Abstract
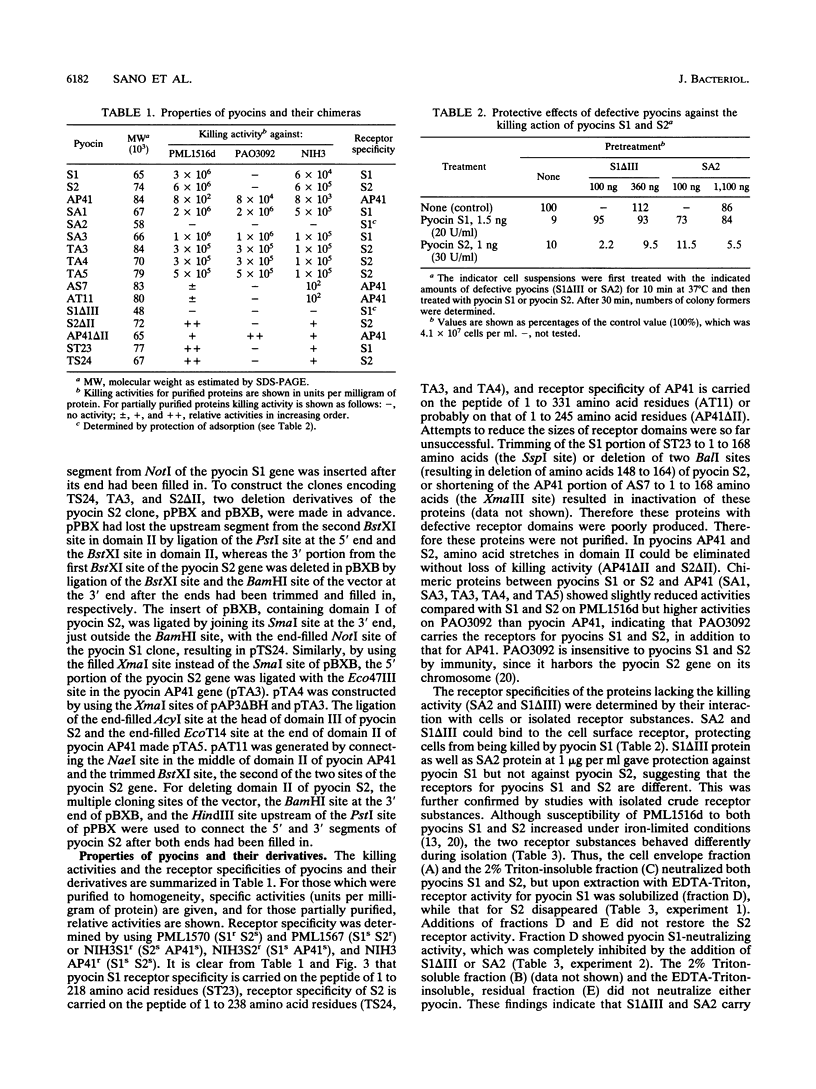
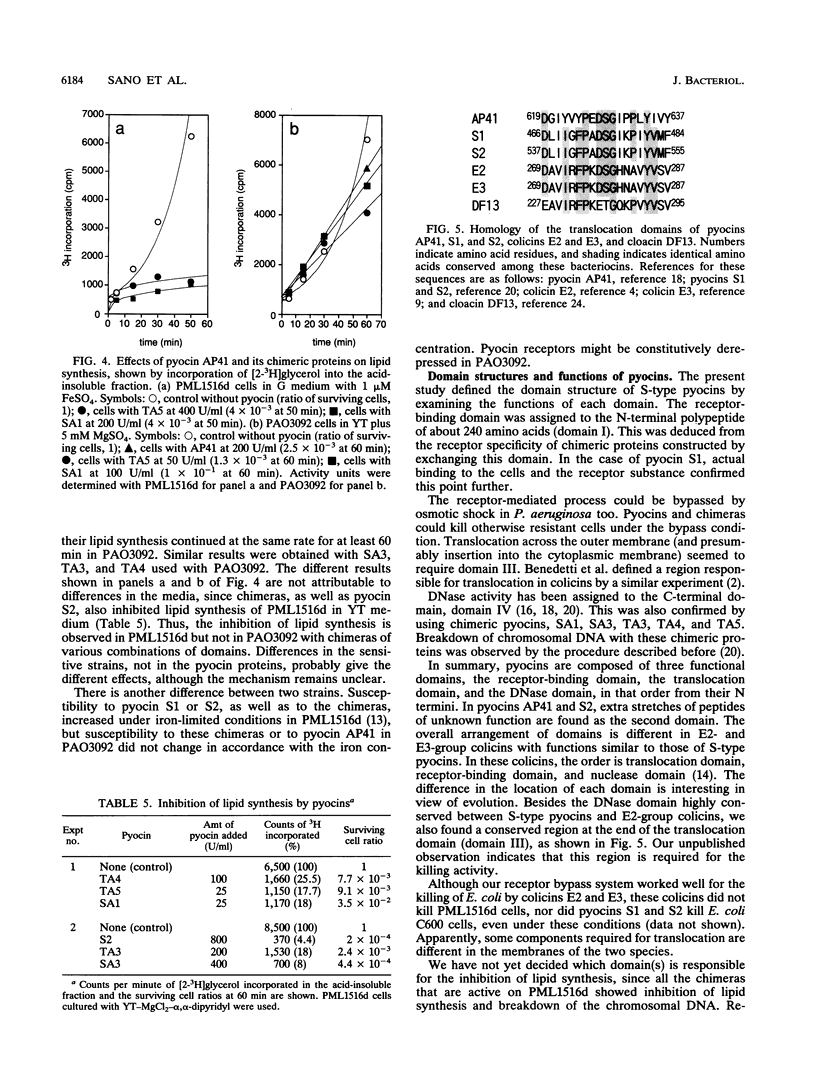
Functional domain structures of pyocins AP41, S1, and S2 were assigned by examining the functions of chimeric pyocins and deletion derivatives. Pyocins AP41, S1, and S2 are essentially composed of three domains, the receptor-binding domain, the translocation domain, and the DNase domain, in that order from the N terminus to the C terminus. The alignment of these domains is distinct from that in E2-group colicins with functions similar to those of these pyocins. Pyocins AP41 and S2 have a fourth domain between the receptor-binding and the translocation domains, which is dispensable for their killing functions.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appleyard R K. Segregation of New Lysogenic Types during Growth of a Doubly Lysogenic Strain Derived from Escherichia Coli K12. Genetics. 1954 Jul;39(4):440–452. doi: 10.1093/genetics/39.4.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti H., Frenette M., Baty D., Lloubès R., Geli V., Lazdunski C. Comparison of the uptake systems for the entry of various BtuB group colicins into Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Dec;135(12):3413–3420. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-12-3413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole S. T., Saint-Joanis B., Pugsley A. P. Molecular characterisation of the colicin E2 operon and identification of its products. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;198(3):465–472. doi: 10.1007/BF00332940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eick-Helmerich K., Braun V. Import of biopolymers into Escherichia coli: nucleotide sequences of the exbB and exbD genes are homologous to those of the tolQ and tolR genes, respectively. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5117–5126. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5117-5126.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., 3rd, Herman L. G. Epidemiological fingerprinting of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by the production of and sensitivity of pyocin and bacteriophage. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):760–765. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.760-765.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazdunski C. J., Baty D., Geli V., Cavard D., Morlon J., Lloubes R., Howard S. P., Knibiehler M., Chartier M., Varenne S. The membrane channel-forming colicin A: synthesis, secretion, structure, action and immunity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Oct 11;947(3):445–464. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masaki H., Ohta T. Colicin E3 and its immunity genes. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 20;182(2):217–227. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90340-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui H., Sano Y., Ishihara H., Shinomiya T. Regulation of pyocin genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by positive (prtN) and negative (prtR) regulatory genes. J Bacteriol. 1993 Mar;175(5):1257–1263. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.5.1257-1263.