Abstract
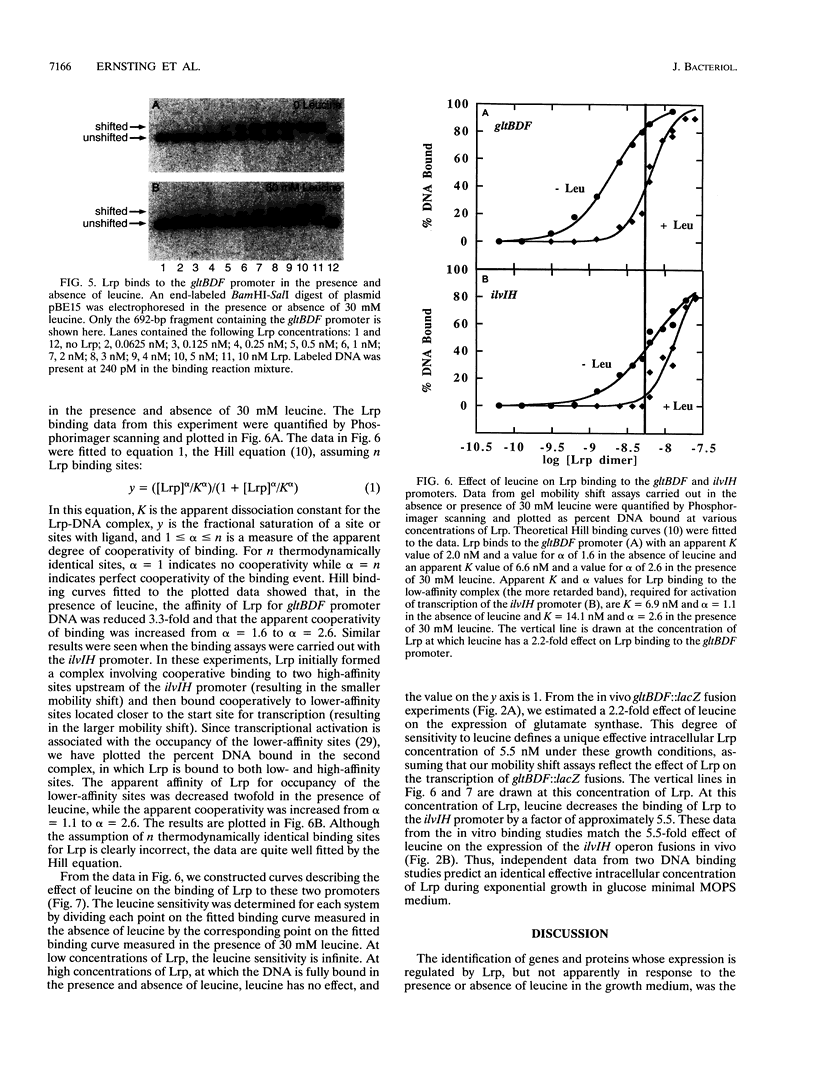
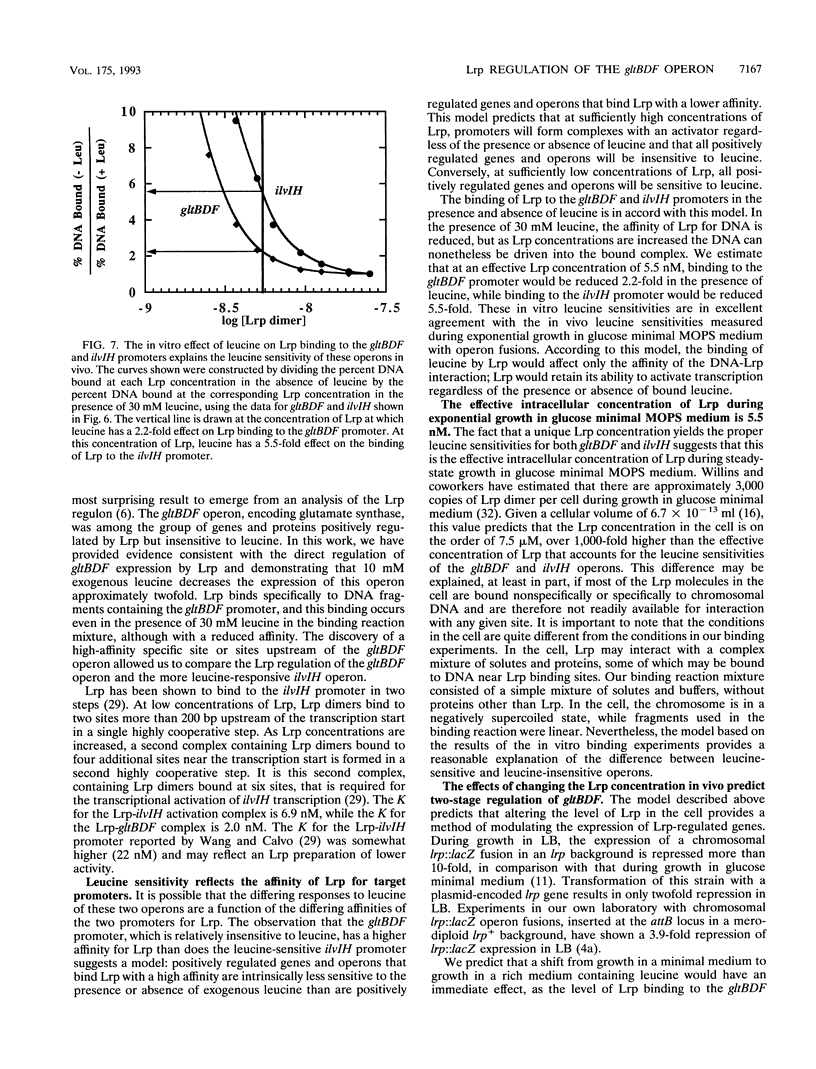
The regulon controlled by the leucine-responsive regulatory protein (Lrp) of Escherichia coli consists of over 40 genes and proteins whose expression is regulated, either positively or negatively, by Lrp. The gltBDF operon, encoding glutamate synthase, was originally identified as a member of the Lrp regulon through a two-dimensional electrophoretic analysis of polypeptides from isogenic strains containing or lacking a functional Lrp protein. We have now demonstrated that Lrp regulates the transcription of gltBDF::lacZ operon fusions. Relative to expression in glucose minimal 3-(N-morpholino)propanesulfonic acid (MOPS) medium, gltBDF::lacZ expression in an lrp+ strain is repressed 2.2-fold in the presence of 10 mM exogenous leucine and 16-fold in Luria broth. Repression of gltBDF::lacZ expression by leucine or Luria broth is not seen for an isogenic strain containing a Tn10 insertion in lrp, and expression of gltBDF::lacZ is 44-fold lower than in the lrp+ strain when both are grown in glucose minimal MOPS medium. Lrp binds specifically to DNA fragments containing the gltBDF promoter region. Saturating levels of leucine do not abolish binding of Lrp upstream of gltBDF but merely increase its apparent dissociation constant from 2.0 to 6.9 nM. Electrophoretic analysis of the Lrp regulon established that target proteins differ greatly in the degree to which the effect of Lrp on their expression is antagonized by leucine. On the basis of our present results, we present a model for positive regulation of target genes by Lrp. Insensitivity to leucine would be expected when the effective intracellular concentration of Lrp is high relative to the affinity of Lrp binding sites required for transcription of the target gene. At lower concentrations of Lrp, transcription of the target gene should be sensitive to leucine. This model suggests that regulation of the concentration of active Lrp is critical to control of the Lrp regulon.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Garges S. Positive control. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10797–10800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomfield I. C., Calie P. J., Eberhardt K. J., McClain M. S., Eisenstein B. I. Lrp stimulates phase variation of type 1 fimbriation in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;175(1):27–36. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.1.27-36.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño I., Bastarrachea F., Covarrubias A. A. gltBDF operon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):821–827. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.821-827.