Abstract
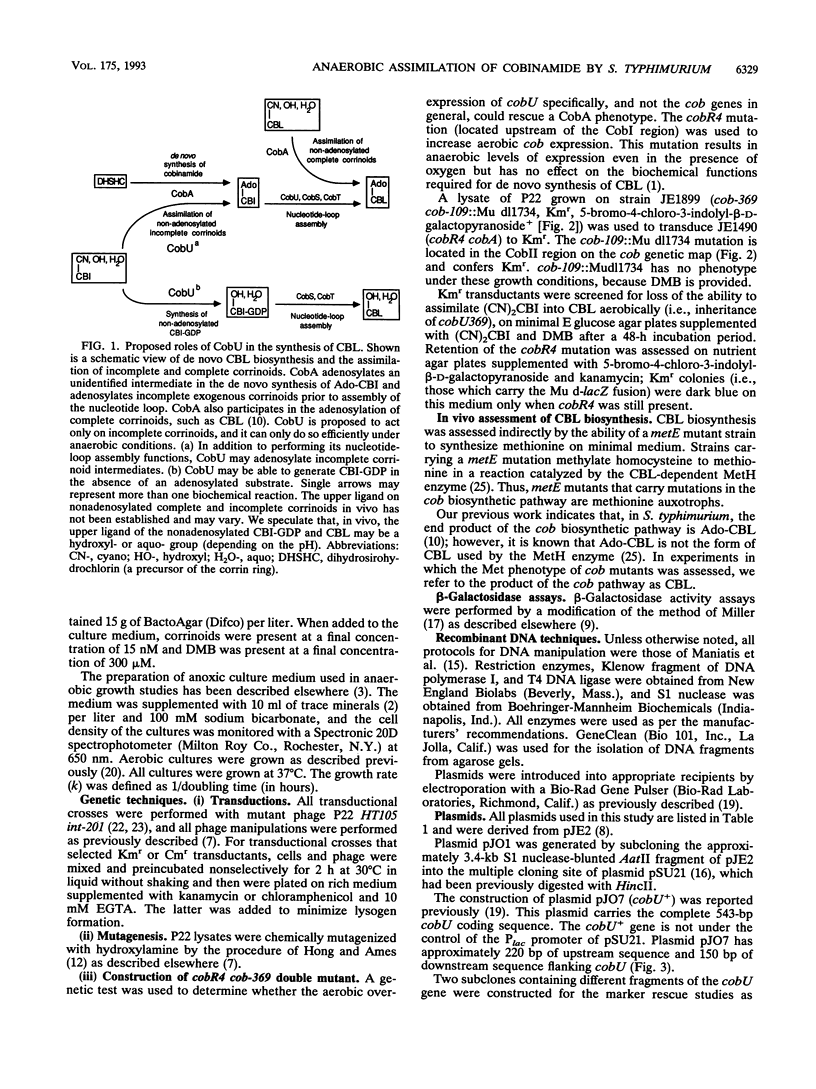
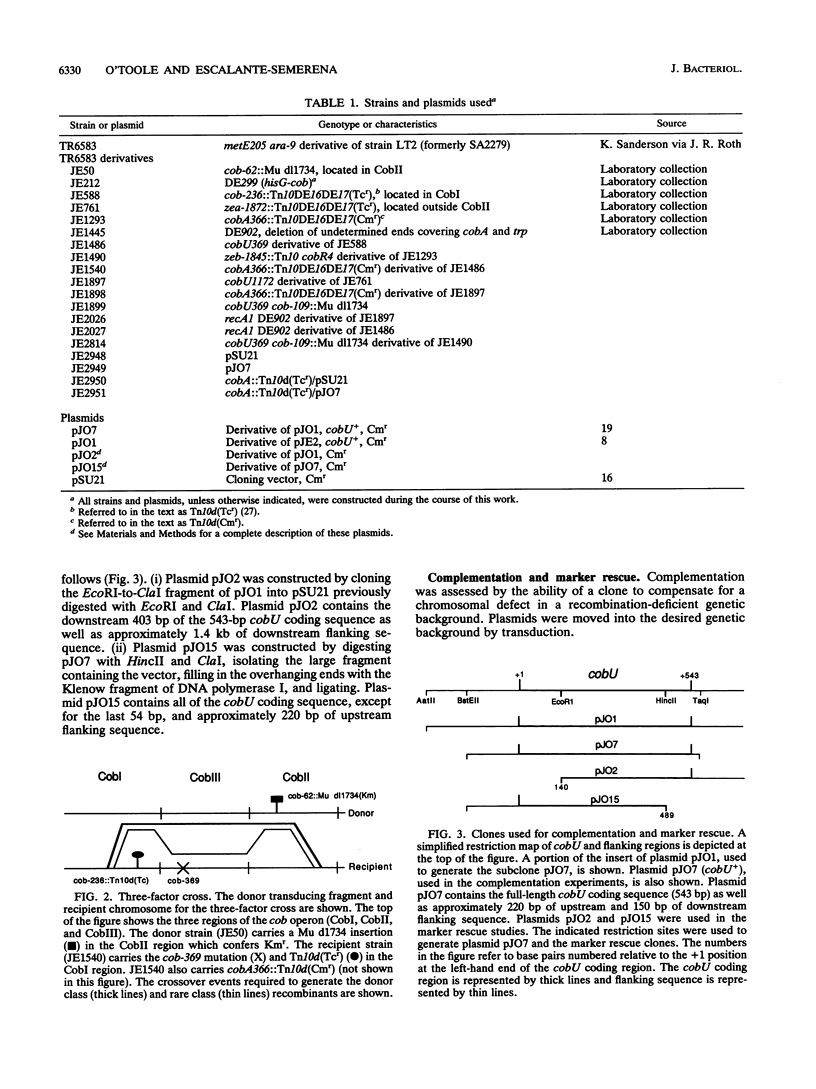
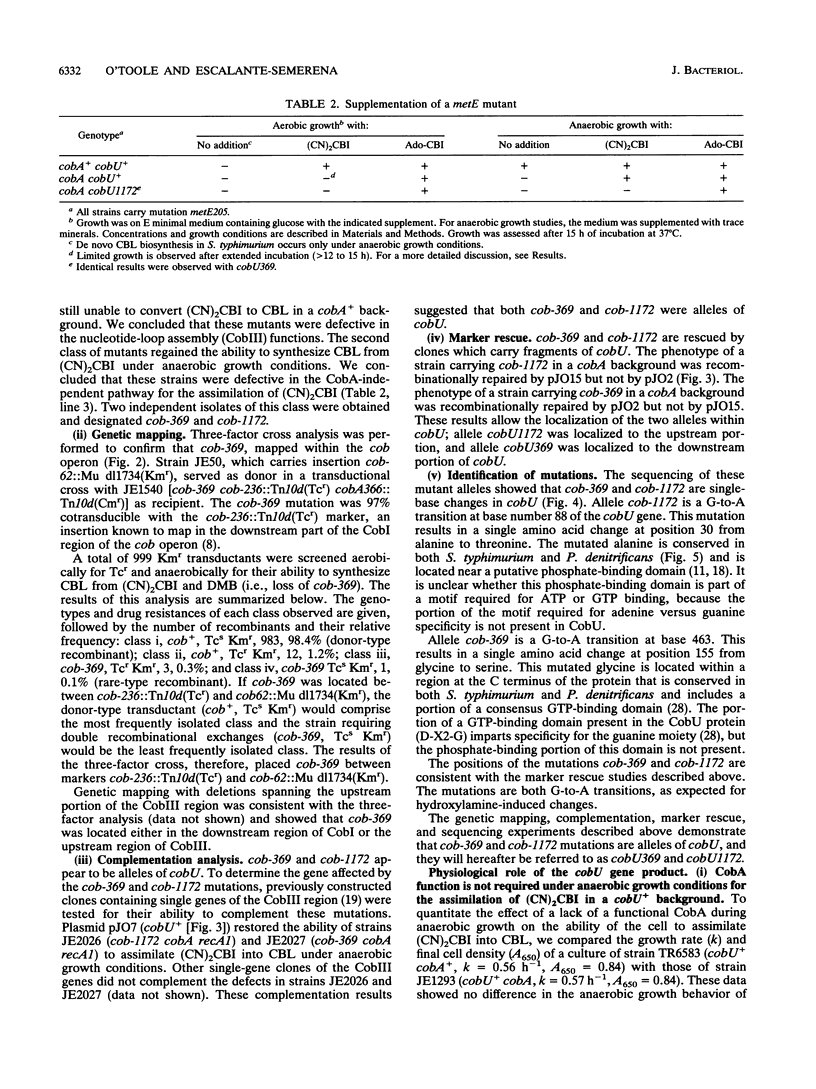
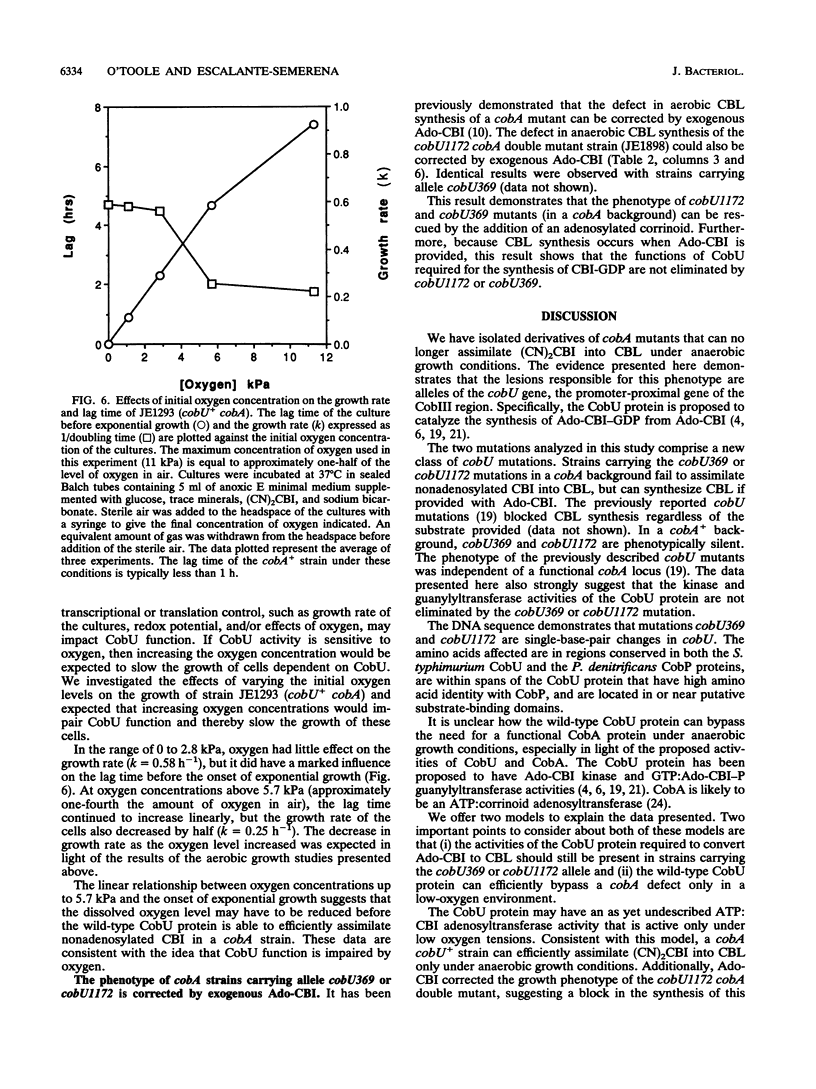
The cobA locus of Salmonella typhimurium is involved in the assimilation of nonadenosylated cobinamide, (CN)2CBI, into cobalamin (CBL) under aerobic and anaerobic growth conditions. Aerobically, cobA mutants are unable to assimilate (CN)2CBI into CBL. However, under anaerobic conditions, cobA mutants assimilate (CN)2CBI into CBL as efficiently as cobA+ strains. On the basis of this observation, we postulated the existence of a cobA-independent pathway for the assimilation of (CN)2CBI into CBL that is functional under anaerobic growth conditions (J. C. Escalante-Semerena, S.-J. Suh, and J. R. Roth, J. Bacteriol. 172:273-280, 1990). In this paper, we report the isolation and initial genetic characterization of derivatives of cobA mutants that are unable to assimilate (CN)2CBI into CBL during anaerobic growth. As demonstrated by complementation analysis, marker rescue, and DNA sequencing data, these mutations are alleles of cobU, a gene involved in the assembly of the nucleotide loop of CBL. We have shown that the block in CBL synthesis in these cobU cobA double mutant strains can be corrected by exogenous adenosyl-CBI. Our data indicate that this new class of cobU mutations blocks CBL biosynthesis but does not destroy the putative kinase-guanylyltransferase activities of the CobU protein. We propose that this new class of cobU mutations may affect an as yet unidentified ATP:corrinoid adenosyltransferase activity of the CobU protein. Alternatively, such mutations may alter the ability of CobU to use nonadenosylated CBI as a substrate.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson D. I., Roth J. R. Redox regulation of the genes for cobinamide biosynthesis in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6734–6739. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6734-6739.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Fox G. E., Magrum L. J., Woese C. R., Wolfe R. S. Methanogens: reevaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Jun;43(2):260–296. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.2.260-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Wolfe R. S. New approach to the cultivation of methanogenic bacteria: 2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid (HS-CoM)-dependent growth of Methanobacterium ruminantium in a pressureized atmosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Dec;32(6):781–791. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.6.781-791.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanche F., Debussche L., Famechon A., Thibaut D., Cameron B., Crouzet J. A bifunctional protein from Pseudomonas denitrificans carries cobinamide kinase and cobinamide phosphate guanylyltransferase activities. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):6052–6057. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.6052-6057.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron B., Blanche F., Rouyez M. C., Bisch D., Famechon A., Couder M., Cauchois L., Thibaut D., Debussche L., Crouzet J. Genetic analysis, nucleotide sequence, and products of two Pseudomonas denitrificans cob genes encoding nicotinate-nucleotide: dimethylbenzimidazole phosphoribosyltransferase and cobalamin (5'-phosphate) synthase. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):6066–6073. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.6066-6073.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouzet J., Levy-Schil S., Cameron B., Cauchois L., Rigault S., Rouyez M. C., Blanche F., Debussche L., Thibaut D. Nucleotide sequence and genetic analysis of a 13.1-kilobase-pair Pseudomonas denitrificans DNA fragment containing five cob genes and identification of structural genes encoding Cob(I)alamin adenosyltransferase, cobyric acid synthase, and bifunctional cobinamide kinase-cobinamide phosphate guanylyltransferase. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):6074–6087. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.6074-6087.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escalante-Semerena J. C., Johnson M. G., Roth J. R. The CobII and CobIII regions of the cobalamin (vitamin B12) biosynthetic operon of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):24–29. