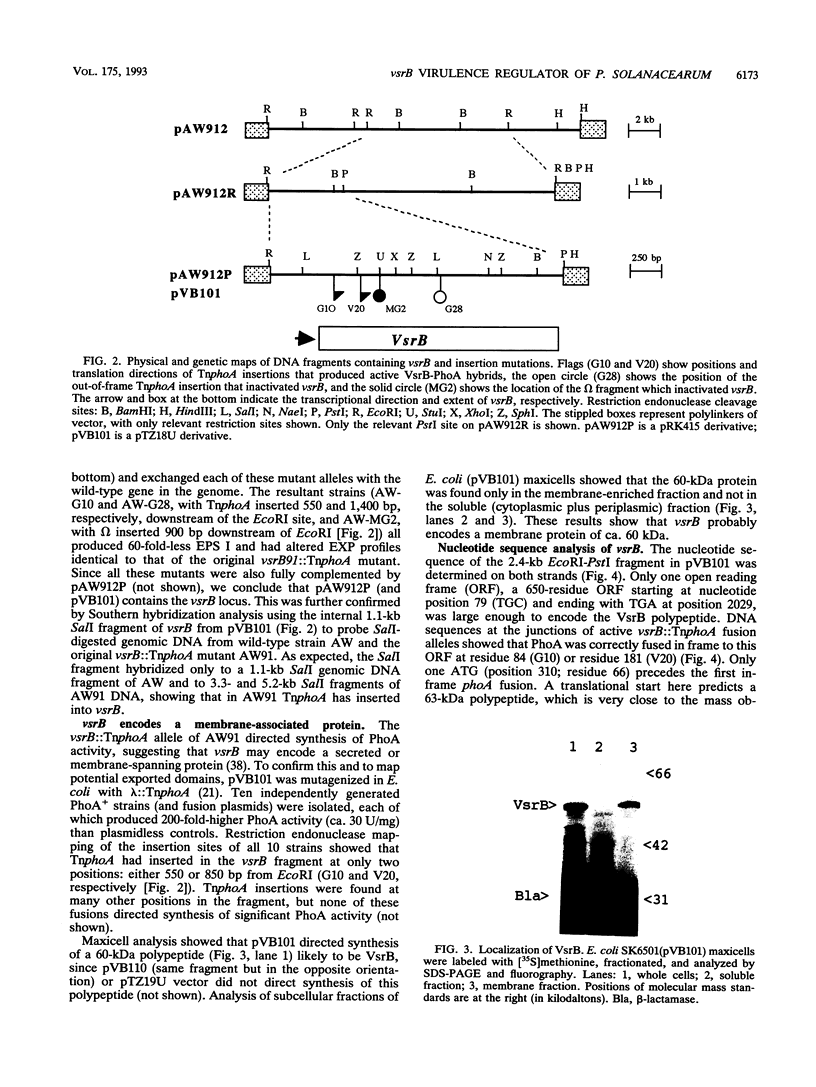
Pseudomonas solanacearum, an important wilt pathogen of many plants, produces several extracellular proteins (EXPs) and extracellular polysaccharides (EPSs) that contribute to its virulence. Using TnphoA mutagenesis, we discovered a new gene, vsrB, that when inactivated causes a major reduction in the virulence and production of an EPS. Analysis of eps::lacZ reporters showed that vsrB is required for maximal expression (transcription) of eps, whose products are required for production of EPS I, a major virulence determinant. Analysis of EXPs in culture supernatants revealed that inactivation of vsrB also causes reduced production of two major EXPs, with molecular masses of 28 and 97 kDa, and a simultaneous 15-fold increase in levels of another EXP, PglA endopolygalacturonase. The vsrB gene was cloned from a P. solanacearum genomic library by complementation of the nonmucoid phenotype of the vsrB::TnphoA mutant and then subcloned on a 2.4-kb DNA fragment. TnphoA fusion analysis and subcellular localization of the vsrB gene product in Escherichia coli maxicells suggest that it is a ca. 60-kDa transmembrane protein. The nucleotide sequence of the 2.4-kb DNA fragment was determined, and a 638-amino-acid open reading frame was found for VsrB. A search of the GenBank data base found that the central part of VsrB has homology with the histidine kinase domain of sensors in the two-component regulator family, while the C terminus has homology with the phosphate receiver domain of response regulators in the same family. Genetic analysis suggests that the receiver domain is not required for vsrB function.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albright L. M., Huala E., Ausubel F. M. Prokaryotic signal transduction mediated by sensor and regulator protein pairs. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:311–336. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldea M., Garrido T., Hernández-Chico C., Vicente M., Kushner S. R. Induction of a growth-phase-dependent promoter triggers transcription of bolA, an Escherichia coli morphogene. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3923–3931. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08573.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher C. A., Van Gijsegem F., Barberis P. A., Arlat M., Zischek C. Pseudomonas solanacearum genes controlling both pathogenicity on tomato and hypersensitivity on tobacco are clustered. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5626–5632. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5626-5632.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumbley S. M., Carney B. F., Denny T. P. Phenotype conversion in Pseudomonas solanacearum due to spontaneous inactivation of PhcA, a putative LysR transcriptional regulator. J Bacteriol. 1993 Sep;175(17):5477–5487. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.17.5477-5487.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumbley S. M., Denny T. P. Cloning of wild-type Pseudomonas solanacearum phcA, a gene that when mutated alters expression of multiple traits that contribute to virulence. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5677–5685. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5677-5685.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cangelosi G. A., Ankenbauer R. G., Nester E. W. Sugars induce the Agrobacterium virulence genes through a periplasmic binding protein and a transmembrane signal protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6708–6712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney B. F., Denny T. P. A cloned avirulence gene from Pseudomonas solanacearum determines incompatibility on Nicotiana tabacum at the host species level. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4836–4843. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4836-4843.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. H., Winans S. C. Functional roles assigned to the periplasmic, linker, and receiver domains of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens VirA protein. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(21):7033–7039. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.21.7033-7039.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D., Sequeira L. Genetic and biochemical characterization of a Pseudomonas solanacearum gene cluster required for extracellular polysaccharide production and for virulence. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1654–1662. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1654-1662.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRita V. J. Co-ordinate expression of virulence genes by ToxR in Vibrio cholerae. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(4):451–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez C., Barondess J., Manoil C., Beckwith J. The use of transposon TnphoA to detect genes for cell envelope proteins subject to a common regulatory stimulus. Analysis of osmotically regulated genes in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 20;195(2):289–297. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90650-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrabak E. M., Willis D. K. The lemA gene required for pathogenicity of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae on bean is a member of a family of two-component regulators. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(9):3011–3020. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.9.3011-3020.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. Z., Sukordhaman M., Schell M. A. Excretion of the egl gene product of Pseudomonas solanacearum. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3767–3774. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3767-3774.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. L., Cangelosi G. A., Halperin W., Nester E. W. A chromosomal Agrobacterium tumefaciens gene required for effective plant signal transduction. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):1814–1822. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.1814-1822.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S., Lin E. C. Mutational analysis of signal transduction by ArcB, a membrane sensor protein responsible for anaerobic repression of operons involved in the central aerobic pathways in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):3972–3980. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.3972-3980.