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung C. T., Niemela S. L., Miller R. H. One-step preparation of competent Escherichia coli: transformation and storage of bacterial cells in the same solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2172–2175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernsting B. R., Atkinson M. R., Ninfa A. J., Matthews R. G. Characterization of the regulon controlled by the leucine-responsive regulatory protein in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(4):1109–1118. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.4.1109-1118.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haney S. A., Platko J. V., Oxender D. L., Calvo J. M. Lrp, a leucine-responsive protein, regulates branched-chain amino acid transport genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):108–115. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.108-115.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R., D'Ari R., Newman E. B. Lambda placMu insertions in genes of the leucine regulon: extension of the regulon to genes not regulated by leucine. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):1948–1955. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.1948-1955.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R., Ernsting B., Hirshfield I. N., Matthews R. G., Neidhardt F. C., Clark R. L., Newman E. B. The lrp gene product regulates expression of lysU in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(9):2779–2784. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.9.2779-2784.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf W. W., Steed P. M., Wanner B. L. Identification of phosphate starvation-inducible genes in Escherichia coli K-12 by DNA sequence analysis of psi::lacZ(Mu d1) transcriptional fusions. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3191–3200. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3191-3200.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. B., D'Ari R., Lin R. T. The leucine-Lrp regulon in E. coli: a global response in search of a raison d'être. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):617–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90135-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Halloran T. V., Frantz B., Shin M. K., Ralston D. M., Wright J. G. The MerR heavy metal receptor mediates positive activation in a topologically novel transcription complex. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):119–129. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90990-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver G., Gosset G., Sanchez-Pescador R., Lozoya E., Ku L. M., Flores N., Becerril B., Valle F., Bolivar F. Determination of the nucleotide sequence for the glutamate synthase structural genes of Escherichia coli K-12. Gene. 1987;60(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90207-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platko J. V., Willins D. A., Calvo J. M. The ilvIH operon of Escherichia coli is positively regulated. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4563–4570. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4563-4570.