Abstract
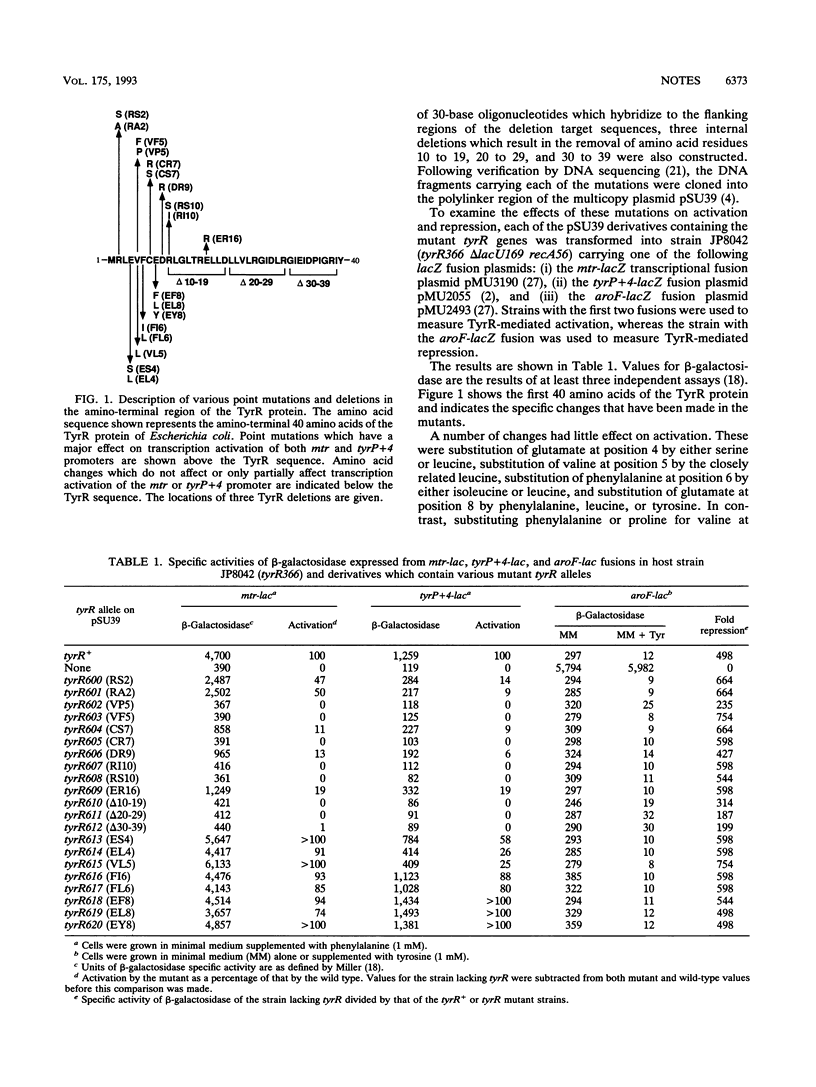
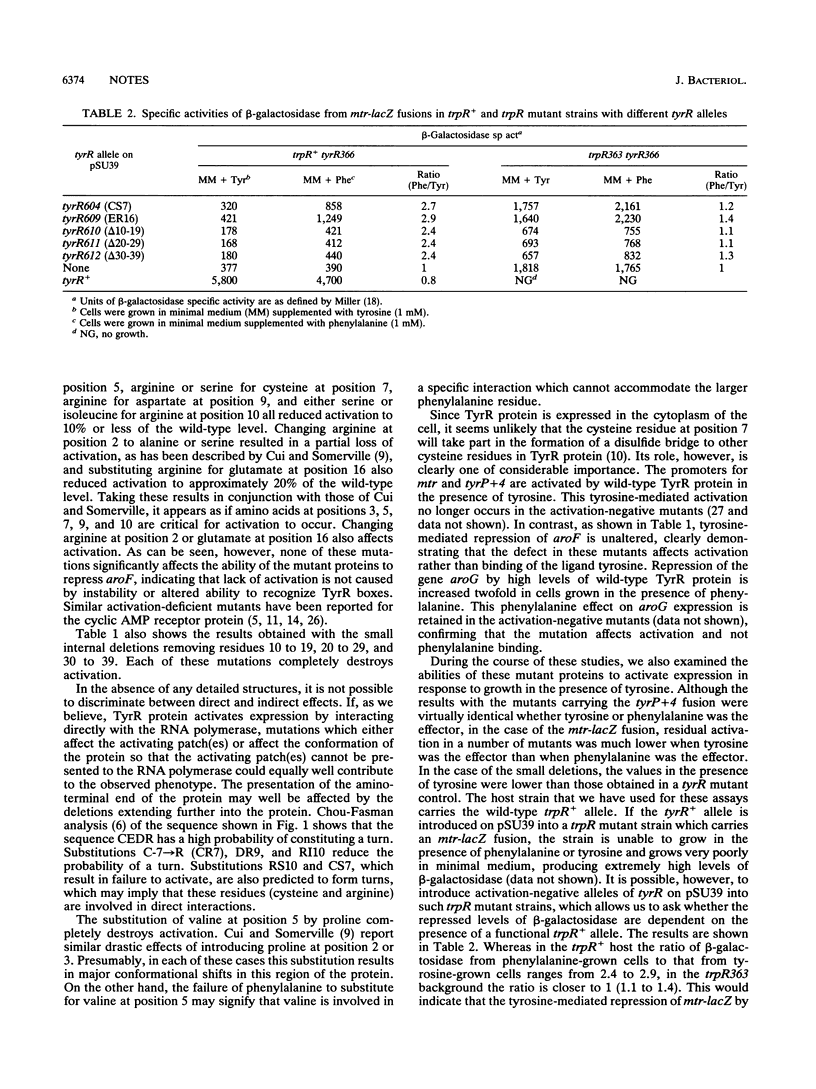
Site-directed mutagenesis has been used to further characterize amino acid residues necessary for the activation of gene expression by the TyrR protein. Amino acid substitutions have been made at positions 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, and 16. TyrR mutants with amino acid substitutions V-5-->P (VP5), VF5, CS7, CR7, DR9, RI10, RS10, and ER16 show no or very little activation of expression of either mtr or tyrP. In each case, however, the ability to repress aroF is unaltered. Amino acid substitutions at positions 4, 6, and 8 have no effect on activation. Small internal deletions of residues 10 to 19, 20 to 29, or 30 to 39 also destroy phenylalanine- or tyrosine-mediated activation of mtr and tyrP. In these mutants repression of aroF is also unaltered. In activation-defective tyrR mutants, expression of mtr is repressed in the presence of tyrosine. This tyrosine-mediated repression is trpR dependent and implies an interaction between TrpR and TyrR proteins in the presence of tyrosine.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews A. E., Dickson B., Lawley B., Cobbett C., Pittard A. J. Importance of the position of TYR R boxes for repression and activation of the tyrP and aroF genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5079–5085. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5079-5085.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews A. E., Lawley B., Pittard A. J. Mutational analysis of repression and activation of the tyrP gene in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5068–5078. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5068-5078.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartolomé B., Jubete Y., Martínez E., de la Cruz F. Construction and properties of a family of pACYC184-derived cloning vectors compatible with pBR322 and its derivatives. Gene. 1991 Jun 15;102(1):75–78. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90541-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell A., Gaston K., Williams R., Chapman K., Kolb A., Buc H., Minchin S., Williams J., Busby S. Mutations that alter the ability of the Escherichia coli cyclic AMP receptor protein to activate transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7243–7250. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cui J., Somerville R. L. A mutational analysis of the structural basis for transcriptional activation and monomer-monomer interaction in the TyrR system of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1993 Mar;175(6):1777–1784. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.6.1777-1784.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cui J., Somerville R. L. Mutational uncoupling of the transcriptional activation function of the TyrR protein of Escherichia coli K-12 from the repression function. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;175(1):303–306. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.1.303-306.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cui J., Somerville R. L. The TyrR protein of Escherichia coli, analysis by limited proteolysis of domain structure and ligand-mediated conformational changes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):5040–5047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman A. I., Beckwith J. Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase fails to acquire disulfide bonds when retained in the cytoplasm. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7719–7722. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7719-7722.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eschenlauer A. C., Reznikoff W. S. Escherichia coli catabolite gene activator protein mutants defective in positive control of lac operon transcription. