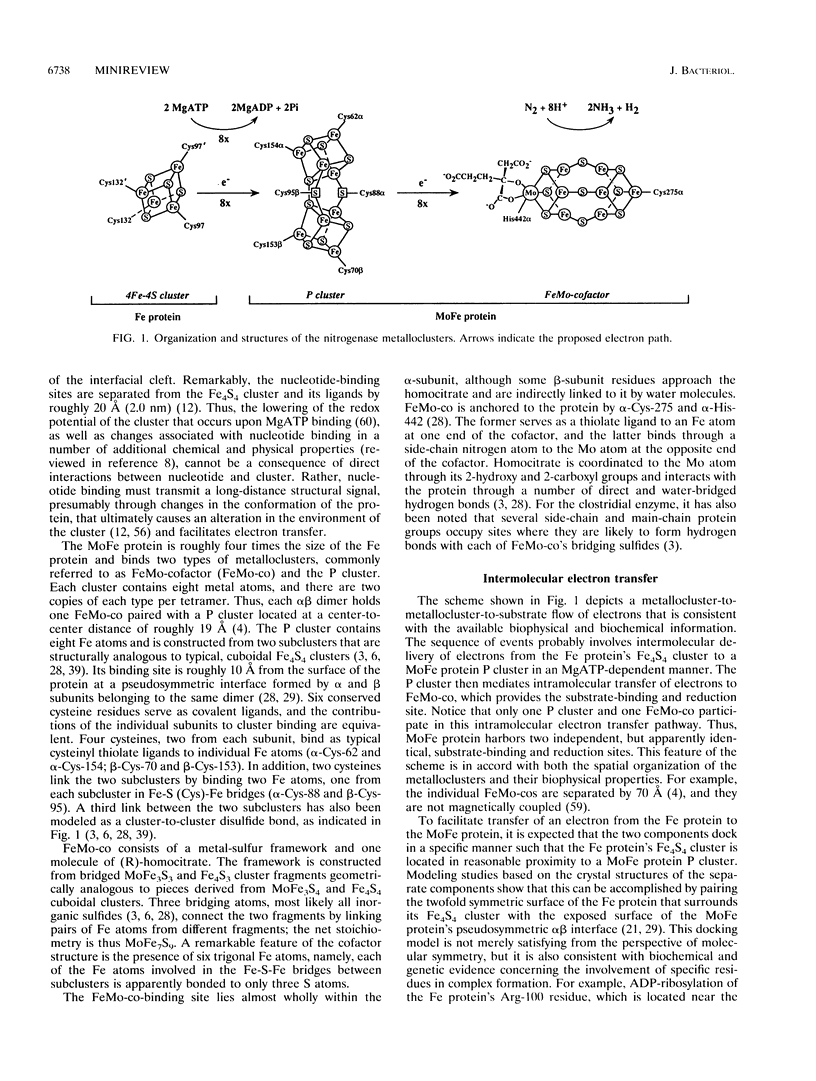
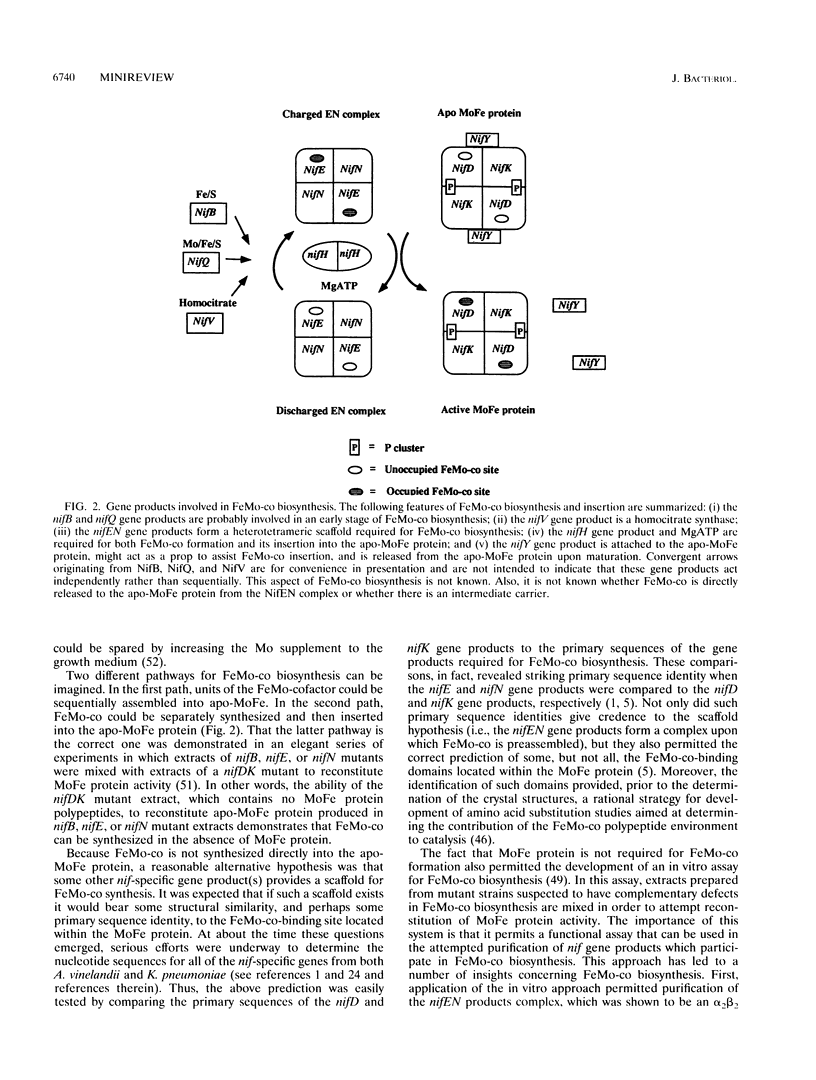
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold W., Rump A., Klipp W., Priefer U. B., Pühler A. Nucleotide sequence of a 24,206-base-pair DNA fragment carrying the entire nitrogen fixation gene cluster of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):715–738. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigle K. E., Weiss M. C., Newton W. E., Dean D. R. Products of the iron-molybdenum cofactor-specific biosynthetic genes, nifE and nifN, are structurally homologous to the products of the nitrogenase molybdenum-iron protein genes, nifD and nifK. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1547–1553. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1547-1553.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan M. K., Kim J., Rees D. C. The nitrogenase FeMo-cofactor and P-cluster pair: 2.2 A resolution structures. Science. 1993 May 7;260(5109):792–794. doi: 10.1126/science.8484118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. R., Setterquist R. A., Brigle K. E., Scott D. J., Laird N. F., Newton W. E. Evidence that conserved residues Cys-62 and Cys-154 within the Azotobacter vinelandii nitrogenase MoFe protein alpha-subunit are essential for nitrogenase activity but conserved residues His-83 and Cys-88 are not. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1505–1512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filler W. A., Kemp R. M., Ng J. C., Hawkes T. R., Dixon R. A., Smith B. E. The nifH gene product is required for the synthesis or stability of the iron-molybdenum cofactor of nitrogenase from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 15;160(2):371–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09981.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavini N., Burgess B. K. FeMo cofactor synthesis by a nifH mutant with altered MgATP reactivity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):21179–21186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiadis M. M., Komiya H., Chakrabarti P., Woo D., Kornuc J. J., Rees D. C. Crystallographic structure of the nitrogenase iron protein from Azotobacter vinelandii. Science. 1992 Sep 18;257(5077):1653–1659. doi: 10.1126/science.1529353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govezensky D., Zamir A. Structure-function relationships in the alpha subunit of Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase MoFe protein from analysis of nifD mutants. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5729–5735. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5729-5735.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hageman R. V., Burris R. H. Nitrogenase and nitrogenase reductase associate and dissociate with each catalytic cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2699–2702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris G. S., White T. C., Flory J. E., Orme-Johnson W. H. Genes required for formation of the apoMoFe protein of Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15909–15919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausinger R. P., Howard J. B. Thiol reactivity of the nitrogenase Fe-protein from Azotobacter vinelandii. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13486–13492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes T. R., McLean P. A., Smith B. E. Nitrogenase from nifV mutants of Klebsiella pneumoniae contains an altered form of the iron-molybdenum cofactor. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 1;217(1):317–321. doi: 10.1042/bj2170317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes T. R., Smith B. E. Purification and characterization of the inactive MoFe protein (NifB-Kp1) of the nitrogenase from nifB mutants of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):43–50. doi: 10.1042/bj2090043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homer M. J., Paustian T. D., Shah V. K., Roberts G. P. The nifY product of Klebsiella pneumoniae is associated with apodinitrogenase and dissociates upon activation with the iron-molybdenum cofactor. J Bacteriol. 1993 Aug;175(15):4907–4910. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.15.4907-4910.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover T. R., Imperial J., Ludden P. W., Shah V. K. Homocitrate is a component of the iron-molybdenum cofactor of nitrogenase. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 4;28(7):2768–2771. doi: 10.1021/bi00433a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. B., Davis R., Moldenhauer B., Cash V. L., Dean D. Fe:S cluster ligands are the only cysteines required for nitrogenase Fe-protein activities. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11270–11274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard K. S., McLean P. A., Hansen F. B., Lemley P. V., Koblan K. S., Orme-Johnson W. H. Klebsiella pneumoniae nifM gene product is required for stabilization and activation of nitrogenase iron protein in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):772–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. R., Brigle K. E., Bennett L. T., Setterquist R. A., Wilson M. S., Cash V. L., Beynon J., Newton W. E., Dean D. R. Physical and genetic map of the major nif gene cluster from Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):1017–1027. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.1017-1027.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. R., Cash V. L., Weiss M. C., Laird N. F., Newton W. E., Dean D. R. Biochemical and genetic analysis of the nifUSVWZM cluster from Azotobacter vinelandii. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Oct;219(1-2):49–57. doi: 10.1007/BF00261156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent H. M., Baines M., Gormal C., Smith B. E., Buck M. Analysis of site-directed mutations in the alpha- and beta-subunits of Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1497–1504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Rees D. C. Structural models for the metal centers in the nitrogenase molybdenum-iron protein. Science. 1992 Sep 18;257(5077):1677–1682. doi: 10.1126/science.1529354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang J., Madden M., Shah V. K., Burris R. H. Citrate substitutes for homocitrate in nitrogenase of a nifV mutant of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 18;29(37):8577–8581. doi: 10.1021/bi00489a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowery R. G., Chang C. L., Davis L. C., McKenna M. C., Stephens P. J., Ludden P. W. Substitution of histidine for arginine-101 of dinitrogenase reductase disrupts electron transfer to dinitrogenase. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):1206–1212. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer W. G., Tabita F. R. Isolation and characterization of the nifUSVW-rpoN gene cluster from Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):3855–3866. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.3855-3866.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. F., Orme-Johnson W. H. The dependence on iron availability of allocation of iron to nitrogenase components in Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9398–9408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortenson L. E., Seefeldt L. C., Morgan T. V., Bolin J. T. The role of metal clusters and MgATP in nitrogenase catalysis. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1993;67:299–374. doi: 10.1002/9780470123133.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W., Merrick M. The roles of the nifW, nifZ and nifM genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae in nitrogenase biosynthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 2;178(3):675–682. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paustian T. D., Shah V. K., Roberts G. P. Apodinitrogenase: purification, association with a 20-kilodalton protein, and activation by the iron-molybdenum cofactor in the absence of dinitrogenase reductase. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 10;29(14):3515–3522. doi: 10.1021/bi00466a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. P., Brill W. J. Gene-product relationships of the nif regulon of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):210–216. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.210-216.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. C., Chun T. W., Li J. G., Burgess B. K. Iron-molybdenum cofactor insertion into the Apo-MoFe protein of nitrogenase involves the iron protein-MgATP complex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):10088–10095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. C., Dean D. R., Burgess B. K. Iron-molybdenum cofactor biosynthesis in Azotobacter vinelandii requires the iron protein of nitrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14327–14332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson R. L. Identification of possible adenine nucleotide-binding sites in nitrogenase Fe- and MoFe-proteins by amino acid sequence comparison. FEBS Lett. 1984 Aug 6;173(2):394–398. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80812-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. J., Dean D. R., Newton W. E. Nitrogenase-catalyzed ethane production and CO-sensitive hydrogen evolution from MoFe proteins having amino acid substitutions in an alpha-subunit FeMo cofactor-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20002–20010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seefeldt L. C., Morgan T. V., Dean D. R., Mortenson L. E. Mapping the site(s) of MgATP and MgADP interaction with the nitrogenase of Azotobacter vinelandii. Lysine 15 of the iron protein plays a major role in MgATP interaction. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6680–6688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Isolation of an iron-molybdenum cofactor from nitrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3249–3253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Imperial J., Ugalde R. A., Ludden P. W., Brill W. J. In vitro synthesis of the iron-molybdenum cofactor of nitrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1636–1640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D., Setlow P. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and regulation of the Bacillus subtilis nadB gene and a nifS-like gene, both of which are essential for NAD biosynthesis. J Bacteriol. 1993 Mar;175(5):1423–1432. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.5.1423-1432.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tal S., Chun T. W., Gavini N., Burgess B. K. The delta nifB (or delta nifE) FeMo cofactor-deficient MoFe protein is different from the delta nifH protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10654–10657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugalde R. A., Imperial J., Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Biosynthesis of iron-molybdenum cofactor in the absence of nitrogenase. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):888–893. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.888-893.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. Z., Dean D. R., Chen J. S., Johnson J. L. The N-terminal and C-terminal portions of NifV are encoded by two different genes in Clostridium pasteurianum. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(10):3041–3046. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.10.3041-3046.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. C., Harris G. S., Orme-Johnson W. H. Electrophoretic studies on the assembly of the nitrogenase molybdenum-iron protein from the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifD and nifK gene products. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):24007–24016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willing A., Howard J. B. Cross-linking site in Azotobacter vinelandii complex. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6596–6599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolle D., Dean D. R., Howard J. B. Nucleotide-iron-sulfur cluster signal transduction in the nitrogenase iron-protein: the role of Asp125. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):992–995. doi: 10.1126/science.1359643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolle D., Kim C., Dean D., Howard J. B. Ionic interactions in the nitrogenase complex. Properties of Fe-protein containing substitutions for Arg-100. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3667–3673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng L., White R. H., Cash V. L., Jack R. F., Dean D. R. Cysteine desulfurase activity indicates a role for NIFS in metallocluster biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2754–2758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann R., Münck E., Brill W. J., Shah V. K., Henzl M. T., Rawlings J., Orme-Johnson W. H. Nitrogenase X: Mössbauer and EPR studies on reversibly oxidized MoFe protein from Azotobacter vinelandii OP. Nature of the iron centers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 20;537(2):185–207. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90504-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumft W. G., Mortenson L. E., Palmer G. Electron-paramagnetic-resonance studies on nitrogenase. Investigation of the oxidation-reduction behaviour of azoferredoxin and molybdoferredoxin with potentiometric and rapid-freeze techniques. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Aug 1;46(3):525–535. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03646.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



