Abstract
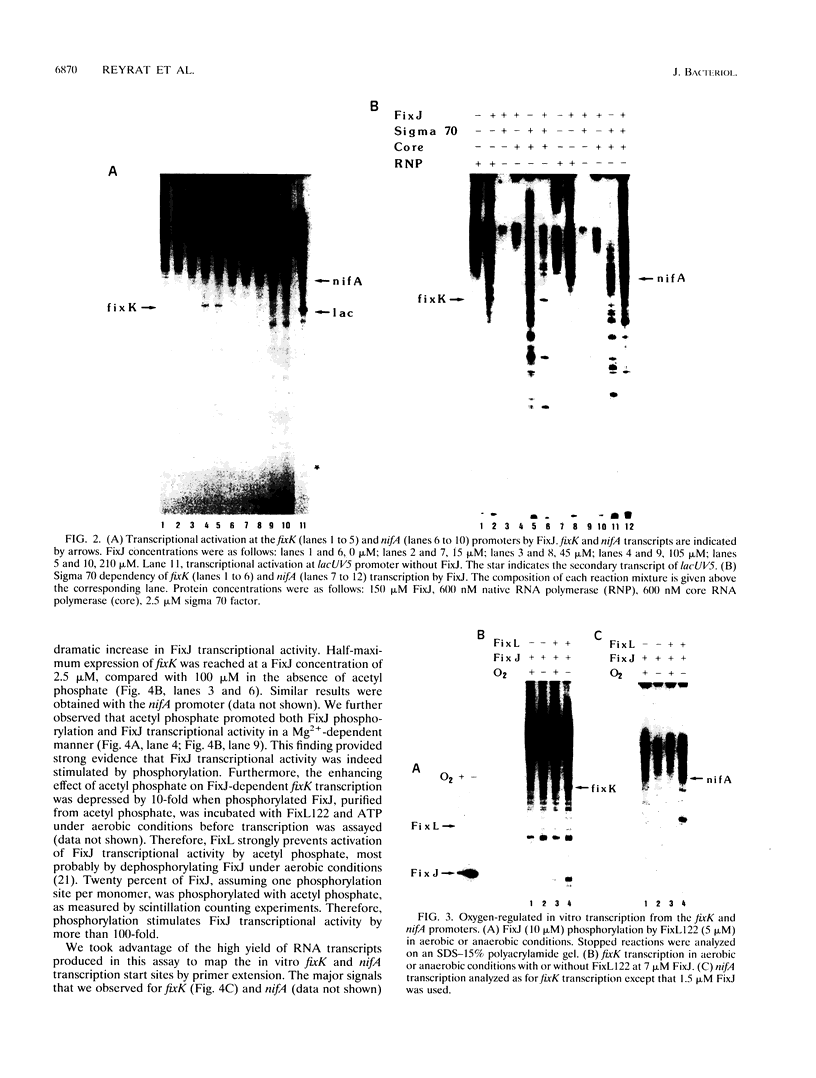
Oxygen concentration regulates the expression of nitrogen fixation genes in the symbiotic bacterium Rhizobium meliloti. We demonstrate that two proteins, FixL and FixJ, that belong to the two-component family of regulatory proteins are necessary and sufficient for oxygen-regulated in vitro transcription of the two key regulatory genes, nifA and fixK. We show directly that FixJ is a transcriptional activator, working in conjunction with the RNA polymerase sigma 70 holoenzyme. Addition of FixL122, a soluble form of the sensor FixL protein, to the transcription assay enhanced FixJ transcriptional activity in response to low oxygen concentration. This enhancement of FixJ activity was correlated with FixJ phosphorylation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agron P. G., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. Oxygen regulation of nifA transcription in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3506–3510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albright L. M., Huala E., Ausubel F. M. Prokaryotic signal transduction mediated by sensor and regulator protein pairs. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:311–336. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batut J., Daveran-Mingot M. L., David M., Jacobs J., Garnerone A. M., Kahn D. fixK, a gene homologous with fnr and crp from Escherichia coli, regulates nitrogen fixation genes both positively and negatively in Rhizobium meliloti. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1279–1286. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03502.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batut J., Santero E., Kustu S. In vitro activity of the nitrogen fixation regulatory protein FIXJ from Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5914–5917. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5914-5917.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourret R. B., Borkovich K. A., Simon M. I. Signal transduction pathways involving protein phosphorylation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:401–441. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke H. R., Leigh J. A., Douglas C. J. Molecular signals in the interactions between plants and microbes. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90348-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzone A. J. Protein phosphorylation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:97–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.000525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Daveran M. L., Batut J., Dedieu A., Domergue O., Ghai J., Hertig C., Boistard P., Kahn D. Cascade regulation of nif gene expression in Rhizobium meliloti. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):671–683. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Virts E., Palomares A., Kim C. H. The nifA gene of Rhizobium meliloti is oxygen regulated. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3217–3223. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3217-3223.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T., Geiduschek E. P. Defining a bacteriophage T4 late promoter: absence of a "-35" region. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng J., Atkinson M. R., McCleary W., Stock J. B., Wanner B. L., Ninfa A. J. Role of phosphorylated metabolic intermediates in the regulation of glutamine synthetase synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(19):6061–6070. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.19.6061-6070.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilles-Gonzalez M. A., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. A haemoprotein with kinase activity encoded by the oxygen sensor of Rhizobium meliloti. Nature. 