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.24-29.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escalante-Semerena J. C., Roth J. R. Regulation of cobalamin biosynthetic operons in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2251–2258. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2251-2258.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escalante-Semerena J. C., Suh S. J., Roth J. R. cobA function is required for both de novo cobalamin biosynthesis and assimilation of exogenous corrinoids in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):273–280. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.273-280.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry D. C., Kuby S. A., Mildvan A. S. ATP-binding site of adenylate kinase: mechanistic implications of its homology with ras-encoded p21, F1-ATPase, and other nucleotide-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):907–911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S., Ames B. N. Localized mutagenesis of any specific small region of the bacterial chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3158–3162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeter R. M., Olivera B. M., Roth J. R. Salmonella typhimurium synthesizes cobalamin (vitamin B12) de novo under anaerobic growth conditions. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):206–213. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.206-213.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi A. K., Baichwal V., Ames G. F. Rapid polymerase chain reaction amplification using intact bacterial cells. Biotechniques. 1991 Jan;10(1):42, 44-5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez E., Bartolomé B., de la Cruz F. pACYC184-derived cloning vectors containing the multiple cloning site and lacZ alpha reporter gene of pUC8/9 and pUC18/19 plasmids. Gene. 1988 Aug 15;68(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90608-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller W., Amons R. Phosphate-binding sequences in nucleotide-binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 1;186(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81326-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole G. A., Rondon M. R., Escalante-Semerena J. C. Analysis of mutants of Salmonella typhimurium defective in the synthesis of the nucleotide loop of cobalamin. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jun;175(11):3317–3326. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.11.3317-3326.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rondon M. R., Escalante-Semerena J. C. The poc locus is required for 1,2-propanediol-dependent transcription of the cobalamin biosynthetic (cob) and propanediol utilization (pdu) genes of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(7):2267–2272. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.7.2267-2272.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. R., Lawrence J. G., Rubenfield M., Kieffer-Higgins S., Church G. M. Characterization of the cobalamin (vitamin B12) biosynthetic genes of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jun;175(11):3303–3316. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.11.3303-3316.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieger H. A method for detection of phage mutants with altered transducing ability. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;110(4):378–381. doi: 10.1007/BF00438281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieger H., Backhaus H. The origin of DNA in transducing particles in P22-mutants with increased transduction-frequencies (HT-mutants). Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Jan 24;120(2):181–190. doi: 10.1007/BF00267246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh S. J., Escalante-Semerena J. C. Cloning, sequencing and overexpression of cobA which encodes ATP:corrinoid adenosyltransferase in Salmonella typhimurium. Gene. 1993 Jul 15;129(1):93–97. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90701-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way J. C., Davis M. A., Morisato D., Roberts D. E., Kleckner N. New Tn10 derivatives for transposon mutagenesis and for construction of lacZ operon fusions by transposition. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):369–379. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



