Abstract
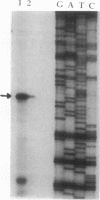
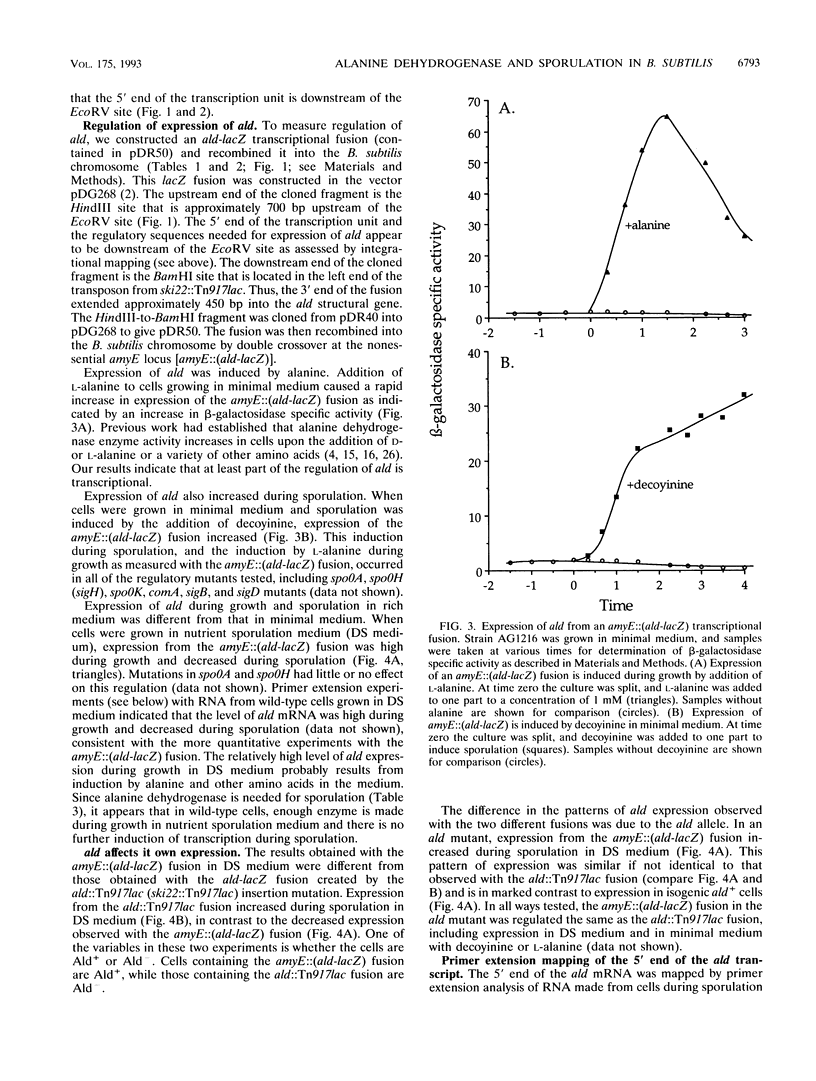
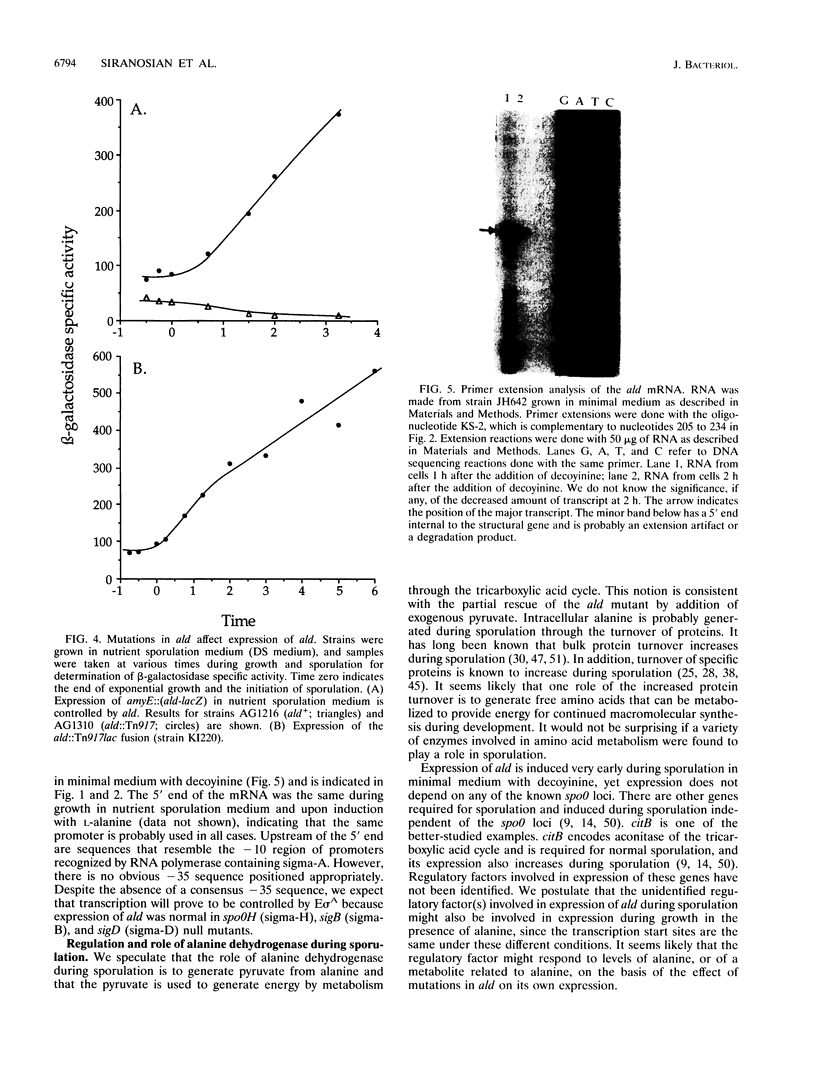
The ski22::Tn917lac insertion mutation in Bacillus subtilis was isolated in a screen for mutations that cause a defect in sporulation but are suppressed by the presence or overexpression of the histidine protein kinase encoded by kinA (spoIIJ). The ski22::Tn917lac insertion mutation was in ald, the gene encoding alanine dehydrogenase. Alanine dehydrogenase catalyzes the deamination of alanine to pyruvate and ammonia and is needed for growth when alanine is the sole carbon or nitrogen source. The sporulation defect caused by null mutations in ald was partly relieved by the addition of pyruvate at a high concentration, indicating that the normal role of alanine dehydrogenase in sporulation might be to generate pyruvate to provide an energy source for sporulation. The spoVN::Tn917 mutation was also found to be an allele of ald. Transcription of ald was induced very early during sporulation and by the addition of exogenous alanine during growth. Expression of ald was normal in all of the regulatory mutants tested, including spo0A, spo0K, comA, sigB, and sigD mutants. The only gene in which mutations affected expression of ald was ald itself. This regulation is probably related to the metabolism of alanine.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albright L. M., Huala E., Ausubel F. M. Prokaryotic signal transduction mediated by sensor and regulator protein pairs. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:311–336. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoniewski C., Savelli B., Stragier P. The spoIIJ gene, which regulates early developmental steps in Bacillus subtilis, belongs to a class of environmentally responsive genes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):86–93. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.86-93.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burbulys D., Trach K. A., Hoch J. A. Initiation of sporulation in B. subtilis is controlled by a multicomponent phosphorelay. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):545–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90238-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedonder R. A., Lepesant J. A., Lepesant-Kejzlarová J., Billault A., Steinmetz M., Kunst F. Construction of a kit of reference strains for rapid genetic mapping in Bacillus subtilis 168. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):989–993. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.989-993.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingman D. W., Rosenkrantz M. S., Sonenshein A. L. Relationship between aconitase gene expression and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3068–3075. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3068-3075.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errington J. Bacillus subtilis sporulation: regulation of gene expression and control of morphogenesis. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Mar;57(1):1–33. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.1.1-33.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREESE E., OOSTERWYK J. THE INDUCTION OF ALANINE DEHYDROGENASE. Biochemistry. 1963 Nov-Dec;2:1212–1216. doi: 10.1021/bi00906a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREESE E., PARK S. W., CASHEL M. THE DEVELOPMENTAL SIGNIFICANCE OF ALANINE DEHYDROGENASE IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jun;51:1164–1172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.6.1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari F. A., Nguyen A., Lang D., Hoch J. A. Construction and properties of an integrable plasmid for Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1513–1515. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1513-1515.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari F. A., Trach K., LeCoq D., Spence J., Ferrari E., Hoch J. A. Characterization of the spo0A locus and its deduced product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2647–2651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortnagel P., Freese E. Analysis of sporulation mutants. II. Mutants blocked in the citric acid cycle. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1431–1438. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1431-1438.