1991 Mar 14;350(6314):170–172. doi: 10.1038/350170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertig C., Li R. Y., Louarn A. M., Garnerone A. M., David M., Batut J., Kahn D., Boistard P. Rhizobium meliloti regulatory gene fixJ activates transcription of R. meliloti nifA and fixK genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1736–1738. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1736-1738.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Karin M. The regulation of transcription by phosphorylation. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):375–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo M. M., Ninfa A. J., Stock J. B., Silhavy T. J. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of a bacterial transcriptional activator by a transmembrane receptor. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1725–1734. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn D., Ditta G. Modular structure of FixJ: homology of the transcriptional activator domain with the -35 binding domain of sigma factors. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Apr;5(4):987–997. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00774.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lois A. F., Weinstein M., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. Autophosphorylation and phosphatase activities of the oxygen-sensing protein FixL of Rhizobium meliloti are coordinately regulated by oxygen. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4370–4375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukat G. S., McCleary W. R., Stock A. M., Stock J. B. Phosphorylation of bacterial response regulator proteins by low molecular weight phospho-donors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):718–722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monson E. K., Weinstein M., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. The FixL protein of Rhizobium meliloti can be separated into a heme-binding oxygen-sensing domain and a functional C-terminal kinase domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4280–4284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa E. G., Stock A., Mowbray S., Stock J. Reconstitution of the bacterial chemotaxis signal transduction system from purified components. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9764–9770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace H. C., Lu P., Lewis M. lac repressor: crystallization of intact tetramer and its complexes with inducer and operator DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1870–1873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Kofoid E. C. Communication modules in bacterial signaling proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:71–112. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Hoopes B. C., McClure W. R., Kleckner N. Three promoters near the termini of IS10: pIN, pOUT, and pIII. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):673–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90400-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virts E. L., Stanfield S. W., Helinski D. R., Ditta G. S. Common regulatory elements control symbiotic and microaerobic induction of nifA in Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3062–3065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Philip P., Batut J., Boistard P. Rhizobium meliloti Fix L is an oxygen sensor and regulates R. meliloti nifA and fixK genes differently in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4255–4262. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4255-4262.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Philip P., Soupène E., Batut J., Boistard P. Modular structure of the FixL protein of Rhizobium meliloti. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Oct;235(1):49–54. doi: 10.1007/BF00286180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]