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkawa I., Shiga S., Kageyama M. Effect of iron concentration in the growth medium on the sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to pyocin S2. J Biochem. 1980 Jan;87(1):323–331. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno-Iwashita Y., Imahori K. Assignment of the functional loci in colicin E2 and E3 molecules by the characterization of their proteolytic fragments. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 19;19(4):652–659. doi: 10.1021/bi00545a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okawa I., Kageyama M., Egami F. Purification and properties of pyocin S2. J Biochem. 1973 Feb;73(2):281–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okawa I., Maruo B., Kageyama M. Preferential inhibition of lipid synthesis by the bacteriocin pyocin S2. J Biochem. 1975 Jul;78(1):213–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano Y., Kageyama M. A novel transposon-like structure carries the genes for pyocin AP41, a Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriocin with a DNase domain homology to E2 group colicins. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Feb;237(1-2):161–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00282797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano Y., Kageyama M. Purification and properties of an S-type pyocin, pyocin AP41. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):733–739. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.733-739.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano Y., Matsui H., Kobayashi M., Kageyama M. Molecular structures and functions of pyocins S1 and S2 in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(10):2907–2916. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.10.2907-2916.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano Y. The inherent DNase of pyocin AP41 causes breakdown of chromosomal DNA. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(3):912–915. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.3.912-915.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Effect of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, Triton X-100, and lysozyme on the morphology and chemical composition of isolate cell walls of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):553–563. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.553-563.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by Triton X-100. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):545–552. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.545-552.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilby M., Hindennach I., Henning U. Bypass of receptor-mediated resistance to colicin E3 in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):1189–1191. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.1189-1191.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Elzen P. J., Walters H. H., Veltkamp E., Nijkamp H. J. Molecular structure and function of the bacteriocin gene and bacteriocin protein of plasmid Clo DF13. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2465–2477. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


