Abstract
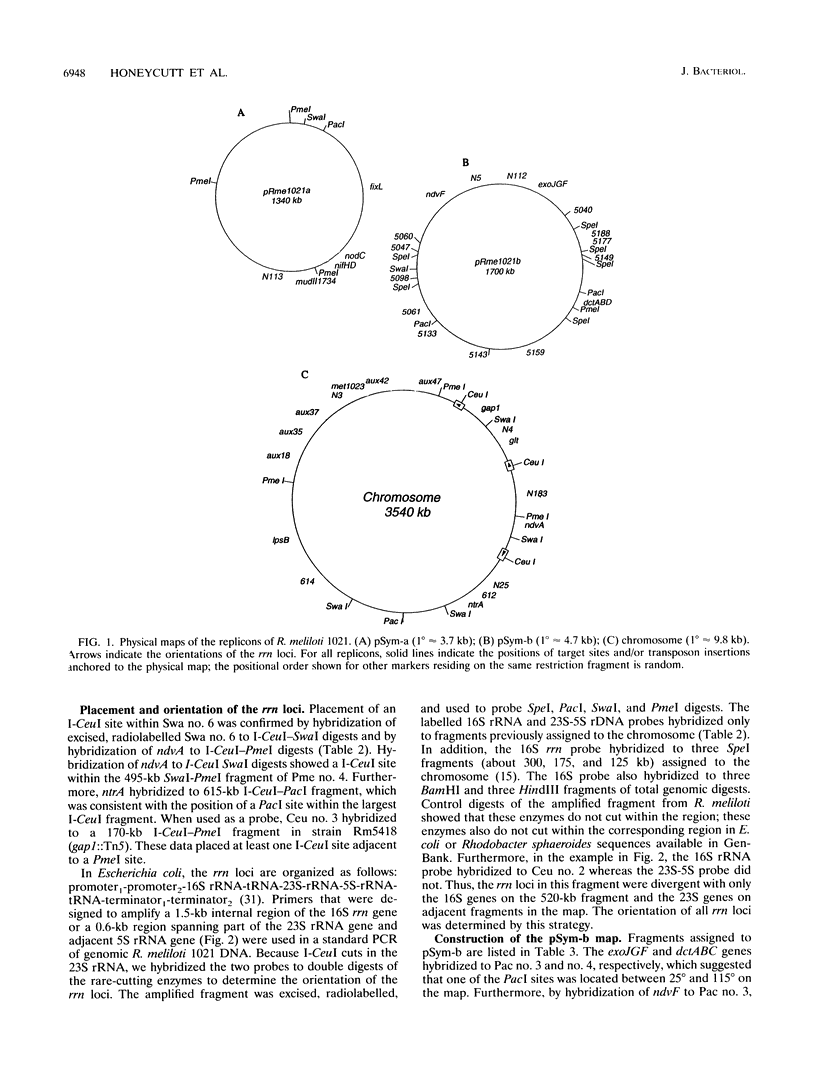
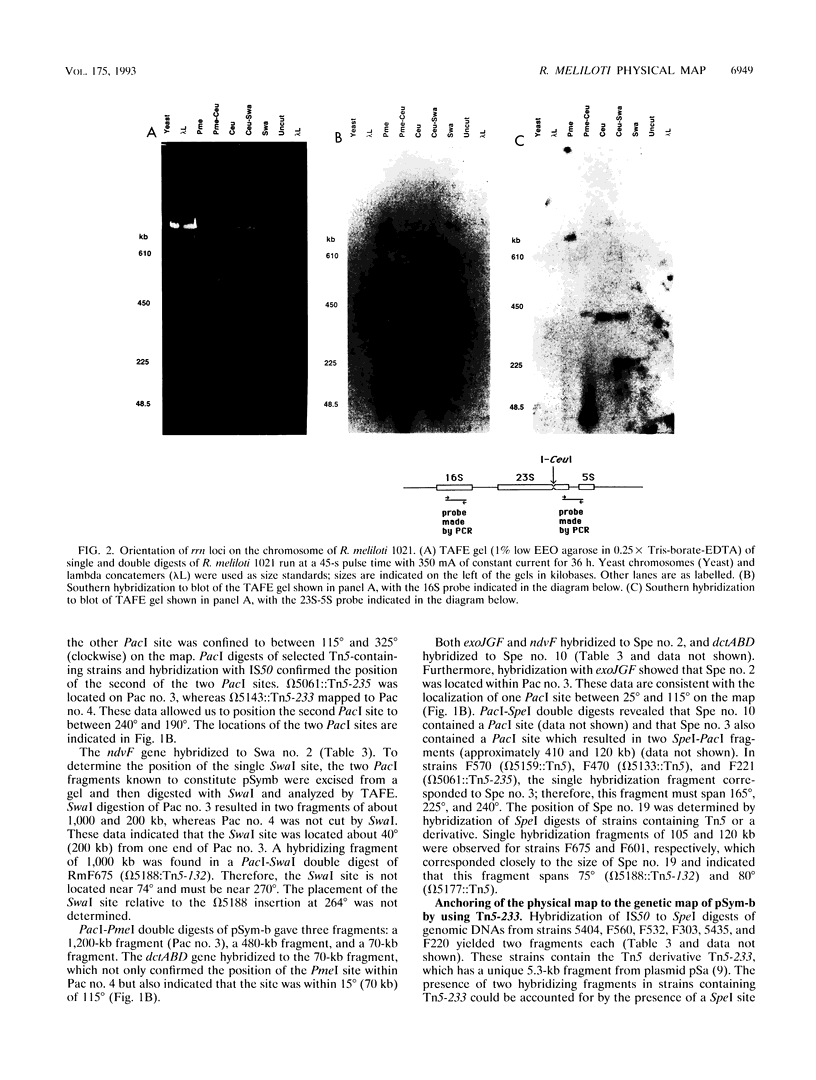
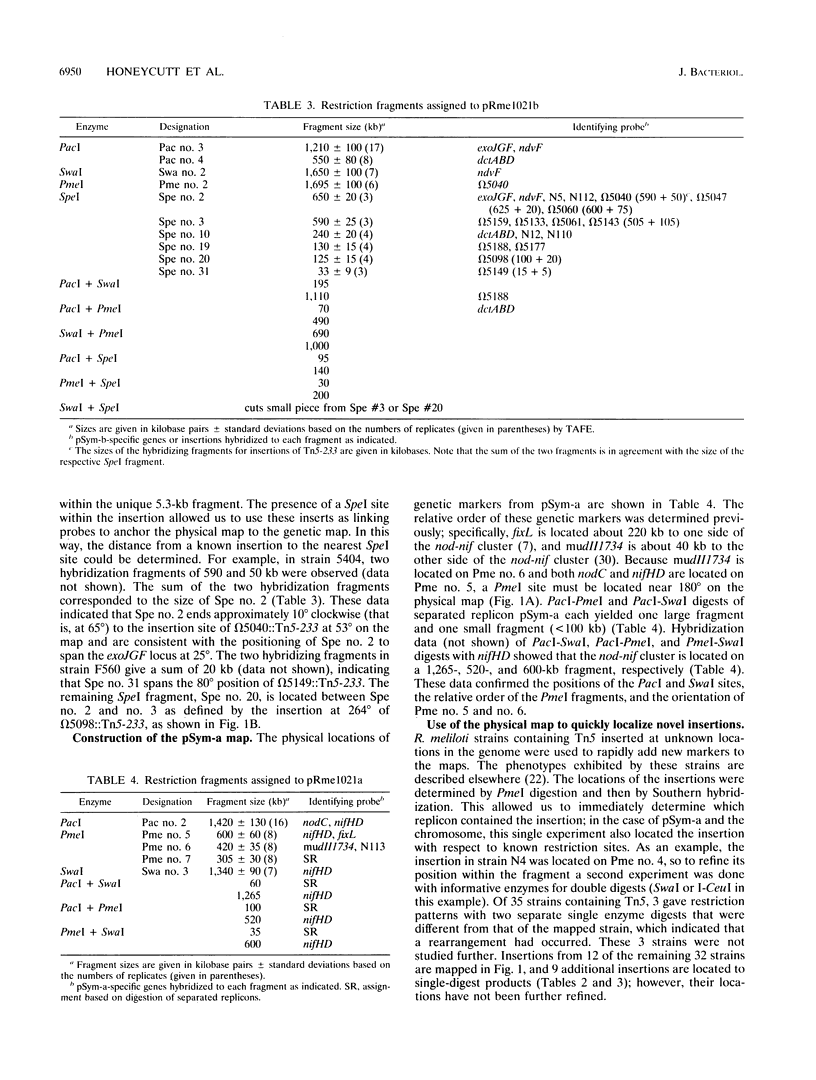
A physical map of the genome of Rhizobium meliloti 1021 is presented. The physical sizes of the three replicons in this genome had previously been determined and are as follows: the chromosome, 3.4 Mb; pSym-b, 1.7 Mb; and pSym-a, 1.4 Mb. The physical maps for this GC-rich genome contain AT-rich restriction sites for SwaI (5'-TAAATTTA-3'), PacI (5'-TTAATTAA-3'), PmeI (5'-GTTTAAAC-3'), and, for pSym-b, SpeI (5'-ACTAGT-3'). In addition, the endonuclease I-CeuI cleaved the 23S rRNA genes in this genome, and perhaps in most eubacterial genomes. I-CeuI digestion and polymerase chain reaction amplification of rrn regions were used to determine that there are at least three rrn loci in R. meliloti, all of which are located on the chromosome. The orientation of the rrn loci was determined by Southern blotting with probes from rrn sequences located 5' and 3' to the I-CeuI site. The rrn loci are clustered in one part of the chromosome and are oriented so that transcription will occur away from a single point in the circle, as observed for the origin of replication in the Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium chromosomes. Fifteen genes that had been tagged by Tn5 insertion were localized to fragments on the chromosome physical map by using the IS50 as a probe in Southern blots. In addition, glt and gap were placed on the physical map by using Southern hybridization with cloned genes. The fortuitous occurrence of SpecI site in Tn5-233 was used to physically map 10 genetically mapped Tn5-233 integrations on pSym-b and to anchor the physical map to the genetic map. Finally, we demonstrate the usefulness of the map by localizing a total of 12 previously unmapped transposon insertions in the genome. This is the first physical map of the genome of a multireplicon member of the family Rhizobiaceae as well as the first physical map of a Rhizobium chromosome.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brewer B. J. When polymerases collide: replication and the transcriptional organization of the E. coli chromosome. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):679–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90086-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkardt B., Burkardt H. J. Visualization and exact molecular weight determination of a Rhizobium meliloti megaplasmid. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 15;175(2):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90475-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkardt B., Schillik D., Pühler A. Physical characterization of Rhizobium meliloti megaplasmids. Plasmid. 1987 Jan;17(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(87)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadesús J., Olivares J. Rough and fine linkage mapping of the Rhizobium meliloti chromosome. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jul 13;174(2):203–209. doi: 10.1007/BF00268356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles T. C., Finan T. M. Analysis of a 1600-kilobase Rhizobium meliloti megaplasmid using defined deletions generated in vivo. Genetics. 