Abstract
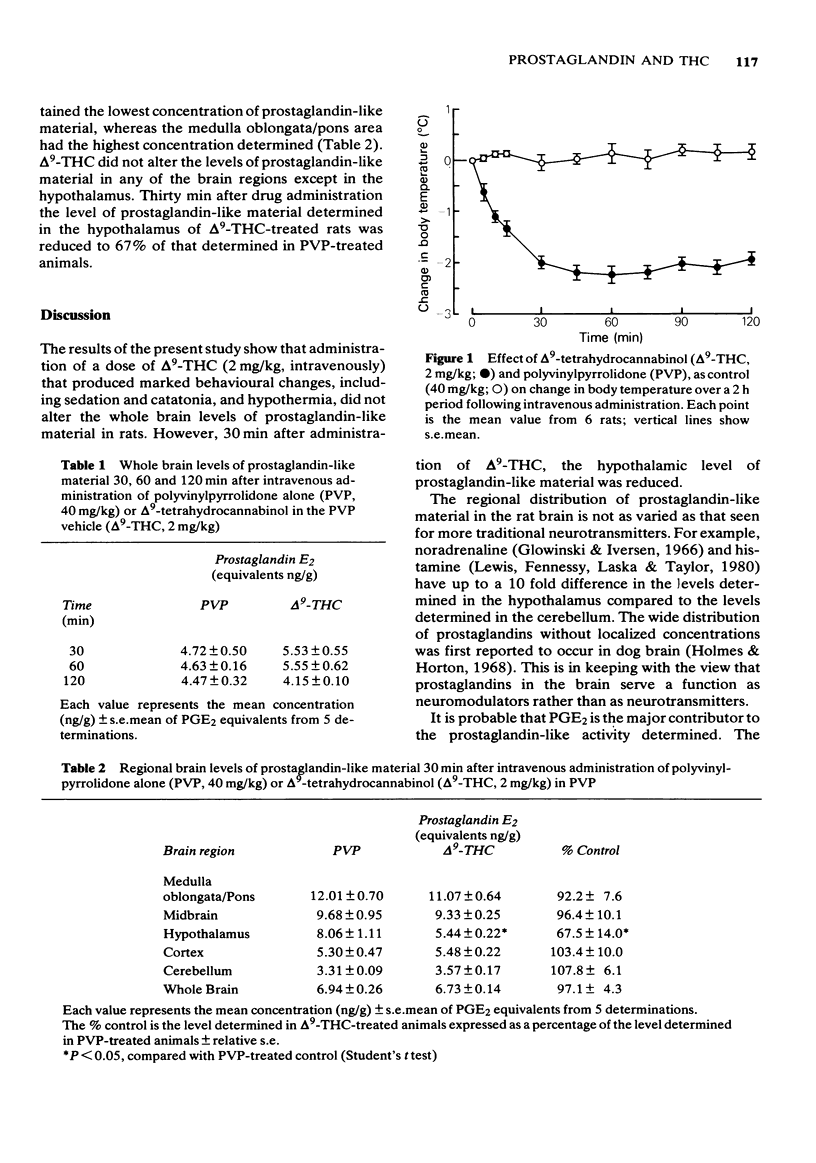
1 Whole brain and regional brain levels of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)-like material have been determined following administration of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol (delta 9 -THC) in rats. 2 Intravenous administration of delta 9-THC 2 mg/kg, resulted in marked behavioural changes and hypothermia. The behavioural changes consisted mainly of catatonia (most apparent at 30 min after administration of delta 9-THC), followed by sedation (most evident at 60 min). Hypothermia was marked from 30 min after administration of delta 9-THC. 3 delta 9-THC did not after the whole brain levels of PGE2-like material 30, 60 or 120 min after administration. 4 delta 9-THC did not alter the levels of PGE2-like material in the medulla oblongata/pons, midbrain, cortex and cerebellum, 30 min after administration. However, there was a significant reduction of PGE2-like material in the hypothalamus, 30 min after delta 9-THC. 5 It is suggested that the delta 9-THC-induced decrease in hypothalamic PGE2-like material may contribute to the hypothermia observed following delta 9-THC administration.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett A., Stamford I. F., Stockley H. L. Estimation and characterization of prostaglandins in the human gastrointestinal tract. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Dec;61(4):579–586. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Carlson L. A., Weeks J. R. The prostaglandins: a family of biologically active lipids. Pharmacol Rev. 1968 Mar;20(1):1–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein S., Hunter S. A. Prostaglandins and cannabis--VI. Release of arachidonic acid from HeLa cells by delta1-tetrahydrocannabinol and other cannabinoids. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(8):1275–1280. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90463-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein S., Levin E., Varanelli C. Prostaglandins and cannabis. II. Inhibition of biosynthesis by the naturally occurring cannabinoids. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Nov 15;22(22):2905–2910. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90158-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein S., Raz A. Inhibition of prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis by delta 1-tetrahydrocannabinol. Prostaglandins. 1972 Nov;2(5):369–374. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(72)80044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. G., Clark Y. L. Changes in body temperature after administration of acetylcholine, histamine, morphine, prostaglandins and related agents. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1980 Summer;4(2):175–240. doi: 10.1016/0149-7634(80)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbairn J. W., Pickens J. T. The effect of conditions influencing endogenous prostaglandins on the activity of delta'-tetrahydrocannabinol in mice. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Jul;69(3):491–493. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb07039.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbairn J. W., Pickens J. T. The oral activity of delta'-tetrahydrocannabinol and its dependence on prostaglandin E2. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;67(3):379–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb08691.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Gupta K. P. Pyrogen fever and prostaglandin-like activity in cerebrospinal fluid. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(1):41–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenimore D. C., Loy P. R. Injectible dispersion of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol in saline using polyvinylpyrrolidone. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1971 Apr;23(4):310–310. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1971.tb08667.