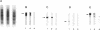Abstract
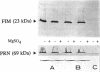
A novel nonhemolytic phase variant of Bordetella pertussis was characterized. This strain is strongly impaired in the transcription of the pertussis and adenylate cyclase toxins, whereas other known virulence-related factors such as the filamentous hemagglutinin, the fimbriae, and the outer membrane protein pertactin are expressed and regulated normally. Complementation and allelic exchange experiments demonstrated that the mutation is localized neither in the bvg locus involved in virulence regulation nor in the genes responsible for synthesis and transport of the toxins pertussis and adenylate cyclase. Instead, the mutation impairing transcription of at least the two toxin genes is located in a new genetic locus, which acts together with the BvgA/S two-component regulatory system on the expression of a subset of virulence genes. Further analysis suggested that most presumably the mutation affects a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein which contributes to transcriptional activation. The mutant was nonlethal in a murine respiratory model, which corresponds well with the lack of expression of the toxins. However, the clearing rate of this mutant from the lungs of mice was much lower than that of a bvg mutant, suggesting that factors other than the toxins may play a role in the persistence of the bacteria in the respiratory tract of mice.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S. Multipartite genetic control elements: communication by DNA loop. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:227–250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aricò B., Scarlato V., Monack D. M., Falkow S., Rappuoli R. Structural and genetic analysis of the bvg locus in Bordetella species. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Oct;5(10):2481–2491. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aricó B., Miller J. F., Roy C., Stibitz S., Monack D., Falkow S., Gross R., Rappuoli R. Sequences required for expression of Bordetella pertussis virulence factors share homology with prokaryotic signal transduction proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6671–6675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beattie D. T., Shahin R., Mekalanos J. J. A vir-repressed gene of Bordetella pertussis is required for virulence. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):571–577. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.571-577.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cookson B. T., Berg D. E., Goldman W. E. Mutagenesis of Bordetella pertussis with transposon Tn5tac1: conditional expression of virulence-associated genes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):1681–1687. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.1681-1687.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covacci A., Rappuoli R. Pertussis toxin export requires accessory genes located downstream from the pertussis toxin operon. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(3):429–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRita V. J., Parsot C., Jander G., Mekalanos J. J. Regulatory cascade controls virulence in Vibrio cholerae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5403–5407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman C. J. DNA supercoiling and environmental regulation of gene expression in pathogenic bacteria. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):745–749. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.745-749.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewanowich C. A., Melton A. R., Weiss A. A., Sherburne R. K., Peppler M. S. Invasion of HeLa 229 cells by virulent Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2698–2704. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2698-2704.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favre D., Viret J. F. Nucleotide sequence of the recA gene of Bordetella pertussis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4243–4243. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Long S. R., Brown S. E., Buikema W. J., Ausubel F. M. Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser P., Ladant D., Sezer O., Pichot F., Ullmann A., Danchin A. The calmodulin-sensitive adenylate cyclase of Bordetella pertussis: cloning and expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Jan;2(1):19–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyard S., Ullmann A. Functional analysis of the cya promoter of Bordetella pertussis. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Mar;7(5):693–704. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01160.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R., Carbonetti N. H., Rossi R., Rappuoli R. Functional analysis of the pertussis toxin promoter. Res Microbiol. 1992 Sep;143(7):671–681. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90062-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R., Rappuoli R. Pertussis toxin promoter sequences involved in modulation. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):4026–4030. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.4026-4030.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R., Rappuoli R. Positive regulation of pertussis toxin expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3913–3917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Dorman C. J., Stirling D. A., Waddell L., Booth I. R., May G., Bremer E. A physiological role for DNA supercoiling in the osmotic regulation of gene expression in S. typhimurium and E. coli. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):569–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90470-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huh Y. J., Weiss A. A. A 23-kilodalton protein, distinct from BvgA, expressed by virulent Bordetella pertussis binds to the promoter region of vir-regulated toxin genes. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2389–2395. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2389-2395.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KASUGA T., NAKASE Y., UKISHIMA K., TAKATSU K. Studies on Haemophilus pertussis. V. Relation between the phase of bacilli and the progress of the whooping-cough. Kitasato Arch Exp Med. 1954 Sep;27(3):57–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khelef N., Sakamoto H., Guiso N. Both adenylate cyclase and hemolytic activities are required by Bordetella pertussis to initiate infection. Microb Pathog. 1992 Mar;12(3):227–235. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(92)90057-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACEY B. W. Antigenic modulation of Bordetella pertussis. J Hyg (Lond) 1960 Mar;58:57–93. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400038134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. K., Roberts A. L., Finn T. M., Knapp S., Mekalanos J. J. A new assay for invasion of HeLa 229 cells by Bordetella pertussis: effects of inhibitors, phenotypic modulation, and genetic alterations. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2516–2522. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2516-2522.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leininger E., Roberts M., Kenimer J. G., Charles I. G., Fairweather N., Novotny P., Brennan M. J. Pertactin, an Arg-Gly-Asp-containing Bordetella pertussis surface protein that promotes adherence of mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):345–349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locht C., Keith J. M. Pertussis toxin gene: nucleotide sequence and genetic organization. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1258–1264. doi: 10.1126/science.3704651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May G., Dersch P., Haardt M., Middendorf A., Bremer E. The osmZ (bglY) gene encodes the DNA-binding protein H-NS (H1a), a component of the Escherichia coli K12 nucleoid. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Oct;224(1):81–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00259454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton A. R., Weiss A. A. Environmental regulation of expression of virulence determinants in Bordetella pertussis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6206–6212. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6206-6212.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Roy C. R., Falkow S. Analysis of Bordetella pertussis virulence gene regulation by use of transcriptional fusions in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6345–6348. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6345-6348.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooi F. R. Virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1988;54(5):465–474. doi: 10.1007/BF00461865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz J. J., Arai H., Cole R. L. Mouse-protecting and histamine-sensitizing activities of pertussigen and fimbrial hemagglutinin from Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):243–250. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.243-250.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Perugini M., Franzini C., Casagli M. C., Borri M. G., Antoni G., Almoni M., Neri P., Ratti G., Rappuoli R. Cloning and sequencing of the pertussis toxin genes: operon structure and gene duplication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4631–4635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relman D. A., Domenighini M., Tuomanen E., Rappuoli R., Falkow S. Filamentous hemagglutinin of Bordetella pertussis: nucleotide sequence and crucial role in adherence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2637–2641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relman D., Tuomanen E., Falkow S., Golenbock D. T., Saukkonen K., Wright S. D. Recognition of a bacterial adhesion by an integrin: macrophage CR3 (alpha M beta 2, CD11b/CD18) binds filamentous hemagglutinin of Bordetella pertussis. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1375–1382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90701-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M., Fairweather N. F., Leininger E., Pickard D., Hewlett E. L., Robinson A., Hayward C., Dougan G., Charles I. G. Construction and characterization of Bordetella pertussis mutants lacking the vir-regulated P.69 outer membrane protein. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jun;5(6):1393–1404. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00786.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C. R., Falkow S. Identification of Bordetella pertussis regulatory sequences required for transcriptional activation of the fhaB gene and autoregulation of the bvgAS operon. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(7):2385–2392. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.7.2385-2392.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C. R., Miller J. F., Falkow S. Autogenous regulation of the Bordetella pertussis bvgABC operon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3763–3767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarlato V., Aricò B., Prugnola A., Rappuoli R. Sequential activation and environmental regulation of virulence genes in Bordetella pertussis. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3971–3975. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04967.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarlato V., Prugnola A., Aricó B., Rappuoli R. Positive transcriptional feedback at the bvg locus controls expression of virulence factors in Bordetella pertussis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6753–6757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stainer D. W., Scholte M. J. A simple chemically defined medium for the production of phase I Bordetella pertussis. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Oct;63(2):211–220. doi: 10.1099/00221287-63-2-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibitz S., Black W., Falkow S. The construction of a cloning vector designed for gene replacement in Bordetella pertussis. Gene. 1986;50(1-3):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90318-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibitz S., Garletts T. L. Derivation of a physical map of the chromosome of Bordetella pertussis Tohama I. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(23):7770–7777. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.23.7770-7777.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibitz S., Yang M. S. Subcellular localization and immunological detection of proteins encoded by the vir locus of Bordetella pertussis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4288–4296. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4288-4296.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of phase change in Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):263–269. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.263-269.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L. Virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:661–686. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Johnson F. D., Burns D. L. Molecular characterization of an operon required for pertussis toxin secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2970–2974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems R., Paul A., van der Heide H. G., ter Avest A. R., Mooi F. R. Fimbrial phase variation in Bordetella pertussis: a novel mechanism for transcriptional regulation. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2803–2809. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07468.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]