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rex J. H., Aronson B. D., Somerville R. L. The tdh and serA operons of Escherichia coli: mutational analysis of the regulatory elements of leucine-responsive genes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):5944–5953. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.5944-5953.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricca E., Aker D. A., Calvo J. M. A protein that binds to the regulatory region of the Escherichia coli ilvIH operon. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1658–1664. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1658-1664.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storz G., Tartaglia L. A., Ames B. N. Transcriptional regulator of oxidative stress-inducible genes: direct activation by oxidation. Science. 1990 Apr 13;248(4952):189–194. doi: 10.1126/science.2183352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabata S., Higashitani A., Takanami M., Akiyama K., Kohara Y., Nishimura Y., Nishimura A., Yasuda S., Hirota Y. Construction of an ordered cosmid collection of the Escherichia coli K-12 W3110 chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):1214–1218. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.1214-1218.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Versalovic J., Koeuth T., McCabe E. R., Lupski J. R. Use of the polymerase chain reaction for physical mapping of Escherichia coli genes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(17):5253–5255. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.17.5253-5255.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q., Calvo J. M. Lrp, a global regulatory protein of Escherichia coli, binds co-operatively to multiple sites and activates transcription of ilvIH. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jan 20;229(2):306–318. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L., Kodaira R., Neidhardt F. C. Physiological regulation of a decontrolled lac operon. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):212–222. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.212-222.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss V., Claverie-Martin F., Magasanik B. Phosphorylation of nitrogen regulator I of Escherichia coli induces strong cooperative binding to DNA essential for activation of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5088–5092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willins D. A., Ryan C. W., Platko J. V., Calvo J. M. Characterization of Lrp, and Escherichia coli regulatory protein that mediates a global response to leucine. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10768–10774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Felice M., Lago C. T., Squires C. H., Calvo J. M. Acetohydroxy acid synthase isoenzymes of Escherichia coli K12 and Salmonella typhimurium. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 Mar-Apr;133(2):251–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




