Abstract
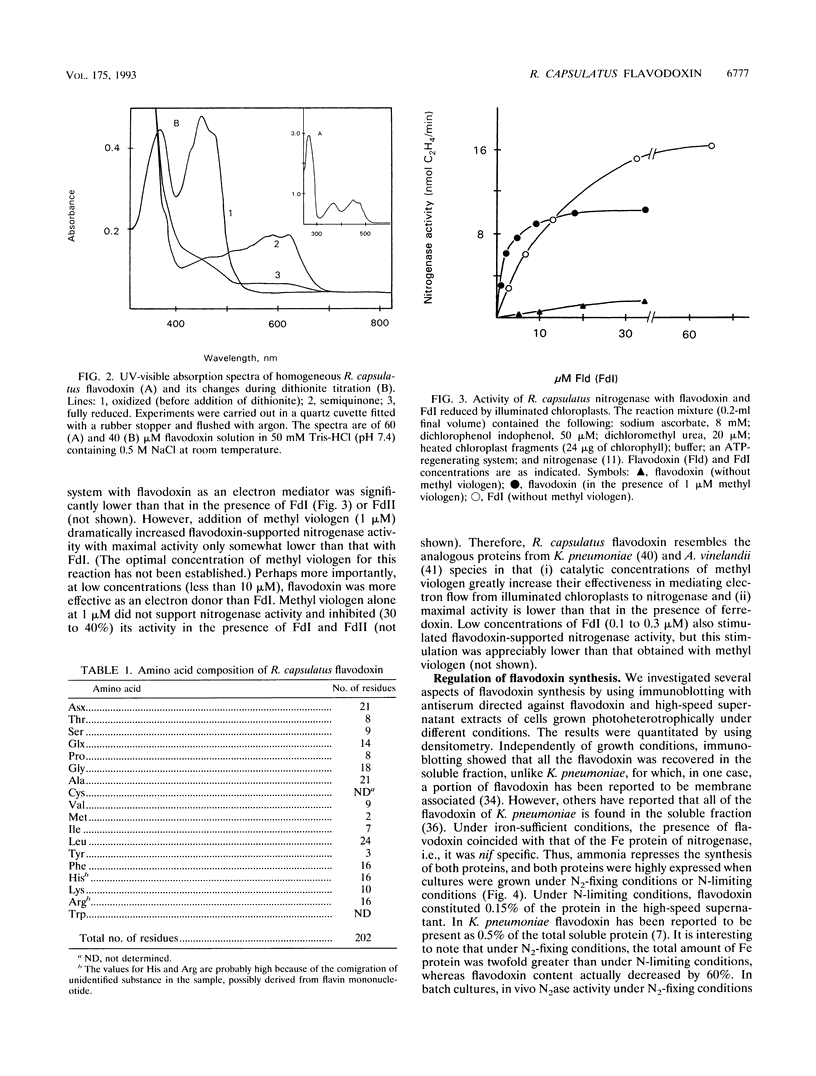
A flavodoxin was isolated from iron-sufficient, nitrogen-limited cultures of the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodobacter capsulatus. Its molecular properties, molecular weight, UV-visible absorption spectrum, and amino acid composition suggest that it is similar to the nif-specific flavodoxin, NifF, of Klebsiella pneumoniae. The results of immunoblotting showed that R. capsulatus flavodoxin is nif specific, since it is absent from ammonia-replete cultures and is not synthesized by the mutant strain J61, which lacks a nif-specific regulator (NifR1). Growth of cultures under iron-deficient conditions causes a small amount of flavodoxin to be synthesized under ammonia-replete conditions and increases its synthesis under N2-fixing conditions, suggesting that its synthesis is under a dual system of control with respect to iron and fixed nitrogen availability. Here we show that flavodoxin, when supplemented with catalytic amounts of methyl viologen, is capable of efficiently reducing nitrogenase in an illuminated chloroplast system. Thus, this nif-specific flavodoxin is a potential in vivo electron carrier to nitrogenase; however, its role in the nitrogen fixation process remains to be established.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arp D. J., Zumft W. G. Overproduction of nitrogenase by nitrogen-limited cultures of Rhodopseudomonas palustris. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1322–1330. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1322-1330.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beynon J., Cannon M., Buchanan-Wollaston V., Cannon F. The nif promoters of Klebsiella pneumoniae have a characteristic primary structure. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):665–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90399-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostedt E., Nordlund S. Purification and partial characterization of a pyruvate oxidoreductase from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum grown under nitrogen-fixing conditions. Biochem J. 1991 Oct 1;279(Pt 1):155–158. doi: 10.1042/bj2790155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusanovich M. A., Edmondson D. E. The isolation and characterization of Rhodospirillum rubrum flavodoxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Oct 15;45(2):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90822-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deistung J., Cannon F. C., Cannon M. C., Hill S., Thorneley R. N. Electron transfer to nitrogenase in Klebsiella pneumoniae. nifF gene cloned and the gene product, a flavodoxin, purified. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 1;231(3):743–753. doi: 10.1042/bj2310743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabau C., Schatt E., Jouanneau Y., Vignais P. M. A new [2Fe-2S] ferredoxin from Rhodobacter capsulatus. Coexpression with a 2[4Fe-4S] ferredoxin in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3294–3299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haaker H., Laane C., Hellingwerf K., Houwer B., Konings W. N., Veeger C. Short-term regulation of the nitrogenase activity in Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Oct;127(3):639–645. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallenbeck P. C., Meyer C. M., Vignais P. M. Nitrogenase from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas capsulata: purification and molecular properties. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):708–717. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.708-717.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S., Kavanagh E. P. Roles of nifF and nifJ gene products in electron transport to nitrogenase in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):470–475. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.470-475.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillmer P., Gest H. H2 metabolism in the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas capsulata: H2 production by growing cultures. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):724–731. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.724-731.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouanneau Y., Richaud P., Grabau C. The nucleotide sequence of a flavodoxin-like gene which precedes two ferredoxin genes in Rhodobacter capsulatus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5284–5284. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klugkist J., Haaker H., Wassink H., Veeger C. The catalytic activity of nitrogenase in intact Azotobacter vinelandii cells. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Feb 1;146(3):509–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klugkist J., Voorberg J., Haaker H., Veeger C. Characterization of three different flavodoxins from Azotobacter vinelandii. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Feb 17;155(1):33–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A. E., Burgess B. K., Iismaa S. E., Smartt C. T., Jacobson M. R., Dean D. R. Construction and characterization of an Azotobacter vinelandii strain with mutations in the genes encoding flavodoxin and ferredoxin I. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3162–3167. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3162-3167.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Vivian C., Hennecke S., Pühler A., Klipp W. Open reading frame 5 (ORF5), encoding a ferredoxinlike protein, and nifQ are cotranscribed with nifE, nifN, nifX, and ORF4 in Rhodobacter capsulatus. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2591–2598. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2591-2598.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieva-Gómez D., Roberts G. P., Klevickis S., Brill W. J. Electron transport to nitrogenase in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2555–2558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. P., MacNeil T., MacNeil D., Brill W. J. Regulation and characterization of protein products coded by the nif (nitrogen fixation) genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):267–279. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.267-279.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saeki K., Miyatake Y., Young D. A., Marrs B. L., Matsubara H. A plant-ferredoxin-like gene is located upstream of ferredoxin I gene (fdxN) of Rhodobacter capsulatus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1060–1060. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.1060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saeki K., Suetsugu Y., Yao Y., Horio T., Marrs B. L., Matsubara H. Two distinct ferredoxins from Rhodobacter capsulatus: complete amino acid sequences and molecular evolution. J Biochem. 1990 Sep;108(3):475–482. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatt E., Jouanneau Y., Vignais P. M. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the structural gene of ferredoxin I from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodobacter capsulatus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6218–6226. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6218-6226.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Stacey G., Brill W. J. Electron transport to nitrogenase. Purification and characterization of pyruvate:flavodoxin oxidoreductase. The nifJ gene product. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):12064–12068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John R. T., Johnston H. M., Seidman C., Garfinkel D., Gordon J. K., Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Biochemistry and genetics of Klebsiella pneumoniae mutant strains unable to fix N2. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):759–765. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.759-765.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suetsugu Y., Saeki K., Matsubara H. Transcriptional analysis of two Rhodobacter capsulatus ferredoxins by translational fusion to Escherichia coli lacZ. FEBS Lett. 1991 Nov 4;292(1-2):13–16. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80822-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl R. C., Orme-Johnson W. H. Clostridial pyruvate oxidoreductase and the pyruvate-oxidizing enzyme specific to nitrogen fixation in Klebsiella pneumoniae are similar enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10489–10496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall J. D., Braddock K. Mapping of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata nif genes. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):404–410. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.404-410.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C., Benemann J. R., Valentine R. C., Arnon D. I. The electron transport system in nitrogen fixation by Azotobacter. II. Isolation and function of a new type of ferredoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1404–1410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C. Dimerization of Azotobacter vinelandii flavodoxin (azotoflavin). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Sep;170(1):326–333. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90124-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C. Electron transport carriers involved in nitrogen fixation by the coliform, Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jul;83(0):153–164. doi: 10.1099/00221287-83-1-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]