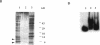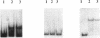Abstract
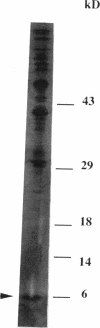
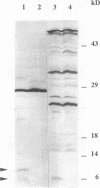
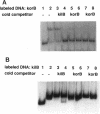
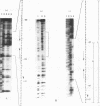
The korB gene of Streptomyces lividans plasmid pIJ101 is known to encode an autoregulated protein that also represses transcription of a gene, kilB, implicated in pIJ101 transfer and in spreading of the plasmid along mycelia of the recipient. Earlier work has indicated that the primary gene product of korB is a 10-kDa protein predicted from the gene sequence (D.S. Stein and S.N. Cohen, Mol. Gen. Genet. 222:337-344, 1990; S. Zamen H. Richards, and J. Ward, Nuleic Acids Res. 20:3693-3700, 1992). We report here that the 10-kDa KorB protein product is processed in vivo into a 6-kDa peptide that has a 20-fold-greater binding affinity for its operator-promoter target; in addition, the 6-kDa peptide binds differentially to the regulatory regions of the two genes it controls, showing 50-fold-greater affinity for the kilB sequence. While both the processed and unprocessed forms of KorB were observed in Escherichia coli following korB gene expression under control of the bacteriophage T7 promoter, only the 6-kDa peptide was found in S. lividans containing pIJ101, implying that this peptide is normally the biologically active form of KorB. The footprint resulting from KorB binding to the korB operator sequence overlaps the sti locus, which affects pIJ101 copy number and incompatibility as well as the size of zones of inhibited recipient cell growth ("pocks") that form around donor cells during mating. The observed ability of the korB gene product to interact with both sti sequences and the kilB promoter region suggests that it may have a role in coordinating the replication and intramycelial spread of plasmids during and/or following bacterial mating.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bedouelle H., Duplay P. Production in Escherichia coli and one-step purification of bifunctional hybrid proteins which bind maltose. Export of the Klenow polymerase into the periplasmic space. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Feb 1;171(3):541–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13823.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Ward J. M., Kieser T., Cohen S. N., Hopwood D. A. Excision of chromosomal DNA sequences from Streptomyces coelicolor forms a novel family of plasmids detectable in Streptomyces lividans. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(2):230–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00272910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng Z. X., Kieser T., Hopwood D. A. "Strong incompatibility" between derivatives of the Streptomyces multi-copy plasmid pIJ101. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Oct;214(2):286–294. doi: 10.1007/BF00337723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Legaz M. E., Davie E. W. Bovine factors X 1 and X 2 (Stuart factor). Isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4882–4891. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Elution of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate, and renaturation of enzymatic activity: results with sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, wheat germ DNA topoisomerase, and other enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A., Chater K. F., Dowding J. E., Vivian A. Advances in Streptomyces coelicolor genetics. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Sep;37(3):371–405. doi: 10.1128/br.37.3.371-405.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A., Kieser T., Wright H. M., Bibb M. J. Plasmids, recombination and chromosome mapping in Streptomyces lividans 66. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jul;129(7):2257–2269. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-7-2257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall K. J., Cohen S. N. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Streptomyces lividans plasmid pIJ101 and correlation of the sequence with genetic properties. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4634–4651. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4634-4651.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall K. J., Cohen S. N. Plasmid transfer in Streptomyces lividans: identification of a kil-kor system associated with the transfer region of pIJ101. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4177–4183. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4177-4183.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieser T., Hopwood D. A., Wright H. M., Thompson C. J. pIJ101, a multi-copy broad host-range Streptomyces plasmid: functional analysis and development of DNA cloning vectors. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(2):223–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00330791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline B. C., Sandhu G. S., Eckloff B. W., Aleff R. A. Site-specific proteolysis of mini-F plasmid replication protein RepE destroys initiator function and generates an incompatibility substance. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(9):3004–3010. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.9.3004-3010.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maina C. V., Riggs P. D., Grandea A. G., 3rd, Slatko B. E., Moran L. S., Tagliamonte J. A., McReynolds L. A., Guan C. D. An Escherichia coli vector to express and purify foreign proteins by fusion to and separation from maltose-binding protein. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Taylor R. K., Mekalanos J. J. Cholera toxin transcriptional activator toxR is a transmembrane DNA binding protein. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Thøgersen H. C. Synthesis and sequence-specific proteolysis of hybrid proteins produced in Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:461–481. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Molecular weight determination of protein-dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis in a discontinuous buffer system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6328–6334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan G. P., Ghosh S., Liou H. C., Tempst P., Baltimore D. DNA binding and I kappa B inhibition of the cloned p65 subunit of NF-kappa B, a rel-related polypeptide. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):961–969. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90320-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russel M., Model P. Replacement of the fip gene of Escherichia coli by an inactive gene cloned on a plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):1034–1039. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.1034-1039.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein D. S., Cohen S. N. Mutational and functional analysis of the korA and korB gene products of Streptomyces plasmid pIJ101. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Jul;222(2-3):337–344. doi: 10.1007/BF00633838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein D. S., Kendall K. J., Cohen S. N. Identification and analysis of transcriptional regulatory signals for the kil and kor loci of Streptomyces plasmid pIJ101. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5768–5775. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5768-5775.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. The study of histone--histone associations by chemical cross-linking. Methods Cell Biol. 1978;18:429–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Rae S., Cundliffe E. Coupled transcription--translation in extracts of Streptomyces lividans. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(1-2):39–43. doi: 10.1007/BF00332721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaman S., Richards H., Ward J. Expression and characterisation of the korB gene product from the Streptomyces lividans plasmid pIJ101 in Escherichia coli and determination of its binding site on the korB and kilB promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 25;20(14):3693–3700. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.14.3693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]