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S., Matsuda Z., Fujiwara T., Lin E. C. The arcB gene of Escherichia coli encodes a sensor-regulator protein for anaerobic repression of the arc modulon. Mol Microbiol. 1990 May;4(5):715–727. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00642.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn D., Ditta G. Modular structure of FixJ: homology of the transcriptional activator domain with the -35 binding domain of sigma factors. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Apr;5(4):987–997. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00774.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen N. T., Tamaki S., Kobayashi D., Trollinger D. Improved broad-host-range plasmids for DNA cloning in gram-negative bacteria. Gene. 1988 Oct 15;70(1):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelman A., Hruschka J. The role of motility and aerotaxis in the selective increase of avirulent bacteria in still broth cultures of Pseudomonas solanacearum. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 May;76(1):177–188. doi: 10.1099/00221287-76-1-177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroux B., Yanofsky M. F., Winans S. C., Ward J. E., Ziegler S. F., Nester E. W. Characterization of the virA locus of Agrobacterium tumefaciens: a transcriptional regulator and host range determinant. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):849–856. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04830.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Mekalanos J. J., Beckwith J. Alkaline phosphatase fusions: sensors of subcellular location. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):515–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.515-518.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride M. J., Weinberg R. A., Zusman D. R. "Frizzy" aggregation genes of the gliding bacterium Myxococcus xanthus show sequence similarities to the chemotaxis genes of enteric bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):424–428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead D. A., Skorupa E. S., Kemper B. Single stranded DNA SP6 promoter plasmids for engineering mutant RNAs and proteins: synthesis of a 'stretched' preproparathyroid hormone. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1103–1118. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J. Environmental signals controlling expression of virulence determinants in bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.1-7.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Mekalanos J. J., Falkow S. Coordinate regulation and sensory transduction in the control of bacterial virulence. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):916–922. doi: 10.1126/science.2537530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa S., Tokishita S., Aiba H., Mizuno T. A novel sensor-regulator protein that belongs to the homologous family of signal-transduction proteins involved in adaptive responses in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Mar;6(6):799–807. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orgambide G., Montrozier H., Servin P., Roussel J., Trigalet-Demery D., Trigalet A. High heterogeneity of the exopolysaccharides of Pseudomonas solanacearum strain GMI 1000 and the complete structure of the major polysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8312–8321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Krisch H. M. In vitro insertional mutagenesis with a selectable DNA fragment. Gene. 1984 Sep;29(3):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. P., Denny T. P., Schell M. A. Cloning of the egl gene of Pseudomonas solanacearum and analysis of its role in phytopathogenicity. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1445–1451. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1445-1451.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell M. A. Purification and Characterization of an Endoglucanase from Pseudomonas solanacearum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Sep;53(9):2237–2241. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.9.2237-2241.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell M. A., Roberts D. P., Denny T. P. Analysis of the Pseudomonas solanacearum polygalacturonase encoded by pglA and its involvement in phytopathogenicity. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4501–4508. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4501-4508.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuurman R., Keulen W. Modified protocol for DNA sequence analysis using Sequenase 2.0. Biotechniques. 1991 Feb;10(2):185–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki T., Yoshikawa H., Takahashi H., Saito H. Nucleotide sequence of the Bacillus subtilis phoR gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5935–5938. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5935-5938.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., Nester E. W. The genetic and transcriptional organization of the vir region of the A6 Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1445–1454. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibitz S., Yang M. S. Subcellular localization and immunological detection of proteins encoded by the vir locus of Bordetella pertussis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4288–4296. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4288-4296.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout V., Gottesman S. RcsB and RcsC: a two-component regulator of capsule synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):659–669. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.659-669.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walderhaug M. O., Polarek J. W., Voelkner P., Daniel J. M., Hesse J. E., Altendorf K., Epstein W. KdpD and KdpE, proteins that control expression of the kdpABC operon, are members of the two-component sensor-effector class of regulators. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(7):2152–2159. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.7.2152-2159.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber R. F., Silverman P. M. The cpx proteins of Escherichia coli K12. Structure of the cpxA polypeptide as an inner membrane component. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 20;203(2):467–478. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winans S. C. An Agrobacterium two-component regulatory system for the detection of chemicals released from plant wounds. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Oct;5(10):2345–2350. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]