Abstract
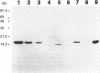
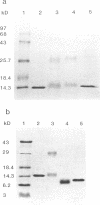
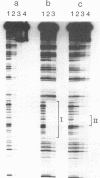
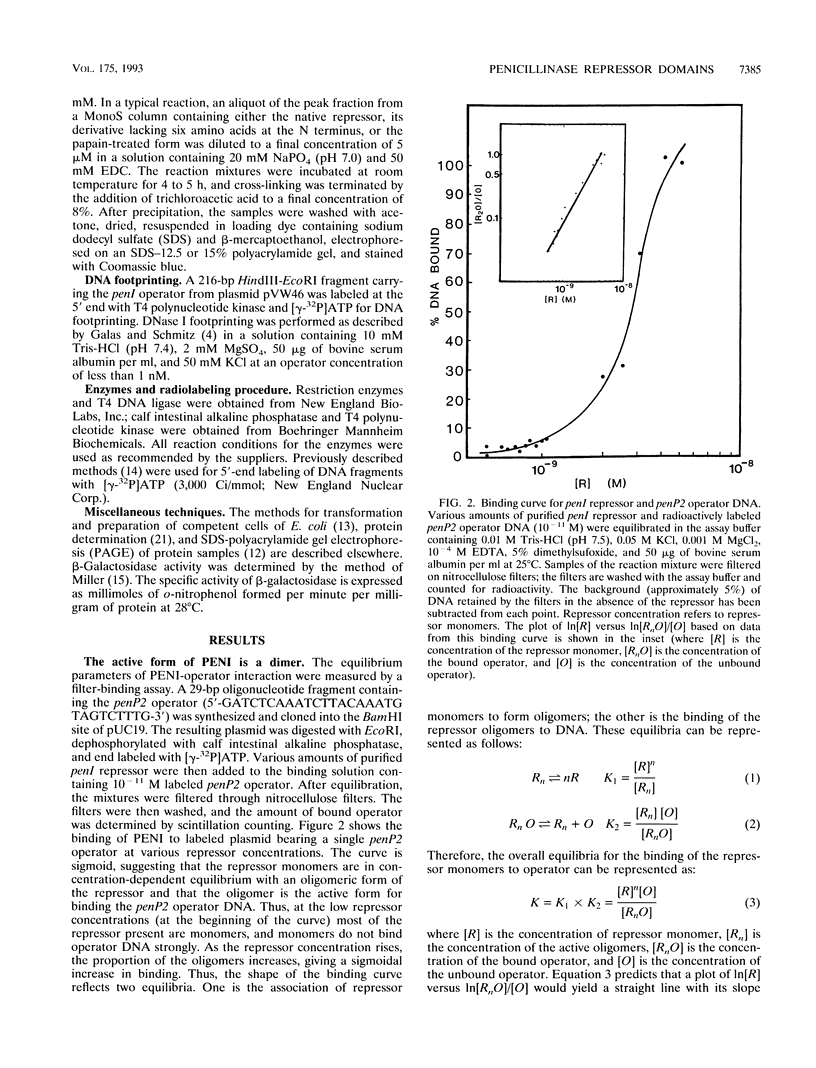
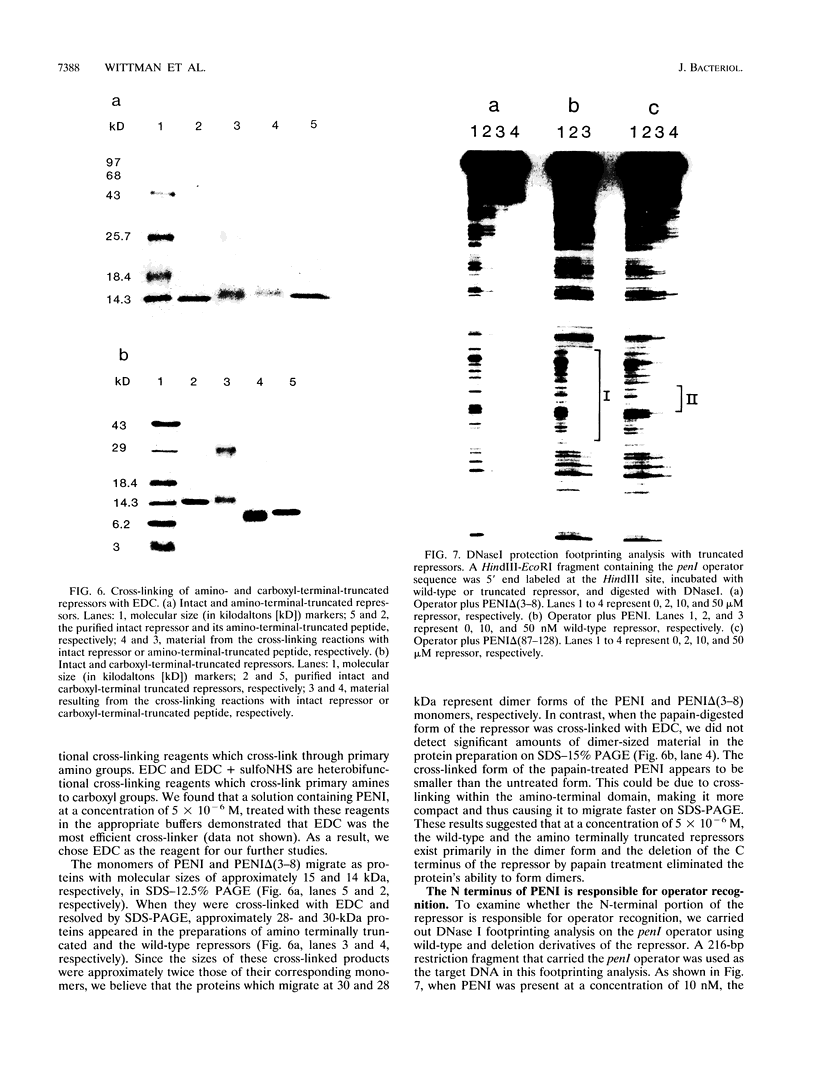
The penicillinase repressor (PENI) negatively regulates expression of the penicillinase gene (penP) in Bacillus licheniformis by binding to its operators located within the promoter region of penP.penI codes for a protein with 128 amino acids. Filter-binding analyses suggest that the active form of the repressor is a dimer. Genetic analyses of PENI derivatives showed that the repressor carrying either a 6-amino-acid deletion near the N terminus or a 14-amino-acid deletion at the C terminus was functionally inactive in vivo. A repressor derivative carrying a 6-amino-acid deletion within its N-terminal region was extensively purified and used in DNA footprinting and subunit cross-linking analyses. The results of these studies showed that the repressor derivative had lost its ability to bind operator specifically even though it could dimerize effectively. In similar studies, we demonstrated that an N-terminal portion of PENI with a molecular mass of 10 kDa derived by digestion with papain was able to bind operator specifically but with reduced affinity and had completely lost its ability to dimerize. These data suggest that the repressor has two functional and separable domains. The amino-terminal domain of the repressor is responsible for operator recognition, and the carboxyl-terminal domain is involved in subunit dimerization.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal A. K., Rodgers D. W., Drottar M., Ptashne M., Harrison S. C. Recognition of a DNA operator by the repressor of phage 434: a view at high resolution. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):899–907. doi: 10.1126/science.3187531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D. A., Pollock M. R. The genetics of Bacillus licheniformis penicillinase: a preliminary analysis from studies on mutation and inter-strain and intra-strain transformations. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Oct;41(1):7–21. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-1-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman M. J., Lampen J. O. Purification and DNA binding properties of the blaI gene product, repressor for the beta-lactamase gene, blaP, of Bacillus licheniformis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):6049–6062. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.6049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Tsuruo T. Determination of membrane antigens by a covalent crosslinking method with monoclonal antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1987 Feb 1;160(2):483–488. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanaka T., Himeno T., Aiba S. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the penicillinase antirepressor gene penJ of Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):3867–3872. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.3867-3872.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. D., Meyer B. J., Ptashne M. Interactions between DNA-bound repressors govern regulation by the lambda phage repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5061–5065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. D., Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Bacteriophage lambda repressor and cro protein: interactions with operator DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):839–856. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight K. L., Sauer R. T. DNA binding specificity of the Arc and Mnt repressors is determined by a short region of N-terminal residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):797–801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi T., Zhu Y. F., Nicholls N. J., Lampen J. O. A second regulatory gene, blaR1, encoding a potential penicillin-binding protein required for induction of beta-lactamase in Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):3873–3878. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.3873-3878.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman L. C., Perham R. N. Quaternary structure of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Bacillus stearothermophilus studied by a new reversible cross-linking procedure with bis(imidoesters). Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 12;21(21):5171–5175. doi: 10.1021/bi00264a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Grimm E. A., McGrogan M., Doyle M., Kawasaki E., Koths K., Mark D. F. Biological activity of recombinant human interleukin-2 produced in Escherichia coli. Science. 1984 Mar 30;223(4643):1412–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6367046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherratt D. J., Collins J. F. Analysis by transformation of the penicillinase system in Bacillus licheniformis. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 May;76(1):217–230. doi: 10.1099/00221287-76-1-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiraishi H., Shimura Y. A rapid and efficient method for targeted random mutagenesis. Gene. 1988 Apr 29;64(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90346-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staros J. V., Wright R. W., Swingle D. M. Enhancement by N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide of water-soluble carbodiimide-mediated coupling reactions. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jul;156(1):220–222. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniuchi M., Schweitzer J. B., Johnson E. M., Jr Nerve growth factor receptor molecules in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1950–1954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. M., Creasey A. A., Ladner M. B., Lin L. S., Strickler J., Van Arsdell J. N., Yamamoto R., Mark D. F. Molecular cloning of the complementary DNA for human tumor necrosis factor. Science. 1985 Apr 12;228(4696):149–154. doi: 10.1126/science.3856324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittman V., Wong H. C. Regulation of the penicillinase genes of Bacillus licheniformis: interaction of the pen repressor with its operators. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3206–3212. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3206-3212.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong H. C., Chang S. Identification of a positive retroregulator that stabilizes mRNAs in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3233–3237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]