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5024–5029. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5024-5029.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heatwole V. M., Somerville R. L. Synergism between the Trp repressor and Tyr repressor in repression of the aroL promoter of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):331–335. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.331-335.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heatwole V. M., Somerville R. L. The tryptophan-specific permease gene, mtr, is differentially regulated by the tryptophan and tyrosine repressors in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3601–3604. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3601-3604.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irwin N., Ptashne M. Mutants of the catabolite activator protein of Escherichia coli that are specifically deficient in the gene-activation function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8315–8319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihama A. Role of the RNA polymerase alpha subunit in transcription activation. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Nov;6(22):3283–3288. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb02196.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasian P. A., Pittard J. Construction of a tyrP-lac operon fusion strain and its use in the isolation and analysis of mutants derepressed for tyrP expression. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):175–183. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.175-183.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieny M. P., Lathe R., Lecocq J. P. New versatile cloning and sequencing vectors based on bacteriophage M13. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muday G. K., Johnson D. I., Somerville R. L., Herrmann K. M. The tyrosine repressor negatively regulates aroH expression in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3930–3932. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3930-3932.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittard A. J., Davidson B. E. TyrR protein of Escherichia coli and its role as repressor and activator. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jul;5(7):1585–1592. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarsero J. P., Pittard A. J. Molecular analysis of the TyrR protein-mediated activation of mtr gene expression in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7701–7704. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7701-7704.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarsero J. P., Wookey P. J., Pittard A. J. Regulation of expression of the Escherichia coli K-12 mtr gene by TyrR protein and Trp repressor. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(13):4133–4143. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.13.4133-4143.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipp M. J., Pittard A. J. Regulation of aromatic amino acid transport systems in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):453–461. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.453-461.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R., Bell A., Sims G., Busby S. The role of two surface exposed loops in transcription activation by the Escherichia coli CRP and FNR proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6705–6712. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Ganesan S., Sarsero J., Pittard A. J. A genetic analysis of various functions of the TyrR protein of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1993 Mar;175(6):1767–1776. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.6.1767-1776.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


