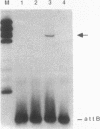
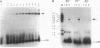Abstract
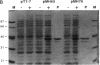
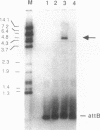
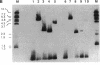
Mycobacteriophage L5, a temperate phage of the mycobacteria, forms stable lysogens in Mycobacterium smegmatis via site-specific integration of the phage genome. Recombination occurs within specific phage and bacterial attachment sites and is catalyzed by the phage-encoded integrase protein in vivo. We describe here the overexpression and purification of L5 integrase and its ability to mediate integrative recombination in vitro. We find that L5 integrase-mediated recombination is greatly stimulated by extracts of M. smegmatis but not by Escherichia coli extracts, purified E. coli integration host factor, or purified HU, indicating the presence of a novel mycobacterial integration host factor.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argos P., Landy A., Abremski K., Egan J. B., Haggard-Ljungquist E., Hoess R. H., Kahn M. L., Kalionis B., Narayana S. V., Pierson L. S., 3rd The integrase family of site-specific recombinases: regional similarities and global diversity. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):433–440. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04229.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K., Rouviere-Yaniv J. Histonelike proteins of bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Sep;51(3):301–319. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.3.301-319.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel S. E., Johnson R. C. The Fis protein: it's not just for DNA inversion anymore. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Nov;6(22):3257–3265. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb02193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I. Integration host factor: a protein for all reasons. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90213-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. D., Nash H. A. Functional replacement of a protein-induced bend in a DNA recombination site. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):251–254. doi: 10.1038/341251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. D., Nicholson S. C., Nash H. A. Deformation of DNA during site-specific recombination of bacteriophage lambda: replacement of IHF protein by HU protein or sequence-directed bends. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11910–11914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. D., Scocca J. J. Nucleotide sequence and expression of the gene for the site-specific integration protein from bacteriophage HP1 of Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4232–4240. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4232-4240.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfull G. F., Sarkis G. J. DNA sequence, structure and gene expression of mycobacteriophage L5: a phage system for mycobacterial genetics. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Feb;7(3):395–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser M. A., Scocca J. J. Site-specific integration of the Haemophilus influenzae bacteriophage HP1. Identification of the points of recombinational strand exchange and the limits of the host attachment site. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6859–6864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu P. L., Landy A. Resolution of synthetic att-site Holliday structures by the integrase protein of bacteriophage lambda. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):721–726. doi: 10.1038/311721a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang E. S., Scocca J. J. Interaction of integration host factor from Escherichia coli with the integration region of the Haemophilus influenzae bacteriophage HP1. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4852–4860. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4852-4860.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Landy A. Lambda Int protein bridges between higher order complexes at two distant chromosomal loci attL and attR. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):198–203. doi: 10.1126/science.1533056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Moitoso de Vargas L., Nunes-Düby S. E., Landy A. Mapping of a higher order protein-DNA complex: two kinds of long-range interactions in lambda attL. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P. A., Nash H. A. Bacteriophage lambda site-specific recombination proceeds with a defined order of strand exchanges. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 5;204(1):95–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90602-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy A. Dynamic, structural, and regulatory aspects of lambda site-specific recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:913–949. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. H., Pascopella L., Jacobs W. R., Jr, Hatfull G. F. Site-specific integration of mycobacteriophage L5: integration-proficient vectors for Mycobacterium smegmatis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and bacille Calmette-Guérin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3111–3115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahan M. J., Slauch J. M., Mekalanos J. J. Selection of bacterial virulence genes that are specifically induced in host tissues. Science. 1993 Jan 29;259(5095):686–688. doi: 10.1126/science.8430319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moitoso de Vargas L., Kim S., Landy A. DNA looping generated by DNA bending protein IHF and the two domains of lambda integrase. Science. 1989 Jun 23;244(4911):1457–1461. doi: 10.1126/science.2544029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moitoso de Vargas L., Pargellis C. A., Hasan N. M., Bushman E. W., Landy A. Autonomous DNA binding domains of lambda integrase recognize two different sequence families. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):923–929. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A., Bauer C. E., Gardner J. F. Role of homology in site-specific recombination of bacteriophage lambda: evidence against joining of cohesive ends. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4049–4053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A., Robertson C. A. Purification and properties of the Escherichia coli protein factor required for lambda integrative recombination. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9246–9253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pargellis C. A., Nunes-Düby S. E., de Vargas L. M., Landy A. Suicide recombination substrates yield covalent lambda integrase-DNA complexes and lead to identification of the active site tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7678–7685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richet E., Abcarian P., Nash H. A. Synapsis of attachment sites during lambda integrative recombination involves capture of a naked DNA by a protein-DNA complex. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90526-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson C. A., Nash H. A. Bending of the bacteriophage lambda attachment site by Escherichia coli integration host factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3554–3557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapper S. B., Lugosi L., Jekkel A., Melton R. E., Kieser T., Bloom B. R., Jacobs W. R., Jr Lysogeny and transformation in mycobacteria: stable expression of foreign genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6987–6991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapper S. B., Melton R. E., Mustafa S., Kieser T., Jacobs W. R., Jr Isolation and characterization of efficient plasmid transformation mutants of Mycobacterium smegmatis. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1911–1919. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder U. K., Thompson J. F., Landy A. Phasing of protein-induced DNA bends in a recombination complex. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):255–257. doi: 10.1038/341255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stover C. K., de la Cruz V. F., Fuerst T. R., Burlein J. E., Benson L. A., Bennett L. T., Bansal G. P., Young J. F., Lee M. H., Hatfull G. F. New use of BCG for recombinant vaccines. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):456–460. doi: 10.1038/351456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]