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennessy M. R., Taylor D. A. Antagonism of the effects on thermoregulation of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol by clomipramine in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Jun;63(2):267–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb09756.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., De Souza Costa F. A laminar flow superfusion technique with much increased sensitivity for the detection of smooth muscle-stimulating substances. Eur J Pharmacol. 1976 Oct;39(2):379–381. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(76)90147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glowinski J., Iversen L. L. Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. I. The disposition of [3H]norepinephrine, [3H]dopamine and [3H]dopa in various regions of the brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Aug;13(8):655–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb09873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORTON E. W. ACTIONS OF PROSTAGLANDINS E1, E2 AND E3 ON THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Feb;22:189–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb01558.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes S. W., Horton E. W. The identification of four prostaglandins in dog brain and their regional distribution in the central nervous system. J Physiol. 1968 Apr;195(3):731–741. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton E. W., Main I. H. Identification of prostaglandins in central nervous tissues of the cat and chicken. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Aug;30(3):582–602. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb02165.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. J., Fennessy M. R., Laska F. J., Taylor D. A. A modified method for the isolation and determination of brain histamine using the Bio-Rex 70. Agents Actions. 1980 Jun;10(3):197–206. doi: 10.1007/BF02025936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milton A. S., Wendlandt S. Effects on body temperature of prostaglandins of the A, E and F series on injection into the third ventricle of unanaesthetized cats and rabbits. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(2):325–336. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickens J. T. Sedative activity of cannabis in relation to its delta'-trans-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol content. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Apr;72(4):649–656. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb09145.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poddubiuk Z. M. A comparison of the central actions of prostaglandins A1, E1, E2, F1alpha, and F2alpha in the rat. I. Behavioral, antinociceptive and anticonvulsant actions of intraventricular prostaglandins in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1976 Oct 20;50(1):89–94. doi: 10.1007/BF00634161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh P. P., Das P. K. Role of catecholamines in the hypothermic activity of cannabis in albino rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1976 Nov 10;50(2):199–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00430493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. A., Fennessy M. R. Biphasic nature of the effects of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol on body temperature and brain amines of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Nov 15;46(2):93–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90244-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger W. G., Stamford I. F., Bennett A. Extraction of prostaglandins from human blood. Nature. 1971 Oct 1;233(5318):336–337. doi: 10.1038/233336b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White H. L., Tansik R. L. Effects of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol on phospholipase and other enzymes regulating arachidonate metabolism. Prostaglandins Med. 1980 Jun;4(6):409–417. doi: 10.1016/0161-4630(80)90049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