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouet A., Sonenshein A. L. A target for carbon source-dependent negative regulation of the citB promoter of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):835–844. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.835-844.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese E. B., Vasantha N., Freese E. Induction of sporulation in developmental mutants of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Feb 16;170(1):67–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00268581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ireton K., Grossman A. D. Interactions among mutations that cause altered timing of gene expression during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3185–3195. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3185-3195.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaacks K. J., Healy J., Losick R., Grossman A. D. Identification and characterization of genes controlled by the sporulation-regulatory gene spo0H in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4121–4129. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4121-4129.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudoh J., Ikeuchi T., Kurahashi K. Nucleotide sequences of the sporulation gene spo0A and its mutant genes of Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2665–2668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton T. New types of RNA polymerase mutations causing temperature-sensitive sporulation in bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):268–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurizi M. R., Brabson J. S., Switzer R. L. Immunochemical studies of the inactivation of aspartate transcarbamylase by stationary phase Bacillus subtilis cells. Evidence for selective, energy-dependent degradation. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5585–5593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCowen S. M., Phibbs P. V., Jr Regulation of alanine dehydrogenase in Bacillus (licheniformis). J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):590–597. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.590-597.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neway J. O., Switzer R. L. Degradation of ornithine transcarbamylase in sporulating Bacillus subtilis cells. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):522–530. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.522-530.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitta Y., Yasuda Y., Tochikubo K., Hachisuka Y. L-amino acid dehydrogenases in Bacillus subtilis spores. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):588–592. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.588-592.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashima T., Soda K. Purification and properties of alanine dehydrogenase from Bacillus sphaericus. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):29–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Kofoid E. C. Communication modules in bacterial signaling proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:71–112. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perego M., Cole S. P., Burbulys D., Trach K., Hoch J. A. Characterization of the gene for a protein kinase which phosphorylates the sporulation-regulatory proteins Spo0A and Spo0F of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6187–6196. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6187-6196.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J., Curtis C. A., de Lencastre H. Use of integrational plasmid vectors to demonstrate the polycistronic nature of a transcriptional unit (spoIIA) required for sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Aug;130(8):2123–2136. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-8-2123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porumb H., Vancea D., Mureşan L., Presecan E., Lascu I., Petrescu I., Porumb T., Pop R., Bârzu O. Structural and catalytic properties of L-alanine dehydrogenase from Bacillus cereus. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4610–4615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricca E., Cutting S., Losick R. Characterization of bofA, a gene involved in intercompartmental regulation of pro-sigma K processing during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3177–3184. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3177-3184.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudner D. Z., LeDeaux J. R., Ireton K., Grossman A. D. The spo0K locus of Bacillus subtilis is homologous to the oligopeptide permease locus and is required for sporulation and competence. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(4):1388–1398. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.4.1388-1398.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppen M. E., Switzer R. L. Degradation of Bacillus subtilis glutamine phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2843–2851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandman K., Kroos L., Cutting S., Youngman P., Losick R. Identification of the promoter for a spore coat protein gene in Bacillus subtilis and studies on the regulation of its induction at a late stage of sporulation. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 5;200(3):461–473. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90536-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandman K., Losick R., Youngman P. Genetic analysis of Bacillus subtilis spo mutations generated by Tn917-mediated insertional mutagenesis. Genetics. 1987 Dec;117(4):603–617. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.4.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satola S. W., Baldus J. M., Moran C. P., Jr Binding of Spo0A stimulates spoIIG promoter activity in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1448–1453. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1448-1453.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satola S., Kirchman P. A., Moran C. P., Jr Spo0A binds to a promoter used by sigma A RNA polymerase during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4533–4537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P., Millet J., Aubert J. P. Catabolic repression of bacterial sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):704–711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizizen J. TRANSFORMATION OF BIOCHEMICALLY DEFICIENT STRAINS OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS BY DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Oct 15;44(10):1072–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.10.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Kornberg A. Biochemical studies of bacterial sporulation and germaination. VII. Protein turnover during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 10;243(17):4600–4605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch M., Webb V., Spiegelman G., Hoch J. A. The SpoOA protein of Bacillus subtilis is a repressor of the abrB gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1801–1805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uratani-Wong B., Lopez J. M., Freese E. Induction of citric acid cycle enzymes during initiation of sporulation by guanine nucleotide deprivation. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):337–344. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.337-344.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasantha N., Freese E. Enzyme changes during Bacillus subtilis sporulation caused by deprivation of guanine nucleotides. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1119–1125. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1119-1125.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinrauch Y., Penchev R., Dubnau E., Smith I., Dubnau D. A Bacillus subtilis regulatory gene product for genetic competence and sporulation resembles sensor protein members of the bacterial two-component signal-transduction systems. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):860–872. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- York K., Kenney T. J., Satola S., Moran C. P., Jr, Poth H., Youngman P. Spo0A controls the sigma A-dependent activation of Bacillus subtilis sporulation-specific transcription unit spoIIE. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(8):2648–2658. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.8.2648-2658.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngman P., Perkins J. B., Losick R. A novel method for the rapid cloning in Escherichia coli of Bacillus subtilis chromosomal DNA adjacent to Tn917 insertions. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(3):424–433. doi: 10.1007/BF00341443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousten A. A., Hanson R. S. Sporulation of tricarboxylic acid cycle mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):886–894. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.886-894.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]