1991 Jan;127(1):5–20. doi: 10.1093/genetics/127.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles T. C., Finan T. M. Genetic map of Rhizobium meliloti megaplasmid pRmeSU47b. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2469–2476. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2469-2476.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Daveran M. L., Batut J., Dedieu A., Domergue O., Ghai J., Hertig C., Boistard P., Kahn D. Cascade regulation of nif gene expression in Rhizobium meliloti. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):671–683. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos G. F., Walker G. C., Signer E. R. Genetic manipulations in Rhizobium meliloti utilizing two new transposon Tn5 derivatives. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Sep;204(3):485–491. doi: 10.1007/BF00331029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujon B., Belfort M., Butow R. A., Jacq C., Lemieux C., Perlman P. S., Vogt V. M. Mobile introns: definition of terms and recommended nomenclature. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finan T. M., Oresnik I., Bottacin A. Mutants of Rhizobium meliloti defective in succinate metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3396–3403. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3396-3403.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazebrook J., Meiri G., Walker G. C. Genetic mapping of symbiotic loci on the Rhizobium meliloti chromosome. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1992 May-Jun;5(3):223–227. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-5-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawiec S., Riley M. Organization of the bacterial chromosome. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):502–539. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.4.502-539.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kündig C., Hennecke H., Göttfert M. Correlated physical and genetic map of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum 110 genome. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(3):613–622. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.3.613-622.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis T. A., Gonzalez R., Botsford J. L. Rhizobium meliloti glutamate synthase: cloning and initial characterization of the glt locus. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2413–2420. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2413-2420.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. L., Hessel A., Sanderson K. E. Genomic mapping with I-Ceu I, an intron-encoded endonuclease specific for genes for ribosomal RNA, in Salmonella spp., Escherichia coli, and other bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6874–6878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall P., Lemieux C. The I-CeuI endonuclease recognizes a sequence of 19 base pairs and preferentially cleaves the coding strand of the Chlamydomonas moewusii chloroplast large subunit rRNA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6401–6407. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M., Jones R., Patel Y., Nelson M. Restriction endonucleases for pulsed field mapping of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):5985–6005. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.5985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade H. M., Signer E. R. Genetic mapping of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2076–2078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perret X., Broughton W. J., Brenner S. Canonical ordered cosmid library of the symbiotic plasmid of Rhizobium species NGR234. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1923–1927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph D., McClelland M., Welsh J., Baranton G., Perolat P. Leptospira species categorized by arbitrarily primed polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and by mapped restriction polymorphisms in PCR-amplified rRNA genes. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(4):973–981. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.4.973-981.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renalier M. H., Batut J., Ghai J., Terzaghi B., Gherardi M., David M., Garnerone A. M., Vasse J., Truchet G., Huguet T. A new symbiotic cluster on the pSym megaplasmid of Rhizobium meliloti 2011 carries a functional fix gene repeat and a nod locus. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2231–2238. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2231-2238.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobral B. W., Honeycutt R. J., Atherly A. G., McClelland M. Electrophoretic separation of the three Rhizobium meliloti replicons. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5173–5180. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5173-5180.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobral B. W., Honeycutt R. J., Atherly A. G. The genomes of the family Rhizobiaceae: size, stability, and rarely cutting restriction endonucleases. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):704–709. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.704-709.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suwanto A., Kaplan S. Physical and genetic mapping of the Rhodobacter sphaeroides 2.4.1 genome: presence of two unique circular chromosomes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5850–5859. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5850-5859.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Barns S. M., Pelletier D. A., Lane D. J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):697–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.697-703.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. K., McClelland M. A BlnI restriction map of the Salmonella typhimurium LT2 genome. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1656–1661. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1656-1661.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. K., McClelland M. Dissection of the Salmonella typhimurium genome by use of a Tn5 derivative carrying rare restriction sites. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3807–3811. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3807-3811.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]